Abstract
1 The haemodynamic mechanism of action of guanfacine 4 mg intravenously was investigated in resting conditions and during exercise for up to 20 h after administration of the drug. Cardiac output and pulmonary arterial pressure were determined by the Swan-Ganz thermodilution method. Blood pressure was measured directly.
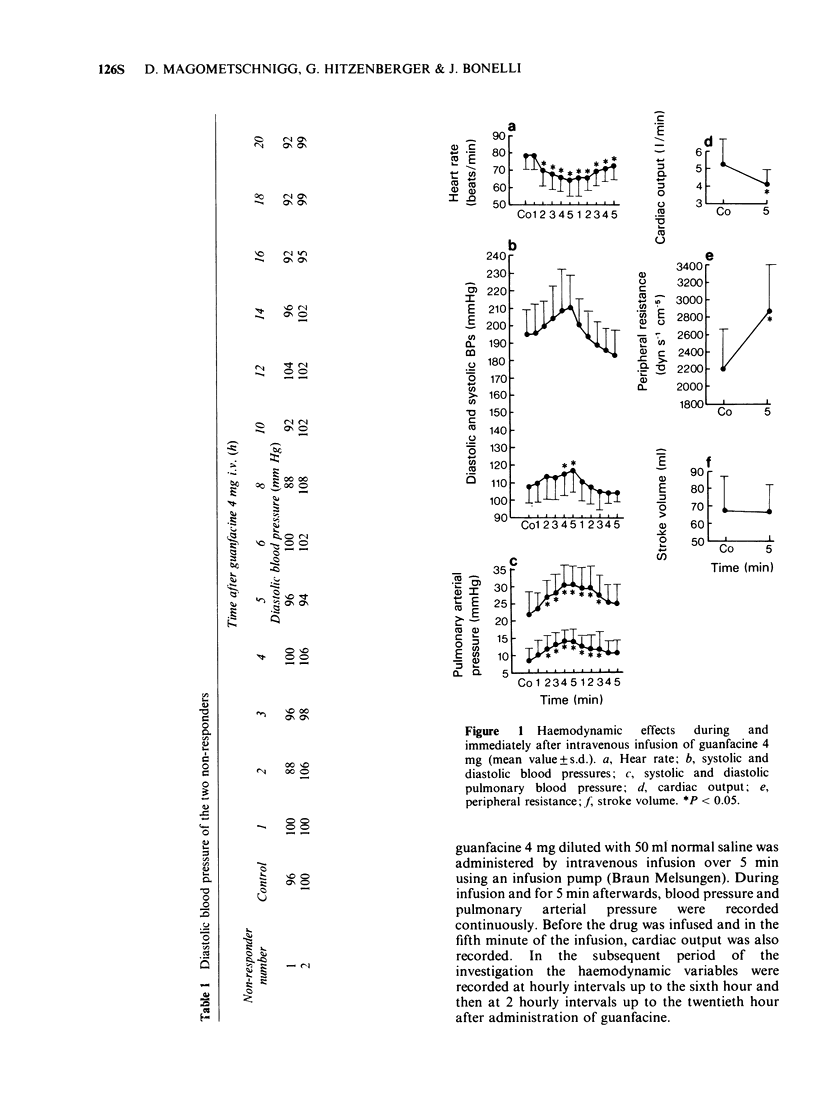
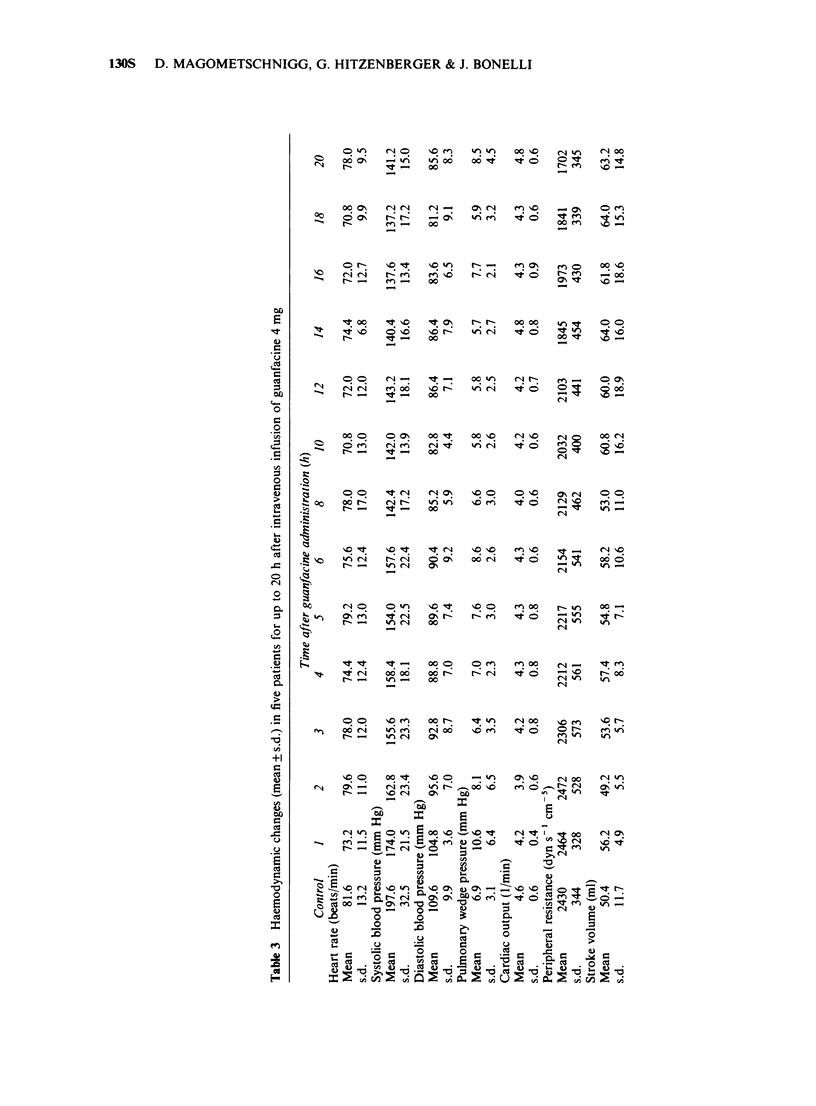
