Abstract
1 The effects of intravenous injections of nicotine bitartrate, given as intermittent `shots', on the magnitude of the contingent negative variation (CNV) were studied in twelve male volunteers.
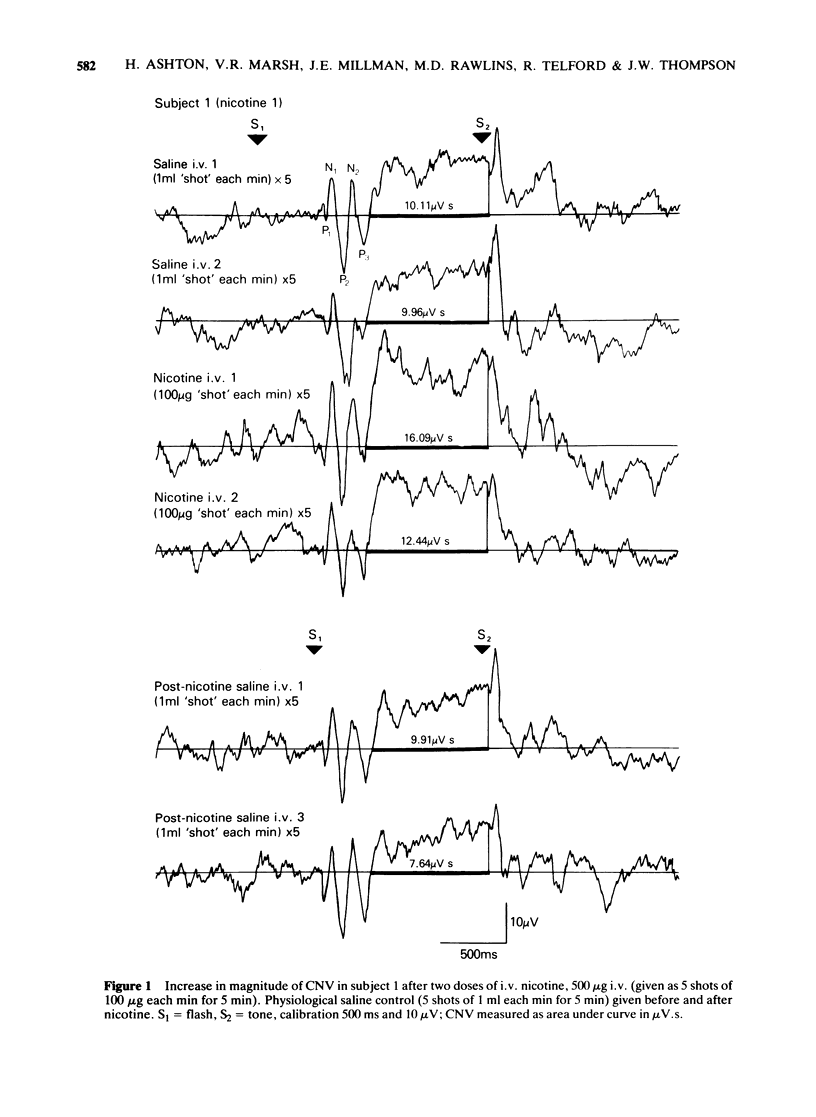
