Abstract
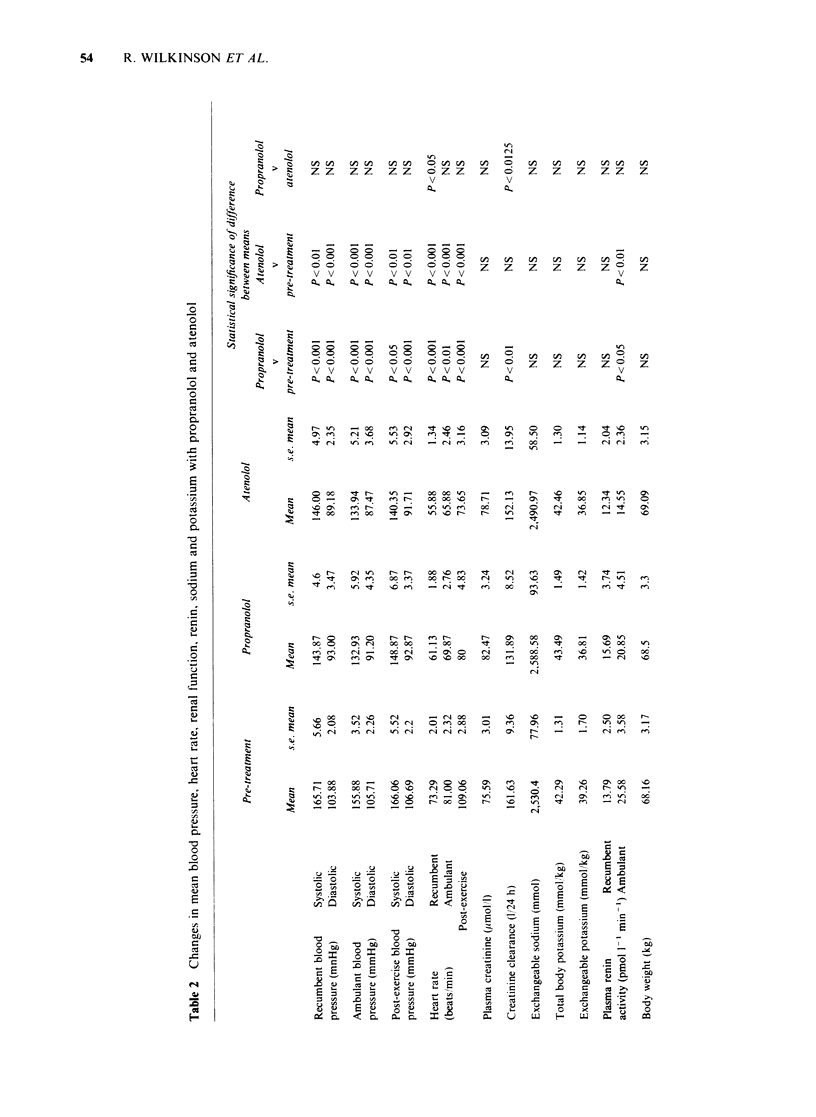
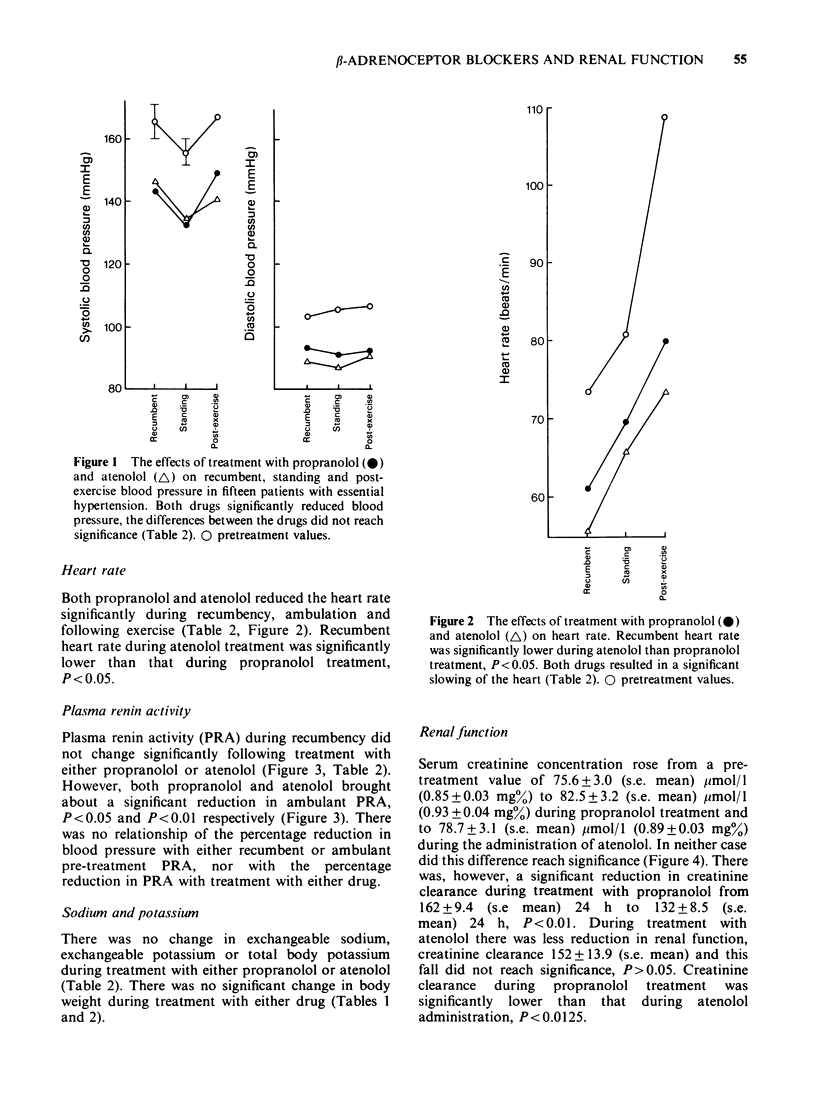
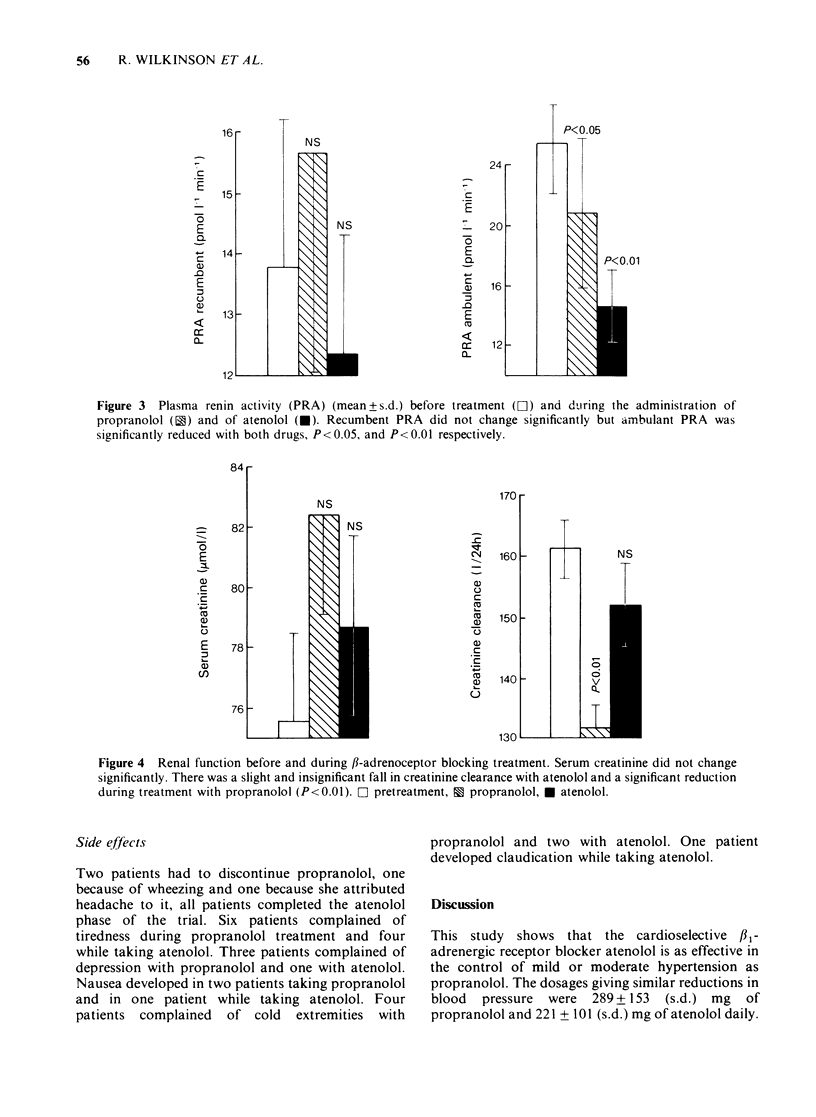
1 The effects of propranolol and atenolol given in random order in a cross-over study to fifteen patients with essential hypertension have been studied. 2 Both drugs were effective in lowering blood pressure and side effects were not markedly different. 3 There was no change in exchangeable sodium or potassium or in total body potassium during treatment with either drug. 4 Ambulant plasma renin activity was reduced by both drugs but the fall in blood pressure was not related to initial plasma renin. 5 Despite equal mean reduction in blood pressure with the two drugs, creatinine clearance fell significantly only during treatment with propranolol. 6 These observations suggest that intra-renal beta 2-adrenoceptors may be of importance in the regulation of renal function.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amery A., Billiet L., Boel A., Fagard R., Reybrouck T., Willems J. Mechanism of hypotensive effect during betaadrenergic blockade in hypertensive patients. Am Heart J. 1976 May;91(5):634–642. doi: 10.1016/s0002-8703(76)80149-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson R. J., Taher M. S., Cronin R. E., McDonald K. M., Schrier R. W. Effect of beta-adrenergic blockade and inhibitors of angiotensin II and prostaglandins on renal autoregulation. Am J Physiol. 1975 Sep;229(3):731–736. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.229.3.731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brecht H. M., Werner E., Schoeppe W. Increase of total body potassium and decrease of exchangeable sodium after long-term treatment with a beta-receptor-blocking agent (prindolol) in essential hypertension. Clin Sci Mol Med Suppl. 1976 Dec;3:551s–554s. doi: 10.1042/cs051551s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bühler F. R., Laragh J. H., Baer L., Vaughan E. D., Jr, Brunner H. R. Propranolol inhibition of renin secretion. A specific approach to diagnosis and treatment of renin-dependent hypertensive diseases. N Engl J Med. 1972 Dec 14;287(24):1209–1214. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197212142872401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein S. E., LUbbe W. F. Effects of propranolol and atenolol on blood pressure and plasma renin activity in patients with moderate hypertension. S Afr Med J. 1977 Nov 19;52(22):875–879. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esler M. D., Nestel P. J. Evaluation of practolol in hypertension. Effects on sympathetic nervous system and renin responsiveness. Br Heart J. 1973 May;35(5):469–474. doi: 10.1136/hrt.35.5.469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falch D. K., Odegaard A. E., Norman N. Renal plasma flow and cardiac output during hydralazine and propranolol treatment in essential hypertension. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1978 Apr;38(2):143–146. doi: 10.1080/00365517809156082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haber E., Koerner T., Page L. B., Kliman B., Purnode A. Application of a radioimmunoassay for angiotensin I to the physiologic measurements of plasma renin activity in normal human subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1969 Oct;29(10):1349–1355. doi: 10.1210/jcem-29-10-1349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heierli C., Thoelen H., Radielovic P. Renal function following a single dose of pindolol in hypertensive patients with varying degrees of impairment of renal function. Int J Clin Pharmacol Biopharm. 1977 Feb;15(2):65–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenberg N. K., Adams D. F., McKinstry D. N., Williams G. H., Borucki L. J., Sullivan J. M. beta-Adrenoceptor-blocking agents and the kidney: effect of nadolol and propranolol on the renal circulation. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1979;7 (Suppl 2):219S–225S. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1979.tb04693.