Abstract
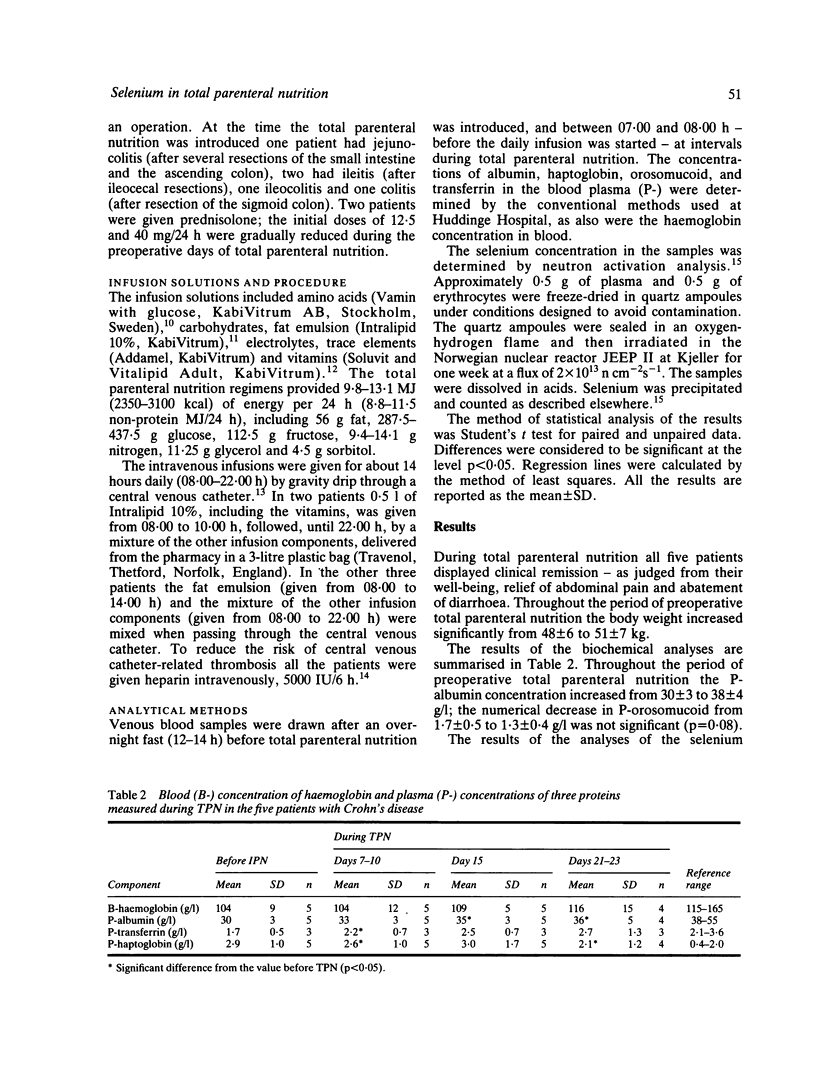
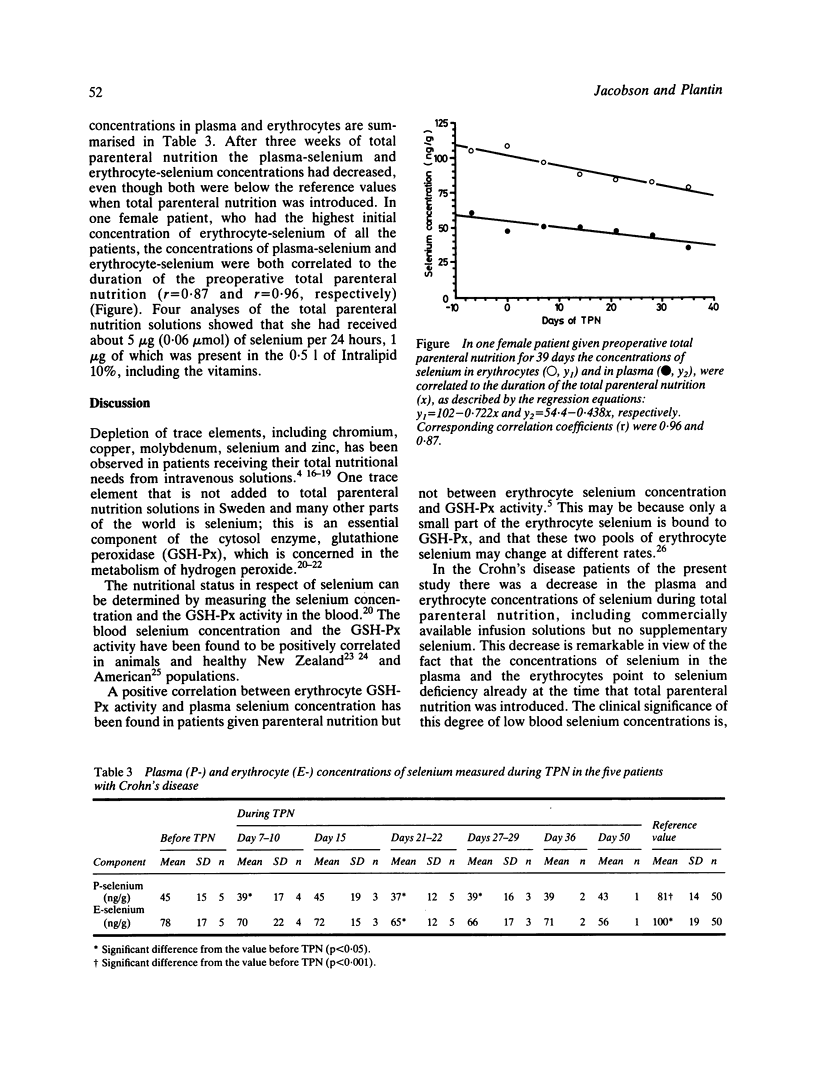
Plasma- and erythrocyte-selenium concentrations were determined in five consecutive patients with Crohn's disease given preoperative total parenteral nutrition - nil per os - for a mean period of 34 days per patient. No blood components were administered during the total parenteral nutrition. Before the total parenteral nutrition the plasma-selenium level and, to a less extent, the erythrocyte-selenium levels were below the reference values. After three weeks of total parenteral nutrition both concentrations had fallen. There were, however, clinical and biochemical signs of improvement during the total parenteral nutrition, as indicated by an increase in body weight, P-albumin and P-transferrin. In one female patient given 39 days of preoperative total parenteral nutrition containing 0.06 mumol (5 micrograms) selenium per 24 h the decreasing levels of plasma-selenium and erythrocyte-selenium were both correlated to the duration of the total parenteral nutrition (r = 0.87 and 0.96, respectively). The results suggest that total parenteral nutrition patients may be at risk for selenium deficiency, and that a supplementary administration of selenium via total parenteral nutrition may be required.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abumrad N. N., Schneider A. J., Steel D., Rogers L. S. Amino acid intolerance during prolonged total parenteral nutrition reversed by molybdate therapy. Am J Clin Nutr. 1981 Nov;34(11):2551–2559. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/34.11.2551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behne D., Wolters W. Selenium content and glutathione peroxidase activity in the plasma and erythrocytes of non-pregnant and pregnant women. J Clin Chem Clin Biochem. 1979 Mar;17(3):133–135. doi: 10.1515/cclm.1979.17.3.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Best W. R., Becktel J. M., Singleton J. W., Kern F., Jr Development of a Crohn's disease activity index. National Cooperative Crohn's Disease Study. Gastroenterology. 1976 Mar;70(3):439–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brismar B., Hårdstedt C., Jacobson S., Kager L., Malmborg A. S. Reduction of catheter-associated thrombosis in parenteral nutrition by intravenous heparin therapy. Arch Surg. 1982 Sep;117(9):1196–1199. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1982.01380330054013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll R. H., Jr, Rosenberg I. H. Total parenteral nutrition in inflammatory bowel disease. Med Clin North Am. 1978 Jan;62(1):185–201. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)31831-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming C. R., Lie J. T., McCall J. T., O'Brien J. F., Baillie E. E., Thistle J. L. Selenium deficiency and fatal cardiomyopathy in a patient on home parenteral nutrition. Gastroenterology. 