2 During and immediately after intravenous administration of guanfacine, blood pressure peripheral resistance and pulmonary arterial pressure increased (in keeping with an α-sympathomimetic effect of the compound), whereas heart rate and cardiac output decreased.
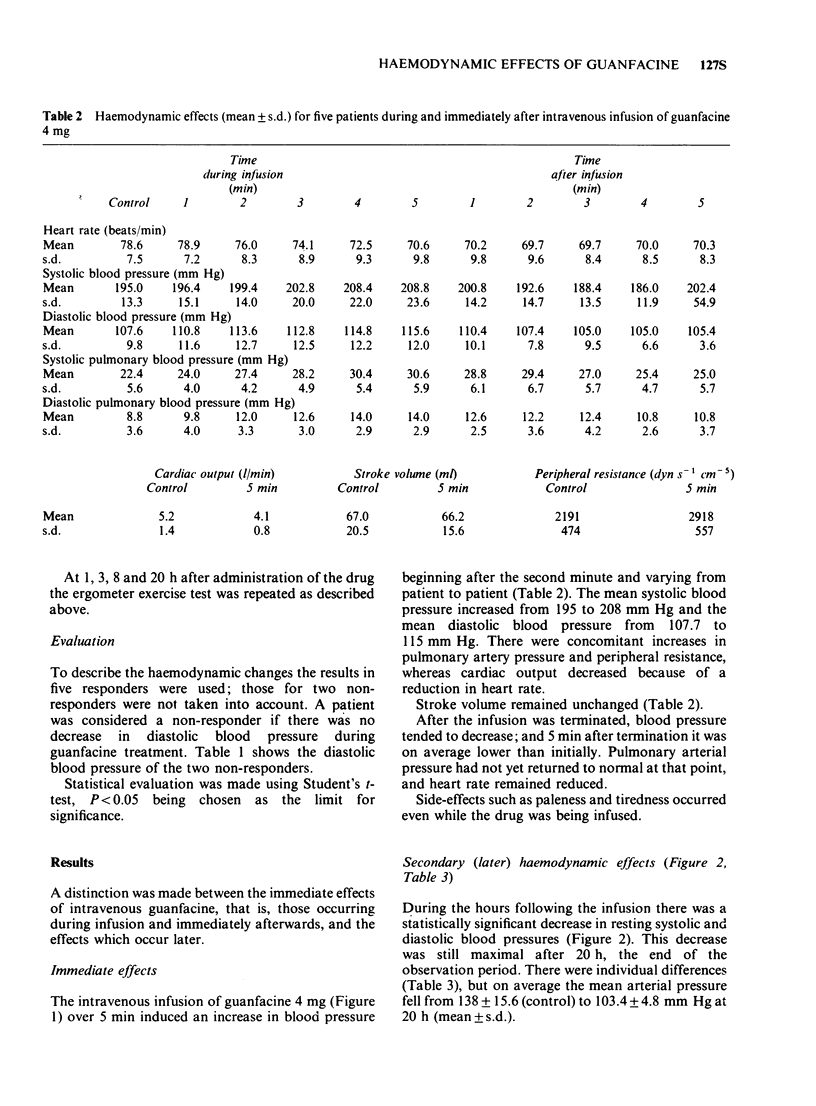
3 Subsequently blood pressure fell as a result of a decrease in cardiac output. From the third hour peripheral resistance decreased, whereas cardiac output increased again, sometimes exceeding the control value.