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenberg N. K., Williams G. H., Taub K. J., Ishikawa I., Brown C., Adams D. F. Renal vascular response to interruption of the renin-angiotensin system in normal man. Kidney Int. 1977 Oct;12(4):285–293. doi: 10.1038/ki.1977.113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ibsen H., Sederberg-Olsen P. Changes in glomerular filtration rate during long-term treatment with propranolol in patients with arterial hypertension. Clin Sci. 1973 Feb;44(2):129–134. doi: 10.1042/cs0440129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kincaid-Smith P., Hua A. S. Letter: Beta-adrenergic blocking agents in renal failure. Br Med J. 1974 Aug 24;3(5929):520–520. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5929.520-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebel M., Schalekamp M. A., Beevers D. G., Brown J. J., Davies D. L., Fraser R., Kremer D., Lever A. F., Morton J. J., Robertson J. I. Sodium and the renin-angiotensin system in essential hypertension and mineralocorticoid excess. Lancet. 1974 Aug 10;2(7876):308–309. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91690-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonetti G., Mayer G., Morganti A., Terzoli L., Zanchetti A., Bianchetti G., Di Salle E., Morselli P. L., Chidsey C. A. Hypotensive and renin-suppressing activities of propranolol in hypertensive patients. Clin Sci Mol Med Suppl. 1975 Jun;48(6):491–499. doi: 10.1042/cs0480491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nayler W. G., McInnes I., Swann J. B., Carson V., Lowe T. E. Effect of propranolol, a beta-adrenergic antagonist, on blood flow in the coronary and other vascular fields. Am Heart J. 1967 Feb;73(2):207–216. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(67)90150-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nies A. S., McNeil J. S., Schrier R. W. Mechanism of increased sodium reabsorption during propranolol administration. Circulation. 1971 Oct;44(4):596–604. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.44.4.596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schirmeister J., Decot M., Hallauer W., Willmann H. Beta-Receptoren und renale Hämodynamik des Menschen. Arzneimittelforschung. 1966 Jul;16(7):847–850. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson F. O. Beta-adrenergic receptor blocking drugs in hypertension. Drugs. 