Abstract
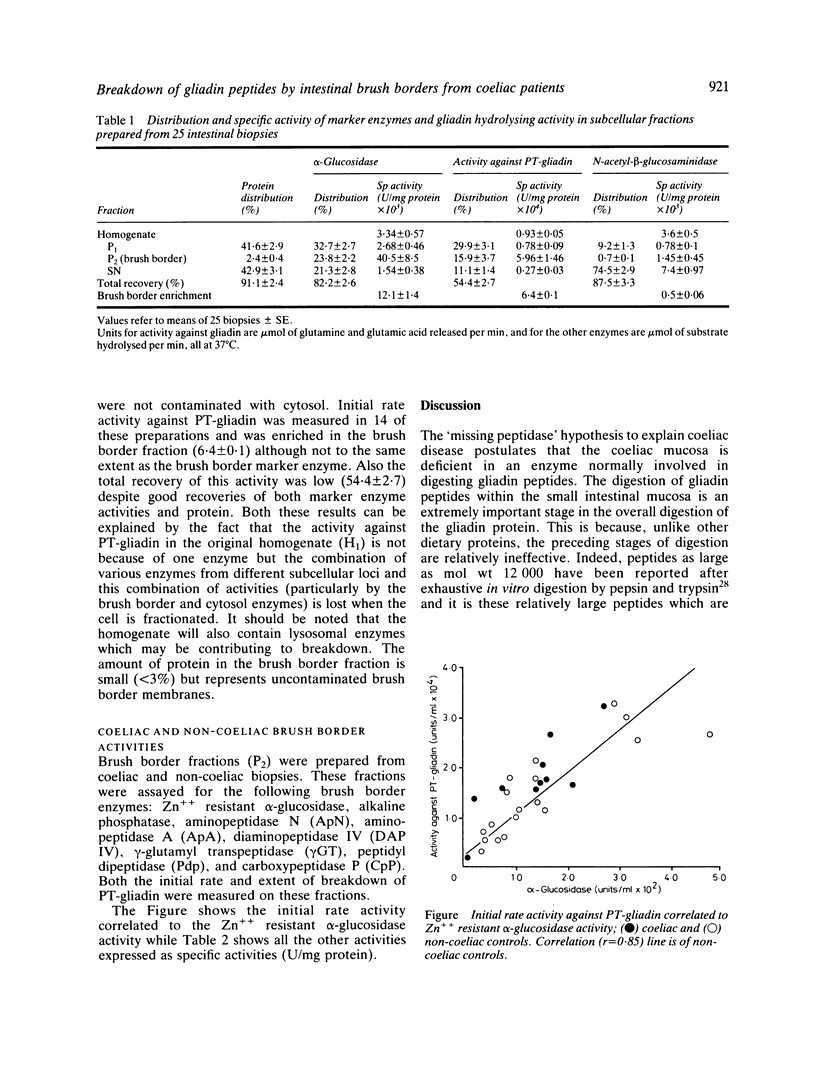
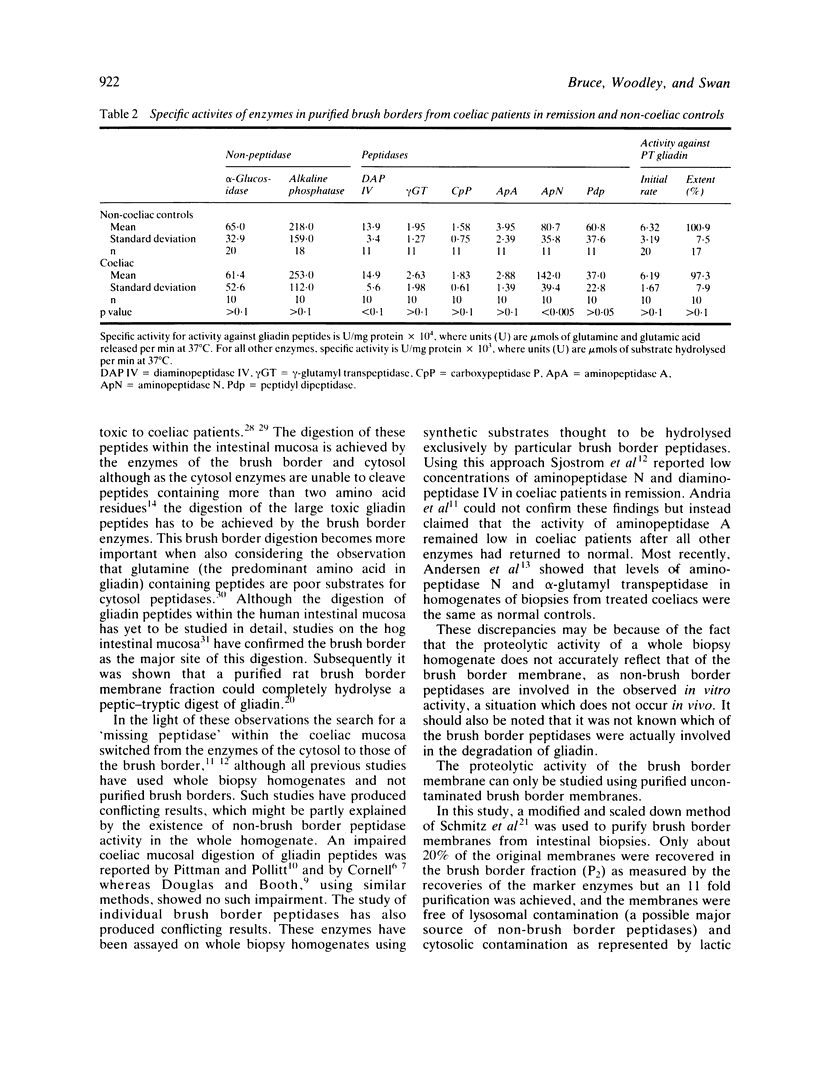
The 'missing peptidase' hypothesis to explain the aetiology of coeliac disease has never been satisfactorily resolved and recent reports suggest that coeliac brush borders may have depressed levels of specific peptidase enzymes. It has been inferred from these studies that the subsequent brush border digestion of gliadin peptides may therefore be defective. In this present study a sensitive fluorometric assay was used to measure the hydrolysis of a peptic-tryptic digest of gliadin by both normal and coeliac brush borders. The coeliac brush borders were as efficient as the normals in hydrolysing gliadin peptides and showed no depression of any specific peptidase activity.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen K. J., Schjønsby H., Skagen D. W. Jejunal mucosal enzymes in untreated and treated coeliac disease. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1983 Mar;18(2):251–256. doi: 10.3109/00365528309181591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andria G., Cucchiara S., De Vizia B., De Ritis G., Mazzacca G., Auricchio S. Brush border and cytosol peptidase activities of human small intestine in normal subjects and celiac patients. Pediatr Res. 1980 Jun;14(6):812–818. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198006000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auricchio S., Greco L., de Vizia B., Buonocore V. Dipeptidylaminopeptidase and carboxypeptidase activities of the brush border of rabbit small intestine. Gastroenterology. 1978 Dec;75(6):1073–1079. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg N. O., Dahlqvist A., Lindberg T., Nordén A. Intestinal dipeptidases and disaccharidases in celiac disease in adults. Gastroenterology. 1970 Oct;59(4):575–582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruce G., Woodley J. F. An accurate fluorometric method to measure the breakdown of gliadin and gliadin peptides. Clin Chim Acta. 1981 Dec 24;117(3):325–332. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(81)90120-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung H. S., Cushman D. W. Inhibition of homogeneous angiotensin-converting enzyme of rabbit lung by synthetic venom peptides of Bothrops jararaca. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 15;293(2):451–463. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(73)90352-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornell H. J., Rolles C. J. Further evidence of a primary mucosal defect in coeliac disease. Gut. 1978 Apr;19(4):253–259. doi: 10.1136/gut.19.4.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornell H. J., Townley R. R. Investigation of possible intestinal peptidase deficiency in coeliac disease. Clin Chim Acta. 1973 Jan 10;43(1):113–125. