Abstract
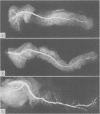
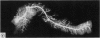
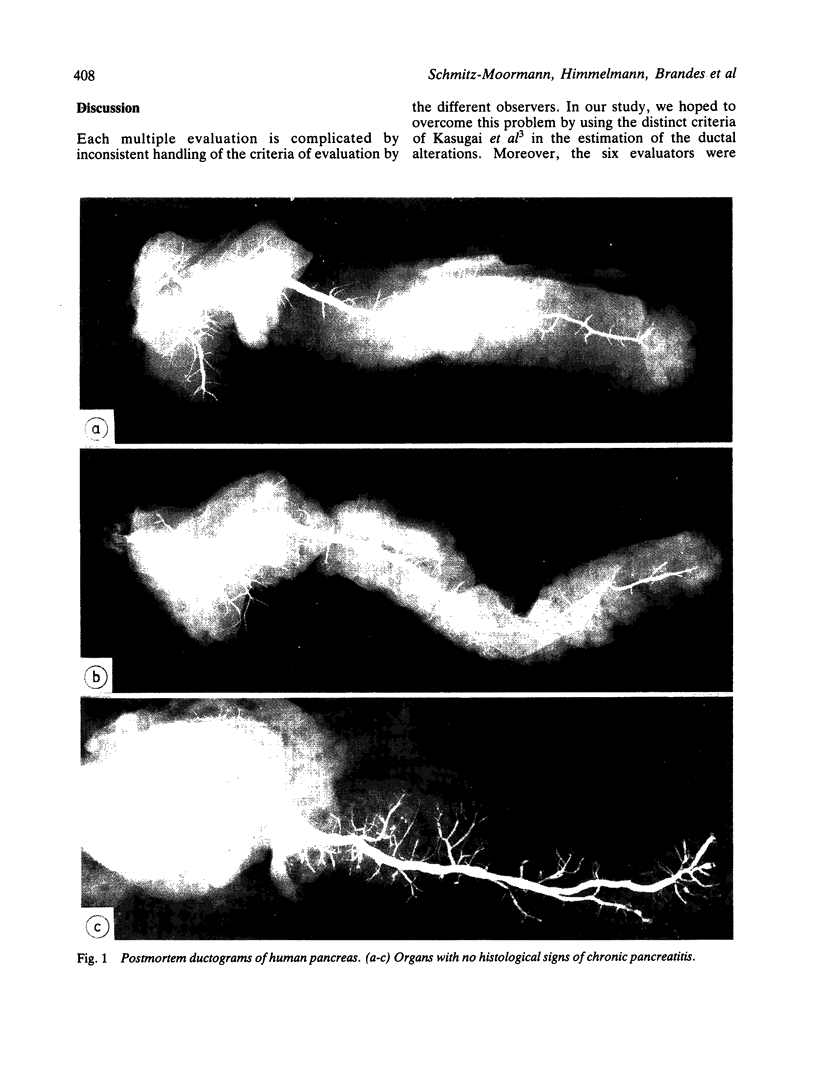
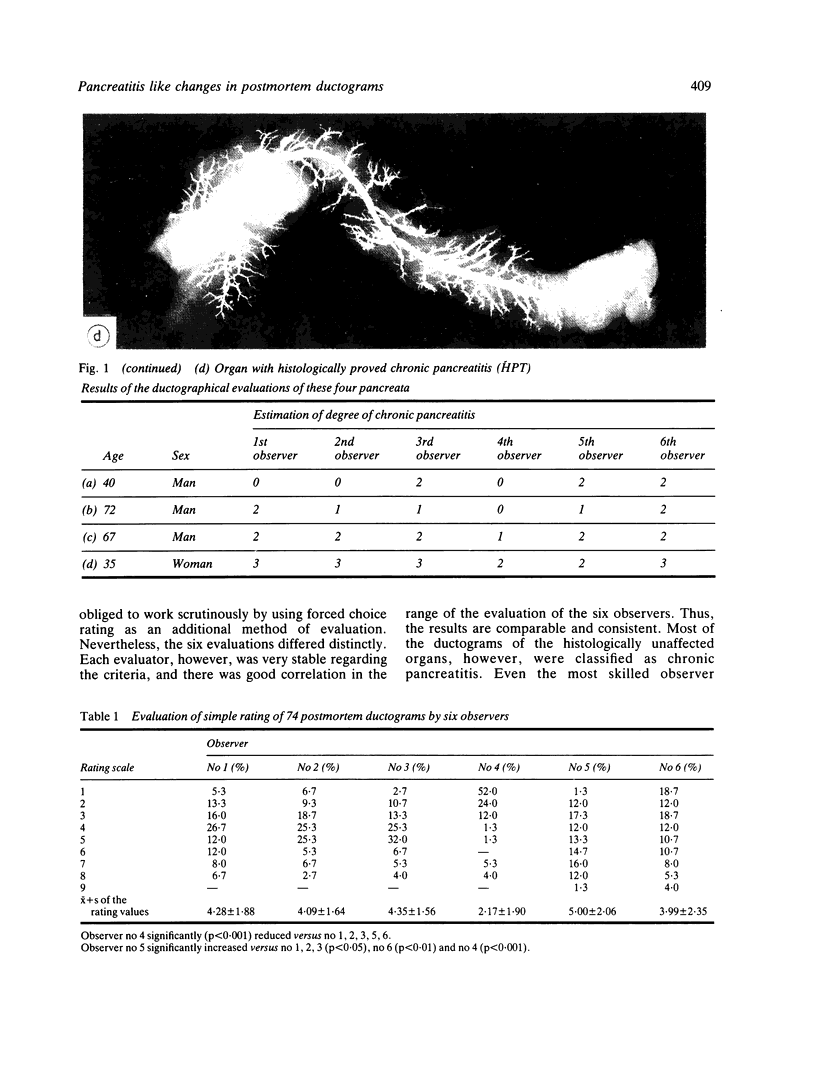
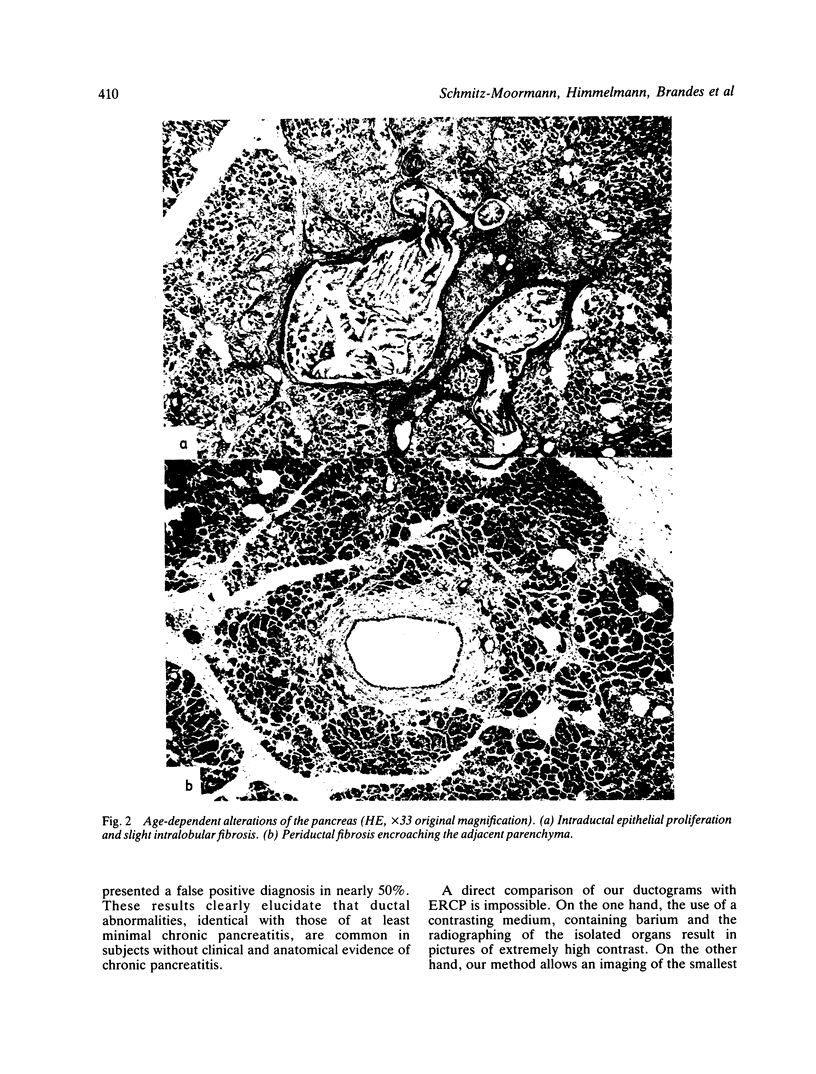
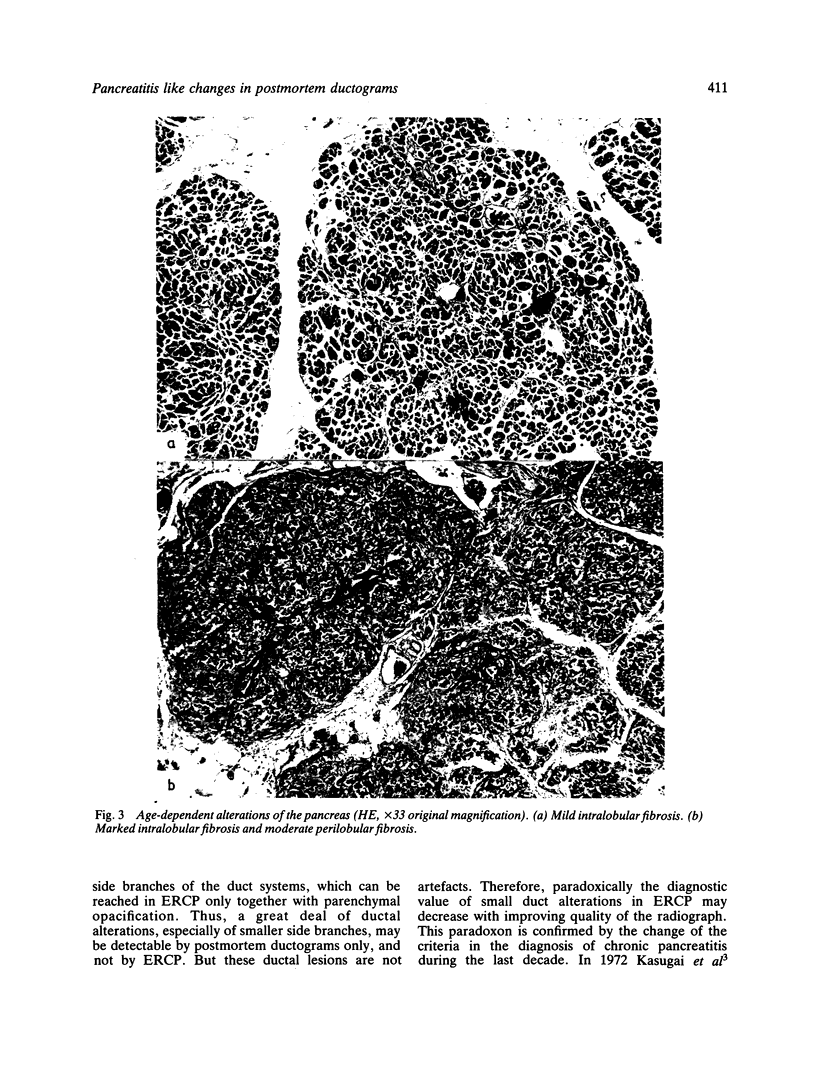
A postmortem study by ductography and histology was performed on 69 human pancreata with no clinical or histological signs of chronic pancreatitis. The ductograms, supplemented by five postmortem ductograms of chronic pancreatitis, were independently evaluated by six clinicians, skilled in ERCP; the degree of alteration was estimated by simple rating, forced choice rating, and by determination of the grade of chronic pancreatitis, Histologically, the amount of intraductal epithelial proliferation, periductal, intralobular and perilobular fibrosis, intraductal protein plugs, and fat necrosis was determined by semiquantitative methods. The six ductographical evaluations significantly differed in the level of their data, but corresponded in the range of distribution. All