1982 Sep;83(3):689–693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forstrom J. W., Zakowski J. J., Tappel A. L. Identification of the catalytic site of rat liver glutathione peroxidase as selenocysteine. Biochemistry. 1978 Jun 27;17(13):2639–2644. doi: 10.1021/bi00606a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg H. I., Caruthers S. B., Jr, Nelson J. A., Singleton J. W. Radiographic findings of the National Cooperative Crohn's Disease Study. Gastroenterology. 1979 Oct;77(4 Pt 2):925–937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huston R. K., Benda G. I., Carlson C. V., Shearer T. R., Reynolds J. W., Neerhout R. C. Selenium and vitamin E sufficiency in premature infants requiring total parenteral nutrition. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1982 Nov-Dec;6(6):507–510. doi: 10.1177/0148607182006006507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson S., Plantin L. O., Carlmark B. Urinary excretion and blood concentrations of trace elements and electrolytes during total parenteral nutrition in Crohn's disease. Dig Dis Sci. 1984 Jul;29(7):606–613. doi: 10.1007/BF01347292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson S. Serum concentrations and urinary excretion of amino acids during total parenteral nutrition after abdominal surgery. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1982 May-Jun;6(3):204–213. doi: 10.1177/0148607182006003204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson S., Wester P-O Balance study of twenty trace elements during total parenteral nutrition in man. Br J Nutr. 1977 Jan;37(1):107–126. doi: 10.1079/bjn19770011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeejeebhoy K. N., Chu R. C., Marliss E. B., Greenberg G. R., Bruce-Robertson A. Chromium deficiency, glucose intolerance, and neuropathy reversed by chromium supplementation, in a patient receiving long-term total parenteral nutrition. Am J Clin Nutr. 1977 Apr;30(4):531–538. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/30.4.531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeejeebhoy K. N., Langer B., Tsallas G., Chu R. C., Kuksis A., Anderson G. H. Total parenteral nutrition at home: studies in patients surviving 4 months to 5 years. Gastroenterology. 1976 Dec;71(6):943–953. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane H. W., Barroso A. O., Englert D., Dudrick S. J., MacFadyen B. S., Jr Selenium status of seven chronic intravenous hyperalimentation patients. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1982 Sep-Oct;6(5):426–431. doi: 10.1177/0148607182006005426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane H. W., Dudrick S., Warren D. C. Blood selenium levels and glutathione-peroxidase activities in university and chronic intravenous hyperalimentation subjects. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1981 Jul;167(3):383–390. doi: 10.3181/00379727-167-41184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehr K., Schober O., Hundeshagen H., Pichlmayr R. Total body potassium depletion and the need for preoperative nutritional support in Chrohn's disease. Ann Surg. 1982 Dec;196(6):709–714. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198212001-00017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milewski P. J., Irving M. H. Parenteral nutrition in Crohn's disease. Dis Colon Rectum. 1980 Sep;23(6):395–400. doi: 10.1007/BF02586786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price A. B., Morson B. C. Inflammatory bowel disease: the surgical pathology of Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Hum Pathol. 1975 Jan;6(1):7–29. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(75)80107-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotruck J. T., Pope A. L., Ganther H. E., Swanson A. B., Hafeman D. G., Hoekstra W. G. Selenium: biochemical role as a component of glutathione peroxidase. Science. 1973 Feb 9;179(4073):588–590. doi: 10.1126/science.179.4073.588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. L., Goos S. M. Selenium nutriture in total parenteral nutrition: intake levels. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1980 Jan-Feb;4(1):23–26. doi: 10.1177/014860718000400108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomons N. W., Layden T. J., Rosenberg I. H., Vo-Khactu K., Sandstead H. H. Plasma trace metals during total parenteral alimentation. Gastroenterology. 1976 Jun;70(6):1022–1025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadtman T. C. Selenium-dependent enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:93–110. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.000521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson C. D., Rea H. M., Doesburg V. M., Robinson M. F. Selenium concentrations and glutathione peroxidase activities in whole blood of New Zealand residents. Br J Nutr. 1977 May;37(3):457–460. doi: 10.1079/bjn19770049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson C. D., Robinson M. F. Selenium in human health and disease with emphasis on those aspects peculiar to New Zealand. Am J Clin Nutr. 1980 Feb;33(2):303–323. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/33.2.303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willett W. C., Polk B. F., Morris J. S., Stampfer M. J., Pressel S., Rosner B., Taylor J. O., Schneider K., Hames C. G. Prediagnostic serum selenium and risk of cancer. Lancet. 1983 Jul 16;2(8342):130–134. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90116-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Rij A. M., Thomson C. D., McKenzie J. M., Robinson M. F. Selenium deficiency in total parenteral nutrition. Am J Clin Nutr. 1979 Oct;32(10):2076–2085. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/32.10.2076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