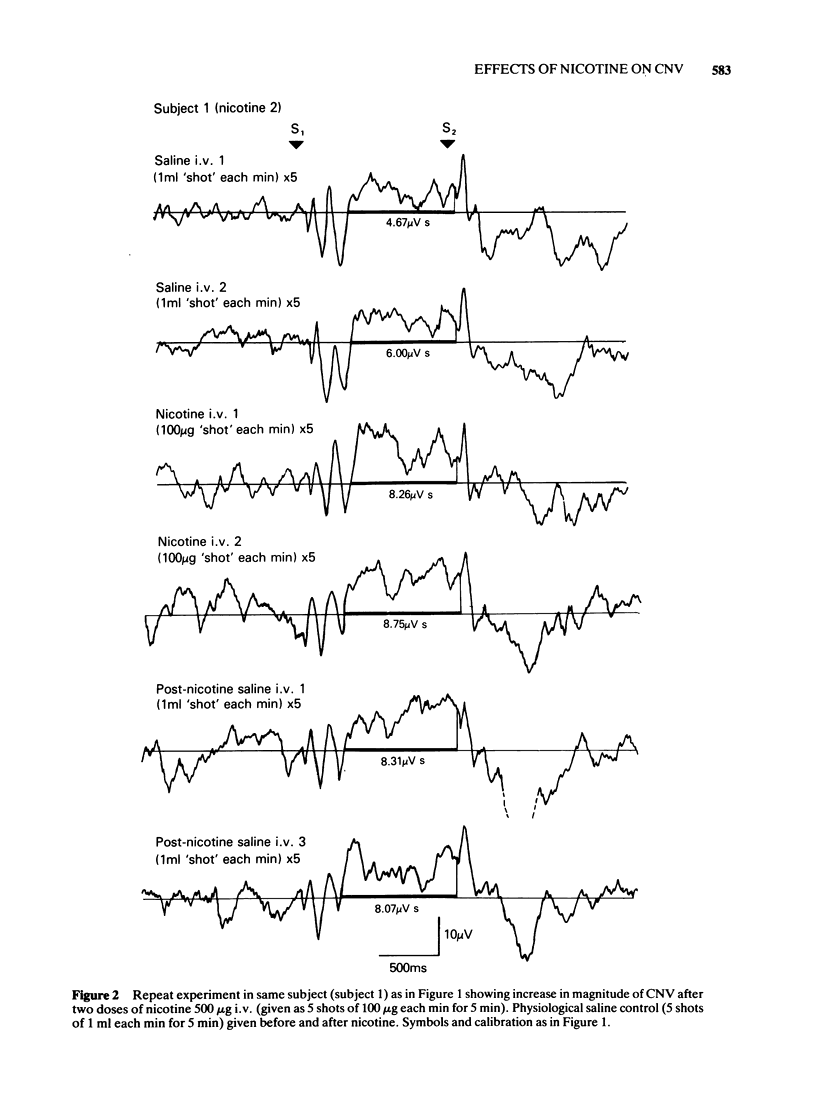
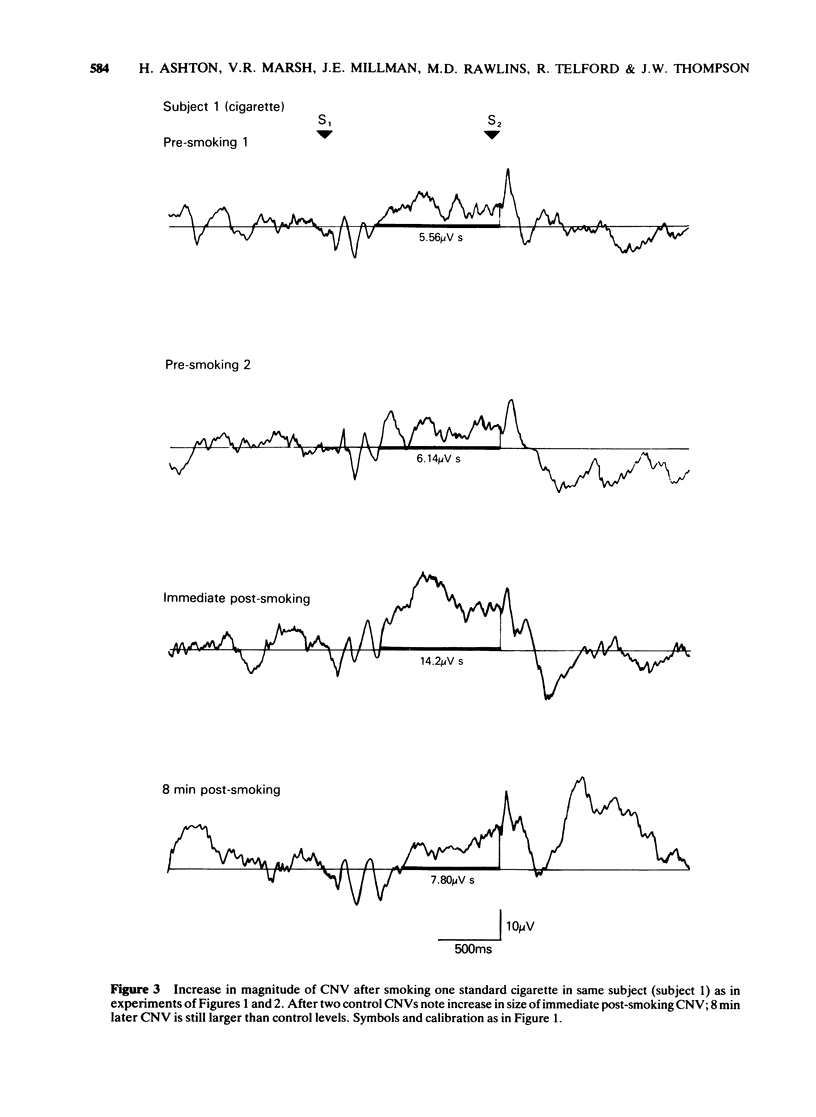
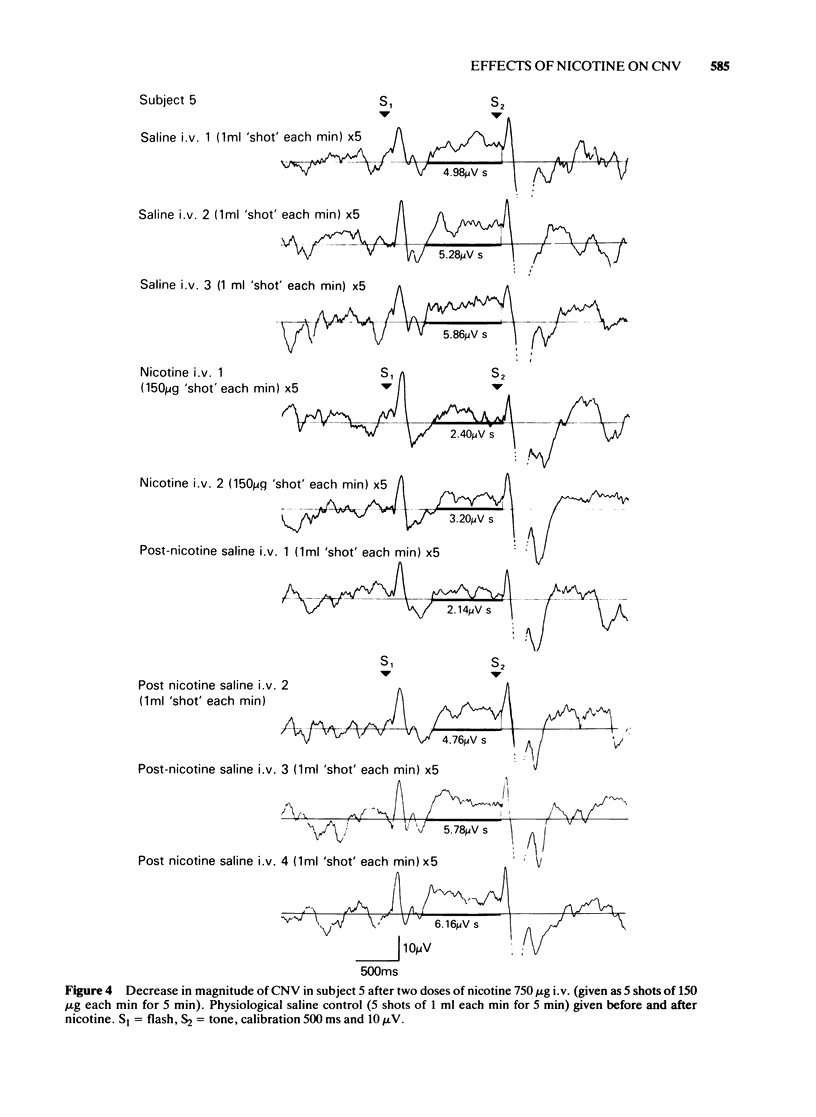
2 In one series of experiments in five subjects, a fixed dose of nicotine was used. In three of these subjects nicotine 500 μg or 750 μg produced a reproducible increase in magnitude of the CNV. In two subjects nictone 750 μg produced a reproducible decrease in magnitude of the CNV. The direction and magnitude of the CNV changes could be reproduced by cigarette smoking.
