Abstract
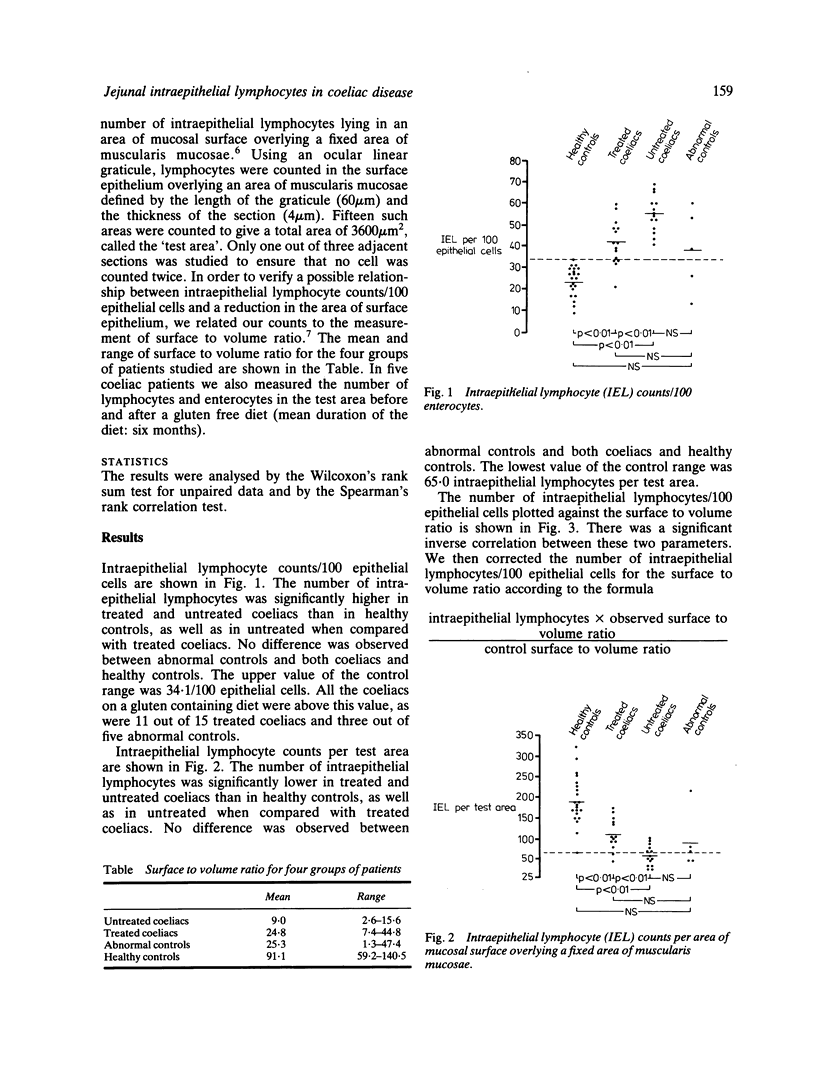
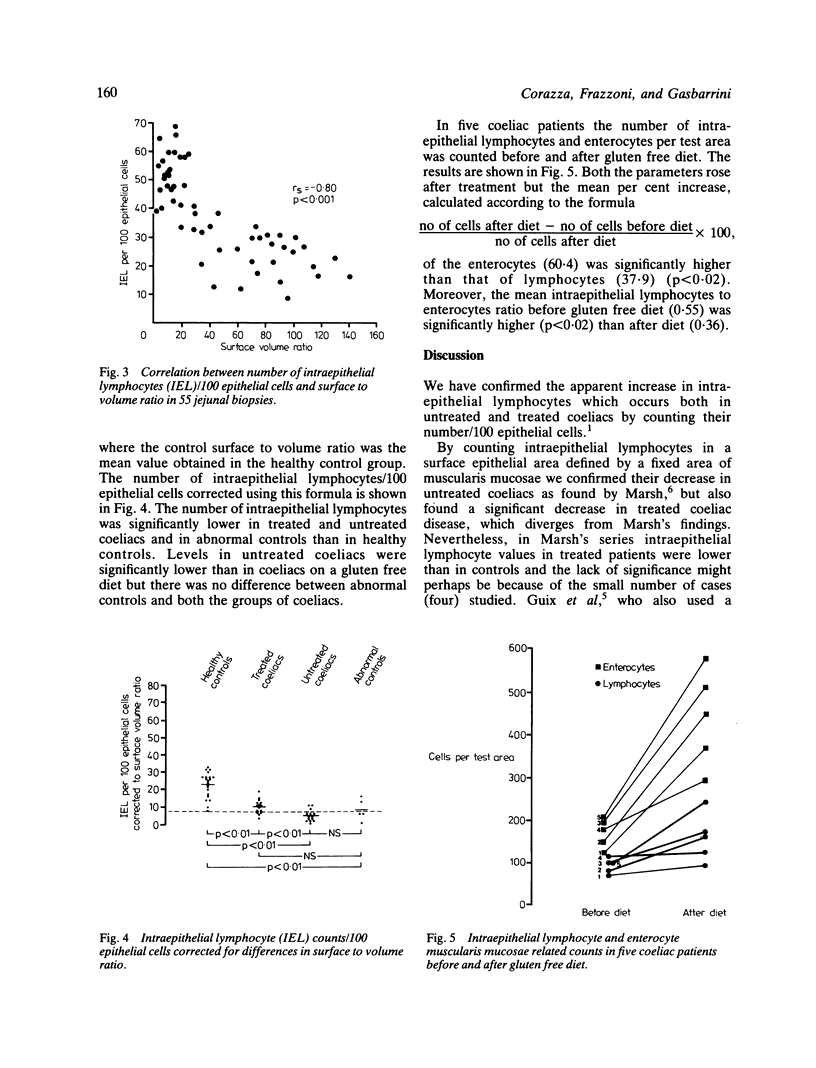
We have quantified intraepithelial lymphocytes in the same biopsy series (21 healthy controls, 14 untreated coeliacs, 15 treated coeliacs, five non-coeliac patients with an abnormal jejunal mucosa) both as counts/100 epithelial cells and using as reference value a fixed area of muscularis mucosae. As expected, the number of intraepithelial lymphocytes/100 epithelial cells was significantly higher in untreated and treated coeliacs than in healthy controls, as well as in untreated when compared with treated coeliac patients. Otherwise, the number of intraepithelial lymphocytes lying in the area of mucosal surface overlying a fixed area of muscularis mucosae was significantly lower in treated and untreated coeliacs, than in healthy controls, as well as in untreated when compared with treated coeliacs. A highly significant inverse correlation was found between the number of intraepithelial lymphocytes/100 epithelial cells and the mucosal surface area measured as surface to volume ratio. When the number of intraepithelial lymphocytes/100 epithelial cells was corrected for differences in surface to volume ratio, the results were very similar to those obtained by a muscularis mucosae related count. In five coeliacs both intraepithelial lymphocyte and enterocyte muscularis mucosae related counts rose after a period of gluten free diet but the mean per cent increase of enterocytes was significantly higher than that of lymphocytes. Our results are compatible with a decrease in the total number of intraepithelial lymphocytes in the entire small bowel in coeliac disease. In untreated coeliac mucosae, however, a derangement in the usual proportions of intraepithelial lymphocytes and enterocytes is evident and may be important in the pathogenesis of coeliac disease.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Douglas A. P., Weetman A. P., Haggith J. W. The distribution and enteric loss of 51Cr-labelled lymphocytes in normal subjects and in patients with coeliac disease and other disorders of the small intestine. Digestion. 1976;14(1):29–43. doi: 10.1159/000197797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunnill M. S., Whitehead R. A method for the quantitation of small intestinal biopsy specimens. J Clin Pathol. 1972 Mar;25(3):243–246. doi: 10.1136/jcp.25.3.243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falchuk Z. M. Update on gluten-sensitive enteropathy. Am J Med. 1979 Dec;67(6):1085–1096. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(79)90651-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson A. Intraepithelial lymphocytes of the small intestine. Gut. 1977 Nov;18(11):921–937. doi: 10.1136/gut.18.11.921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson A., McClure J. P., Townley R. R. Intraepithelial lymphocyte counts in small intestinal biopsies from children with diarrhoea. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1976 Sep;65(5):541–546. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1976.tb04929.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson A., Murray D. Quantitation of intraepithelial lymphocytes in human jejunum. Gut. 1971 Dec;12(12):988–994. doi: 10.1136/gut.12.12.988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glasgow J. F., Corkey C. W., Molla A. Critical assessment of small bowel biopsy in children. Arch Dis Child. 1979 Aug;54(8):604–608. doi: 10.1136/adc.54.8.604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guix M., Skinner J. M., Whitehead R. Measuring intraepithelial lymphocytes, surface area, and volume of lamina propria in the jejunal mucosa of coeliac patients. Gut. 1979 Apr;20(4):275–278. doi: 10.1136/gut.20.4.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes G. K., Asquith P., Stokes P. L., Cooke W. T. Cellular infiltrate of jejunal biopsies in adult coeliac disease in relation to gluten withdrawal. Gut. 1974 Apr;15(4):278–283. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh M. N. Studies of intestinal lymphoid tissue. III. Quantitative analyses of epithelial lymphocytes in the small intestine of human control subjects and of patients with celiac sprue. Gastroenterology. 1980 Sep;79(3):481–492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh M. N. Studies of intestinal lymphoid tissue: the cytology and electron microscopy of gluten-sensitive enteropathy, with particular reference to its immunopathology. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1981;70:87–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mavromichalis J., Brueton M. J., McNeish A. S., Anderson C. M. Evaluation of the intraepithelial lymphocyte count in the jejunum in childhood enteropathies. Gut. 1976 Aug;17(8):600–603. doi: 10.1136/gut.17.8.600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selby W. S., Janossy G., Goldstein G., Jewell D. P. T lymphocyte subsets in human intestinal mucosa: the distribution and relationship to MHC-derived antigens. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Jun;44(3):453–458. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selby W. S., Janossy G., Jewell D. P. Immunohistological characterisation of intraepithelial lymphocytes of the human gastrointestinal tract. Gut. 1981 Mar;22(3):169–176. doi: 10.1136/gut.22.3.169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright N., Watson A., Morley A., Appleton D., Marks J. Cell kinetics in flat (avillous) mucosa of the human small intestine. Gut. 1973 Sep;14(9):701–710. doi: 10.1136/gut.14.9.701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