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(73)90126-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donlon J., Fottrell P. F. Purification and characterization of one of the forms of peptide hydrolases from guinea-pig small intestinal mucosa. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Dec 19;327(2):425–436. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(73)90426-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas A. P., Booth C. C. Digestion of gluten peptides by normal human jejunal mucosa and by mucosa from patients with adult coeliac disease. Clin Sci. 1970 Jan;38(1):11–25. doi: 10.1042/cs0380011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRAZER A. C. On the growth defect in coelic disease. Proc R Soc Med. 1956 Dec;49(12):1009–1013. doi: 10.1177/003591575604901210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grävinghoff J., Hütter H. J. The activities of alanine aminopeptidase, leucine aminopeptidase, proline dipeptidase and prolyl dipeptidase in the mucosa of the small intestine. Investigations on normal children and patients with the malabsorption syndrome. Eur J Pediatr. 1977 Dec 30;127(1):57–62. doi: 10.1007/BF00465566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall R. P., Strober W., Katz S. I., Lawley T. J. IgA-containing circulating immune complexes in gluten-sensitive enteropathy. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Aug;45(2):234–239. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iijima K. I., Takei T., Hino M., Hayakawa T. A new fluorescence assay for dipeptidylpeptidase IV using tripeptide L-prolyl-L-prolyl-L-alanine as substrate. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1980 Aug;3(2):89–96. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(80)90031-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. S., Kim Y. W., Gaines H. D., Sleisenger M. H. Zymogram studies of human intestinal brush border and cytoplasmic peptidases. Gut. 1979 Nov;20(11):987–991. doi: 10.1136/gut.20.11.987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROBERTS N. R., KAPPHAHN J. I. The fluorometric measurement of pyridine nucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1957 Feb;224(2):1047–1064. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh M. N. The small intestine: mechanisms of local immunity and gluten sensitivity. Clin Sci (Lond) 1981 Nov;61(5):497–503. doi: 10.1042/cs0610497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson J. A., Peters T. J. The subcellular localization of peptidase activity in the human jejunum. Eur J Clin Invest. 1979 Oct;9(5):349–354. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1979.tb00895.