Abstract
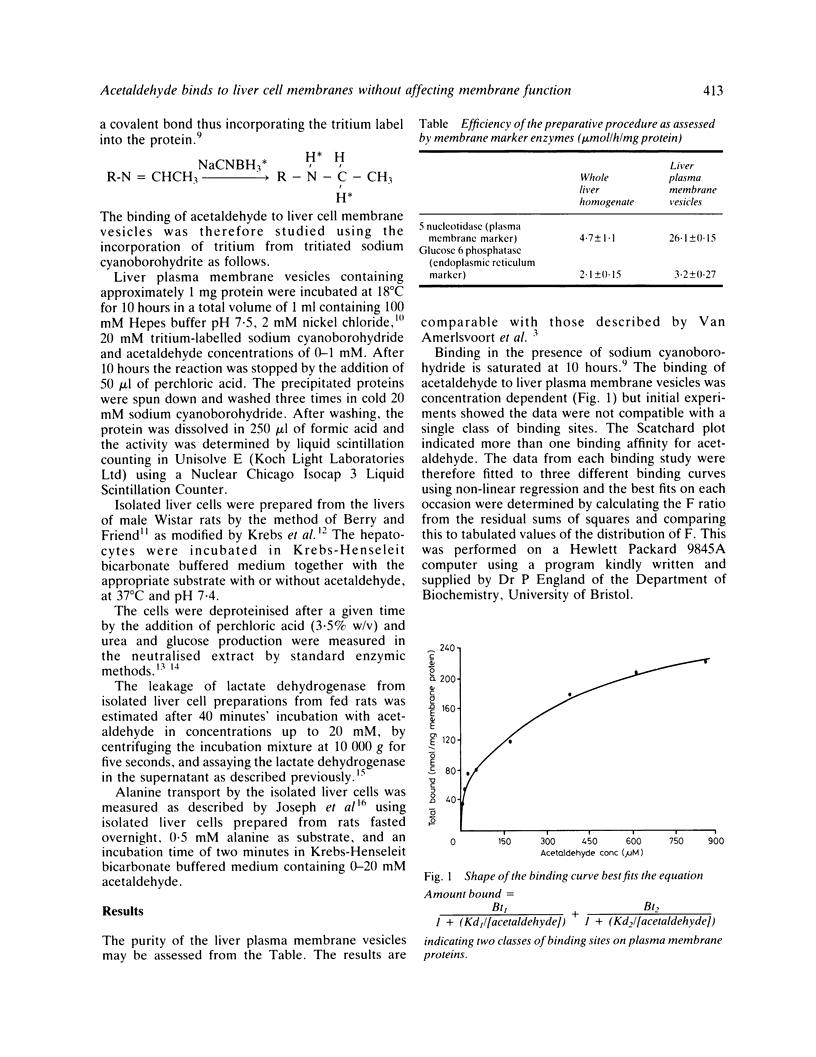
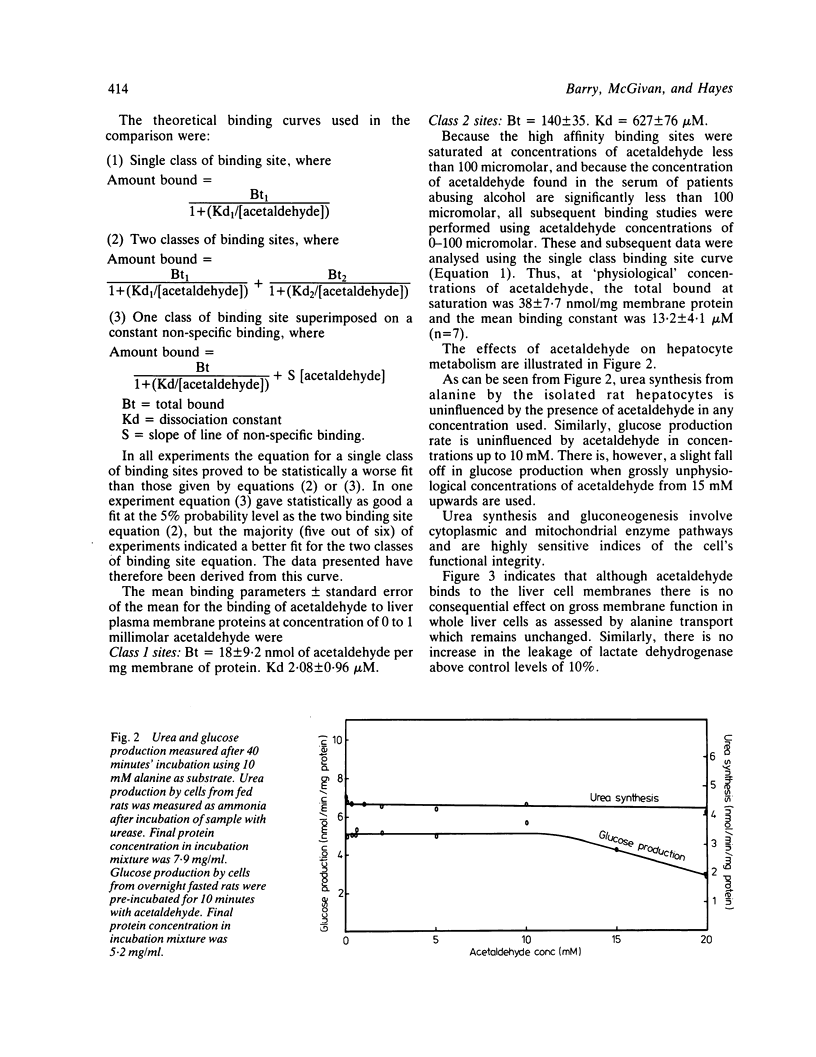
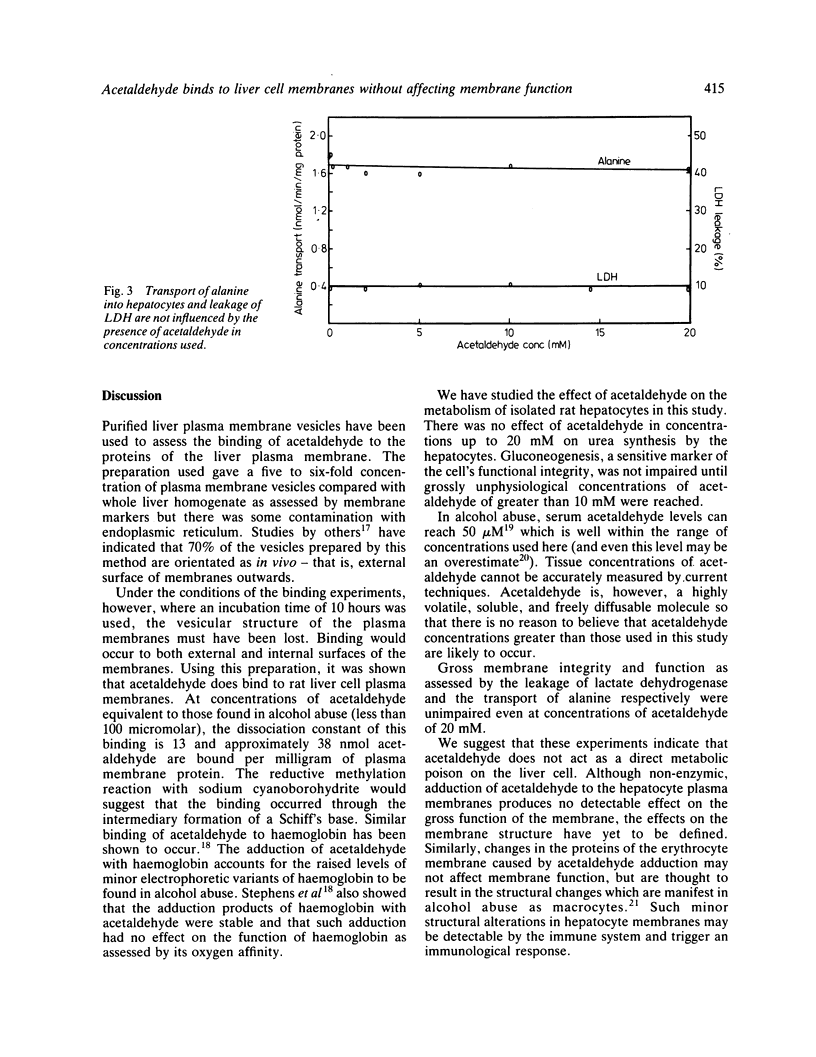
Acetaldehyde is a major metabolic product of ethanol and is found in high concentrations in the serum during alcohol abuse. The effects of acetaldehyde on isolated rat liver cells and on purified hepatocyte plasma membrane vesicles have been studied. In concentrations of 0-10 millimolar acetaldehyde has been shown to have no detectable effect on either hepatocyte metabolism or gross membrane function and is therefore unlikely to act as a direct metabolic poison. Acetaldehyde, however, is shown to bind to hepatocyte membranes via intermediary Schiff's base formation. The adduction of acetaldehyde to liver cell plasma membranes may have an effect on membrane structure. These findings are consistent with the hypothesis that any injurious effect of acetaldehyde on the liver may be mediated via the immune system rather than being a direct effect on cell metabolism.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berry M. N., Friend D. S. High-yield preparation of isolated rat liver parenchymal cells: a biochemical and fine structural study. J Cell Biol. 1969 Dec;43(3):506–520. doi: 10.1083/jcb.43.3.506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane A. M., Moussouros A., Portmann B., McFarlane I. G., Thomson A. D., Eddleston, Williams R. Lymphocyte cytotoxicity for isolated hepatocytes in alcoholic liver disease. Gastroenterology. 1977 May;72(5 Pt 1):918–923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson C. J. Elevated blood acetaldehyde levels in alcoholics and their relatives: a reevaluation. Science. 