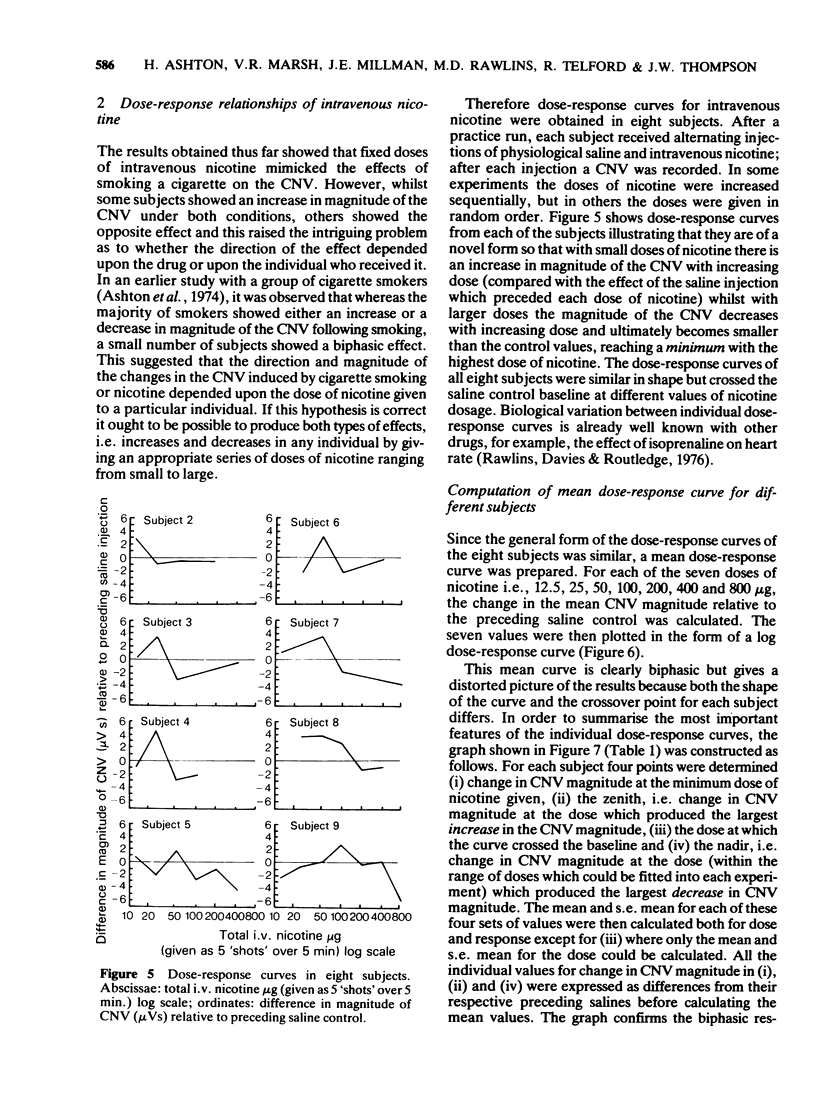
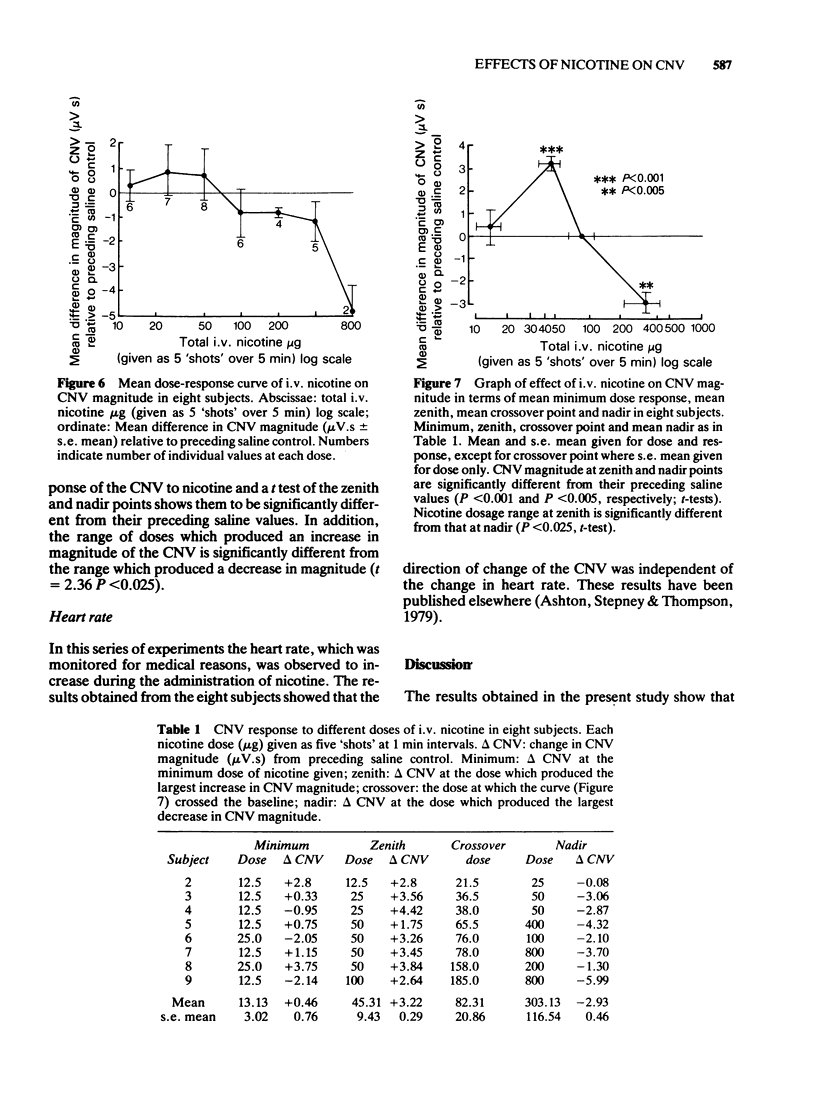
3 In another series of experiments in eight subjects, dose-response relationships for the effect of nicotine on the CNV were measured using a range of doses from 12.5 to 800 μg. Individual and mean dose-response curves were found to be biphasic so that whilst smaller doses produced an increase of CNV magnitude (stimulant effect), larger doses produced a decrease of the CNV (depressant effect).