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters T. J., Jones P. E., Wells G. Analytical subcellular fractionation of jejunal biopsy specimens: enzyme activities, organelle pathology and response to gluten withdrawal in patients with coeliac disease. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1978 Sep;55(3):285–292. doi: 10.1042/cs0550285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman F. E., Pollitt R. J. Studies of jejunal mucosal digestion of peptic-tryptic digests of wheat protein in coeliac disease. Gut. 1966 Aug;7(4):368–371. doi: 10.1136/gut.7.4.368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preiser H., Menard D., Crane R. K., Cerda J. J. Deletion of enzyme protein from the brush border membrane in sucrase-isomaltase deficiency. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Sep 6;363(2):279–282. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90067-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz J., Preiser H., Maestracci D., Ghosh B. K., Cerda J. J., Crane R. K. Purification of the human intestinal brush border membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Sep 27;323(1):98–112. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90434-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöström H., Norén O., Krasilnikoff P. A., Gudmand-Høyer E. Intestinal peptidases and sucrase in coeliac disease. Clin Chim Acta. 1981 Jan 8;109(1):53–58. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(81)90136-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skovbjerg H. Immunoelectrophoretic studies on human small intestinal brush border proteins--the longitudinal distribution of peptidases and disaccharidases. Clin Chim Acta. 1981 May 5;112(2):205–212. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(81)90379-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterchi E. E., Woodley J. F. Peptide hydrolases of the human small intestinal mucosa: distribution of activities between brush border membranes and cytosol. Clin Chim Acta. 1980 Mar 14;102(1):49–56. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(80)90432-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterchi E. E., Woodley J. F. Peptide hydrolases of the human small intestinal mucosa: identification of six distinct enzymes in the brush border membrane. Clin Chim Acta. 1980 Mar 14;102(1):57–65. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(80)90433-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster A. D., Slavin G., Shiner M., Platts-Mills T. A., Asherson G. L. Coeliac disease with severe hypogammaglobulinaemia. Gut. 1981 Feb;22(2):153–157. doi: 10.1136/gut.22.2.153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