1980 Mar 21;207(4437):1383–1384. doi: 10.1126/science.7355298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaines K. C., Salhany J. M., Tuma D. J., Sorrell M. F. Reaction of acetaldehyde with human erythrocyte membrane proteins. FEBS Lett. 1977 Mar 15;75(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80065-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jentoft N., Dearborn D. G. Labeling of proteins by reductive methylation using sodium cyanoborohydride. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 10;254(11):4359–4365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jentoft N., Dearborn D. G. Protein labeling by reductive methylation with sodium cyanoborohydride: effect of cyanide and metal ions on the reaction. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jul 15;106(1):186–190. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90135-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph S. K., Bradford N. M., McGivan J. D. Characteristics of the transport of alanine, serine and glutamine across the plasma membrane of isolated rat liver cells. Biochem J. 1978 Dec 15;176(3):827–836. doi: 10.1042/bj1760827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIRSTEN E., GEREZ C., KIRSTEN R. [An enzymatic microdetermination method for ammonia, specifically for extracts of animal tissues and fluids. Determination of NH4 ions in blood]. Biochem Z. 1963;337:312–319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KREBS H. A., BENNETT D. A., DE GASQUET P., GASQUET P., GASCOYNE T., YOSHIDA T. Renal gluconeogenesis. The effect of diet on the gluconeogenic capacity of rat-kidney-cortex slices. Biochem J. 1963 Jan;86:22–27. doi: 10.1042/bj0860022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanagasundaram N., Leevy C. M. Ethanol, immune reactions and the digestive system. Clin Gastroenterol. 1981 May;10(2):295–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korsten M. A., Matsuzaki S., Feinman L., Lieber C. S. High blood acetaldehyde levels after ethanol administration. Difference between alcoholic and nonalcoholic subjects. N Engl J Med. 1975 Feb 20;292(8):386–389. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197502202920802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samson M., Fehlmann M. Plasma membrane vesicles from isolated hepatocytes retain the increase of amino acid transport induced by dibutyryl cyclic AMP in intact cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Apr 23;687(1):35–41. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90167-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sear J. W., McGivan J. D. Cytotoxicity of i.v. anaesthetic agents on the isolated rat hepatocyte. Br J Anaesth. 1979 Aug;51(8):733–739. doi: 10.1093/bja/51.8.733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens V. J., Fantl W. J., Newman C. B., Sims R. V., Cerami A., Peterson C. M. Acetaldehyde adducts with hemoglobin. J Clin Invest. 1981 Feb;67(2):361–369. doi: 10.1172/JCI110043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Amelsvoort J. M., Sips H. J., van Dam K. Sodium-dependent alanine transport in plasma-membrane vesicles from rat liver. Biochem J. 1978 Sep 15;174(3):1083–1086. doi: 10.1042/bj1741083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