4 The results are discussed in relation to the possible mechanism of action on the brain of nicotine as obtained by inhaling cigarette smokers.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armitage A. K., Dollery C. T., George C. F., Houseman T. H., Lewis P. J., Turner D. M. Absorption and metabolism of nicotine from cigarettes. Br Med J. 1975 Nov 8;4(5992):313–316. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5992.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armitage A. K., Hall G. H., Morrison C. F. Pharmacological basis for the tobacco smoking habit. Nature. 1968 Jan 27;217(5126):331–334. doi: 10.1038/217331a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armitage A. K., Hall G. H., Sellers C. M. Effects of nicotine on electrocortical activity and acetylcholine release from the cat cerebral cortex. Br J Pharmacol. 1969 Jan;35(1):152–160. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1969.tb07976.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashton H., Milliman J. E., Telford R., Thompson J. W. Stimulant and depressant effects of cigarette smoking on brain activity in man. Br J Pharmacol. 1973 Aug;48(4):715–717. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1973.tb08260.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashton H., Millman J. E., Telford R., Thompson J. W. A comparison of some physiological and psychological effects of Motival (fluphenazine and nortriptyline) and diazepam in normal subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1978 Feb;5(2):141–147. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1978.tb01615.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashton H., Millman J. E., Telford R., Thompson J. W. The effect of caffeine, nitrazepam and cigarette smoking on the contingent negative variation in man. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1974 Jul;37(1):59–71. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(74)90245-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashton H., Stepney R., Thompson J. W. Self-titration by cigarette smokers. Br Med J. 1979 Aug 11;2(6186):357–360. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6186.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashton H., Watson D. W. Puffing frequency and nicotine intake in cigarette smokers. Br Med J. 1970 Sep 19;3(5724):679–681. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5724.679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldberg W., Vartiainen A. Further observations on the physiology and pharmacology of a sympathetic ganglion. J Physiol. 1934 Dec 14;83(1):103–128. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1934.sp003214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopell B. S., Tinklenberg J. R., Hollister L. E. Contingent negative variation amplitudes. Marihuana and alcohol. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1972 Dec;27(6):809–811. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1972.01750300071012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopell B. S., Wittner W. K., Lunde D. T., Wolcott L. J., Tinklenberg J. R. The effects of methamphetamine and secobarbital on the contingent negative variation amplitude. Psychopharmacologia. 1974 Jan 9;34(1):55–62. doi: 10.1007/BF00421220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. D., Klonoff H., Marcus A. The neurophysiological basis of the marijuana experience. Can Med Assoc J. 1973 Jan 20;108(2):157–165. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATON W. D. M., PERRY W. L. M. The relationship between depolarization and block in the cat's superior cervical ganglion. J Physiol. 1953 Jan;119(1):43–57. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebert C. S. Cortical and subcortical slow potentials in the monkey's brain during a preparatory interval. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1972 Oct;33(4):389–402. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(72)90119-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Routtenberg A. The two-arousal hypothesis: reticular formation and limbic system. Psychol Rev. 1968 Jan;75(1):51–80. doi: 10.1037/h0025303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMITERLOW C. G., HANSSON E. Physiological disposition and fate of nicotine labelled with carbon-14 in mice. Nature. 1962 Apr 21;194:298–299. doi: 10.1038/194298b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tecce J. J., Cole J. O., Savignano-Bowman J. Chlorpromazine effects on brain activity (contingent negative variation) and reaction time in normal women. Psychopharmacologia. 1975 Sep 17;43(3):293–295. doi: 10.1007/BF00429268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALTER W. G., COOPER R., ALDRIDGE V. J., MCCALLUM W. C., WINTER A. L. CONTINGENT NEGATIVE VARIATION: AN ELECTRIC SIGN OF SENSORIMOTOR ASSOCIATION AND EXPECTANCY IN THE HUMAN BRAIN. Nature. 1964 Jul 25;203:380–384. doi: 10.1038/203380a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALTER W. G. SLOW POTENTIAL WAVES IN THE HUMAN BRAIN ASSOCIATED WITH EXPECTANCY, ATTENTION AND DECISION. Arch Psychiatr Nervenkr. 1964 Dec 2;206:309–322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