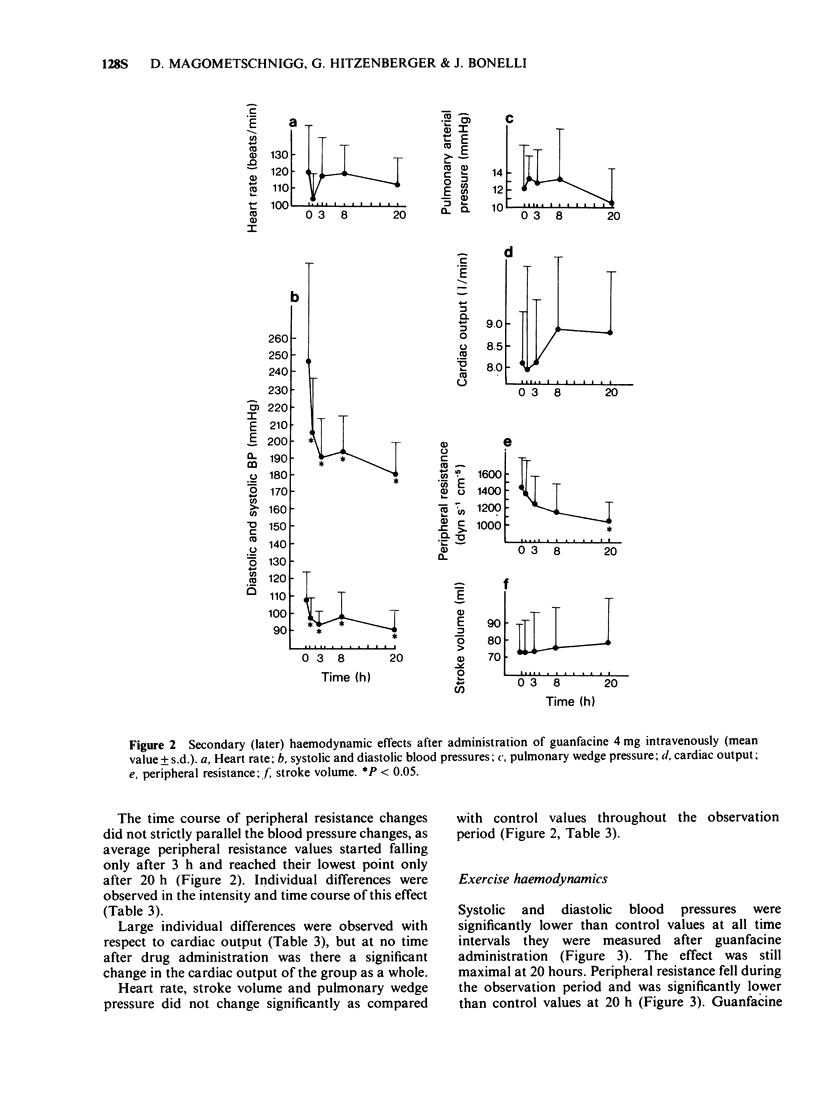
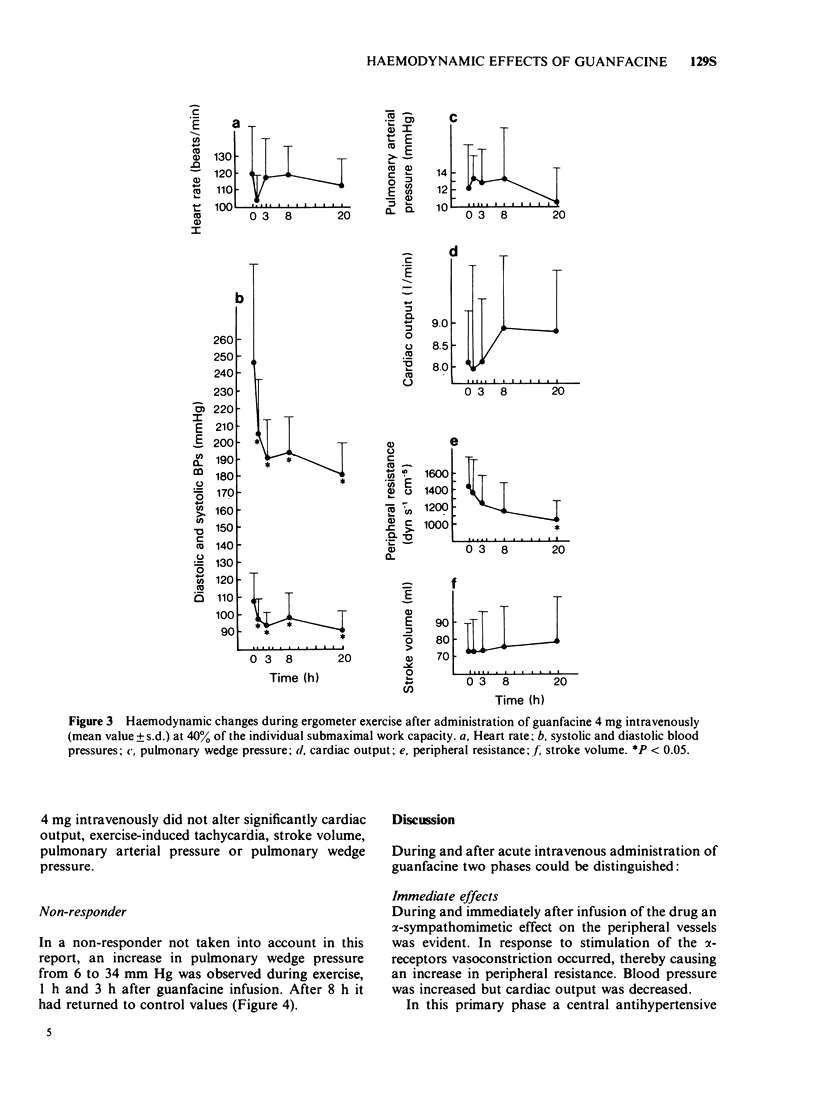
4 During exercise blood pressure was reduced from the third hour after administration, as in resting conditions, as a result of the reduction in peripheral resistance.
5 In resting conditions guanfacine reduced heart rate at the beginning and during the whole course of the investigation, whereas during exercise a reduction in heart rate was only demonstrable for 1 h after administration of the drug.
6 Side-effects noted included fatigue, drowsiness and bradycardia.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bühlmann A. Klinische Funktionsprüfung des Herzens. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1965 Oct 2;95(40):1327–1332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubach U. C., Huwyler R., Radielovic P., Singeisen M. A new centrally action antihypertensive agent guanfacine (BS 100-141). Arzneimittelforschung. 1977;27(3):674–676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esch I. Erste Erfahrungen mit BS 100-141, einer neuen blutdrucksenkenden Substanz. Int J Clin Pharmacol Biopharm. 1976 Sep;14(2):109–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirch W., Distler A. Antihypertensive effect of N-amidino-2-(2,6-dichlorophenyl) acetamide hydrochloride. A double-blind cross-over trial versus clonidine. Int J Clin Pharmacol Biopharm. 1978 Mar;16(3):132–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Röckel A., Sabel B., Heidland A. Guanfacinum (BS 100-141) in der Langzeittherapie der schweren Hypertonie. Verh Dtsch Ges Inn Med. 1977 Apr 17;83:314–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


