Full text
PDF
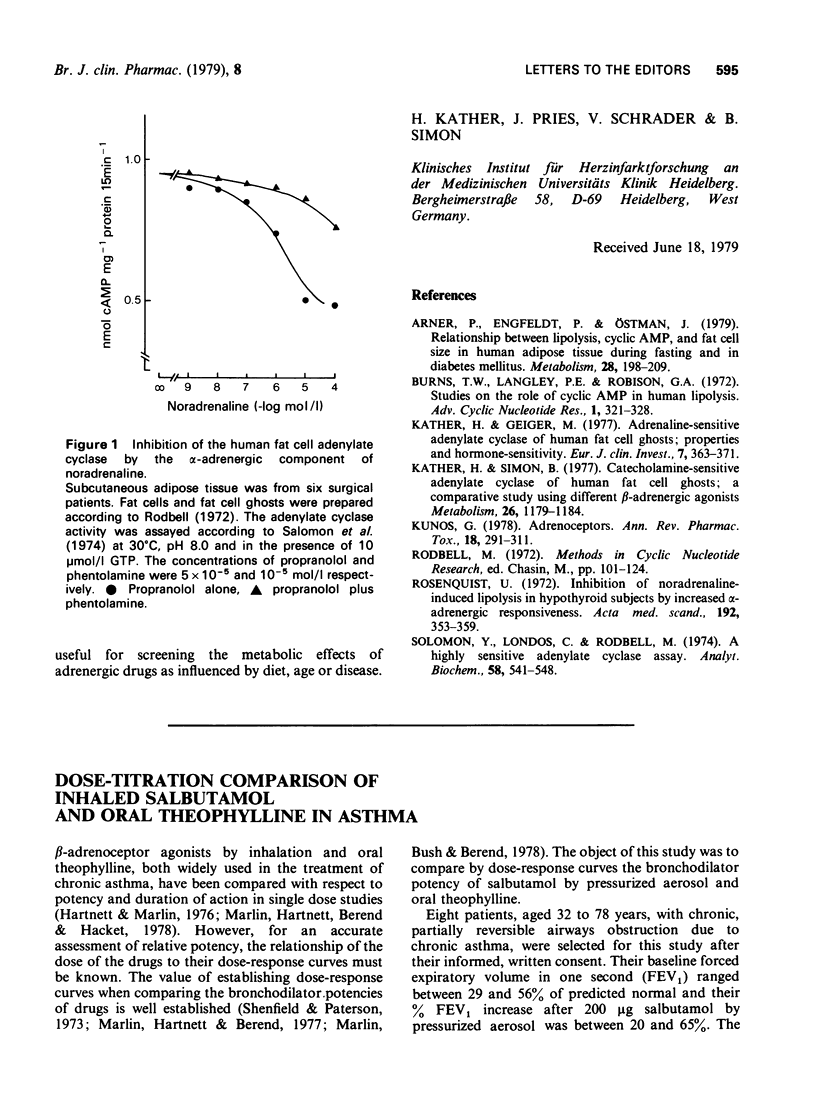
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arner P., Engfeldt P., Ostman J. Relationship between lipolysis, cyclic AMP, and fat-cell size in human adipose tissue during fasting and in diabetes mellitus. Metabolism. 1979 Mar;28(3):198–209. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(79)90065-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kather H., Geiger M. Adrenaline-sensitive adenylate cyclase of human fat cell ghosts: properties and hormone-sensitivity. Eur J Clin Invest. 1977 Oct;7(5):363–371. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1977.tb01621.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kather H., Simon B. Catecholamine-sensitive adenylate cyclase of human fat cell ghosts: a comparative study using different beta-adrenergic agents. Metabolism. 1977 Nov;26(11):1179–1184. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(77)90109-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunos G. Adrenoceptors. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1978;18:291–311. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.18.040178.001451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenqvist U. Inhibition of noradrenaline-induced lipolysis in hypothyroid subjects by increased -adrenergic responsiveness. An effect mediated through the reduction of cyclic AMP levels in adipose tissue. Acta Med Scand. 1972 Nov;192(5):353–359. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1972.tb04830.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon Y., Londos C., Rodbell M. A highly sensitive adenylate cyclase assay. Anal Biochem. 1974 Apr;58(2):541–548. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90222-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


