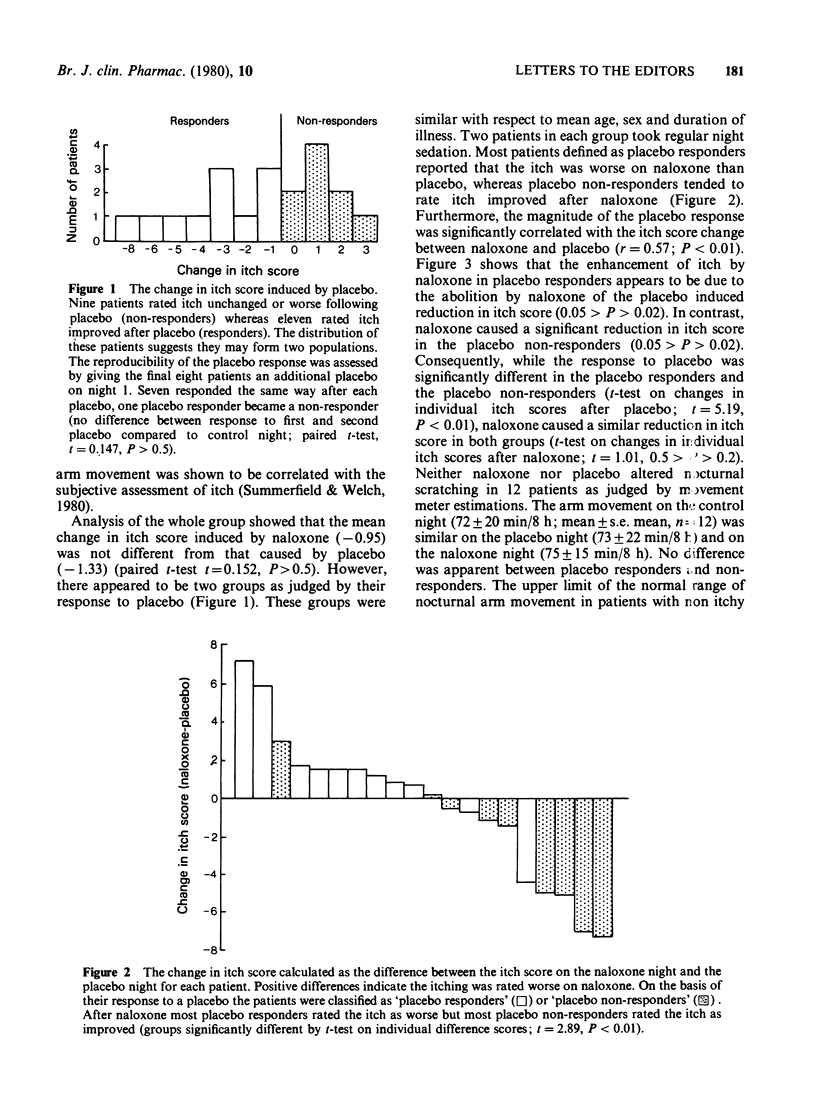
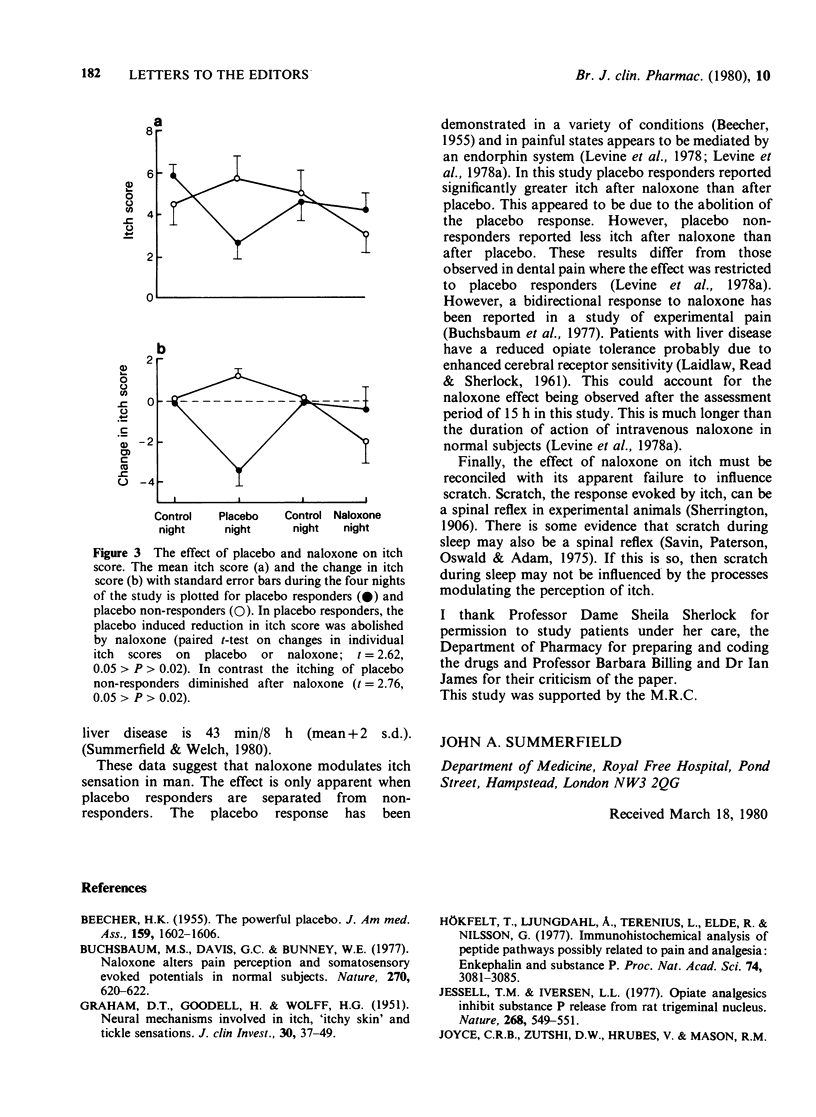
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BEECHER H. K. The powerful placebo. J Am Med Assoc. 1955 Dec 24;159(17):1602–1606. doi: 10.1001/jama.1955.02960340022006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchsbaum M. S., Davis G. C., Bunney W. E., Jr Naloxone alters pain perception and somatosensory evoked potentials in normal subjects. Nature. 1977 Dec 15;270(5638):620–622. doi: 10.1038/270620a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAHAM D. T., GOODELL H., WOLFF H. G. Neural mechanisms involved in itch, itchy skin, and tickle sensations. J Clin Invest. 1951 Jan;30(1):37–49. doi: 10.1172/JCI102414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt T., Ljungdahl A., Terenius L., Elde R., Nilsson G. Immunohistochemical analysis of peptide pathways possibly related to pain and analgesia: enkephalin and substance P. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):3081–3085. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.3081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jessell T. M., Iversen L. L. Opiate analgesics inhibit substance P release from rat trigeminal nucleus. Nature. 1977 Aug 11;268(5620):549–551. doi: 10.1038/268549a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAIDLAW J., READ A. E., SHERLOCK S. Morphine tolerance in hepatic cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 1961 Mar;40:389–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasagna L. Drug interaction in the field of analgesic drugs. Proc R Soc Med. 1965 Nov;58(11 Pt 2):978–983. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine J. D., Gordon N. C., Fields H. L. Naloxone dose dependently produces analgesia and hyperalgesia in postoperative pain. Nature. 1979 Apr 19;278(5706):740–741. doi: 10.1038/278740a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine J. D., Gordon N. C., Fields H. L. The mechanism of placebo analgesia. Lancet. 1978 Sep 23;2(8091):654–657. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)92762-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine J. D., Gordon N. C., Jones R. T., Fields H. L. The narcotic antagonist naloxone enhances clinical pain. Nature. 1978 Apr 27;272(5656):826–827. doi: 10.1038/272826a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savin J. A., Paterson W. D., Oswald I., Adam K. Further studies of scratching during sleep. Br J Dermatol. 1975 Sep;93(3):297–302. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1975.tb06495.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J., Huskisson E. C. Graphic representation of pain. Pain. 1976 Jun;2(2):175–184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherrington C. S. Observations on the scratch-reflex in the spinal dog. J Physiol. 1906 Mar 13;34(1-2):1–50. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1906.sp001139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zotterman Y. Touch, pain and tickling: an electro-physiological investigation on cutaneous sensory nerves. J Physiol. 1939 Feb 14;95(1):1–28. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1939.sp003707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