1974;7(1):85–105. doi: 10.2165/00003495-197407010-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarazi R. C., Frohlich E. D., Dustan H. P. Plasma volume changes with long-term beta-adrenergic blockade. Am Heart J. 1971 Dec;82(6):770–776. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(71)90198-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson F. D., Joekes A. M. Letter: Beta-blockade in the presence of renal disease and hypertension. Br Med J. 1974 Jun 8;2(5918):555–556. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5918.555-b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren D. J., Swainson C. P., Wright N. Deterioration in renal function after beta-blockade in patients with chronic renal failure and hypertension. Br Med J. 1974 Apr 27;2(5912):193–194. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5912.193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster J., Jeffers T. A., Galloway D. B., Petrie J. C., Barker N. P. Atenolol, methyldopa, and chlorthalidone in moderate hypertension. Br Med J. 1977 Jan 8;1(6053):76–78. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6053.76. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winer N., Chokshi D. S., Walkenhorst W. G. Effects of cyclic AMP, sympathomimetic amines, and adrenergic receptor antagonists on renin secretion. Circ Res. 1971 Sep;29(3):239–248. doi: 10.1161/01.res.29.3.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods J. W., Pittman A. W., Pulliam C. C., Werk E. E., Jr, Waider W., Allen C. A. Renin profiling in hypertension and its use in treatment with propranolol and chlorthalidone. N Engl J Med. 1976 May 20;294(21):1137–1143. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197605202942101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright A. D., Barber S. G., Kendall M. J., Poole P. H. Beta-adrenoceptor-blocking drugs and blood sugar control in diabetes mellitus. Br Med J. 1979 Jan 20;1(6157):159–161. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6157.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