evaluations were correct regarding judgement of ductograms from patients with chronic pancreatitis. Ductograms of patients without chronic pancreatitis, however, were also frequently classified as chronic pancreatitis; overall 81% (minimal 37%, moderate 33%, severe 11%). This high level of false positive diagnosis indicates the frequency of pancreatitis like lesions in the main duct and its side branches in patients without chronic pancreatitis. Ductal lesions were significantly correlated with perilobular fibrosis. This finding favours the assumption, that in the non-inflamed pancreas, perilobular fibrosis plays a key-role in the development of ductal alterations, as in chronic pancreatitis. Perilobular fibrosis may result from intralobular inflammation caused by age-dependent intraductal epithelial hyperplasia.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Howard J. M., Nedwich A. Correlation of the histologic observations and operative findings in patients with chronic pancreatitis. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1971 Mar;132(3):387–395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasugai T., Kuno N., Kizu M., Kobayashi S., Hattori K. Endoscopic pancreatocholangiography. II. The pathological endoscopic pancreatocholangiogram. Gastroenterology. 1972 Aug;63(2):227–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCune W. S., Shorb P. E., Moscovitz H. Endoscopic cannulation of the ampulla of vater: a preliminary report. Ann Surg. 1968 May;167(5):752–756. doi: 10.1097/00000658-196805000-00013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuben A., Johnson A. L., Cotton P. B. Is pancreatogram interpretation reliable?--a study of observer variation and error. Br J Radiol. 1978 Dec;51(612):956–962. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-51-612-956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarner M., Cotton P. B. Classification of pancreatitis. Gut. 1984 Jul;25(7):756–759. doi: 10.1136/gut.25.7.756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz-Moormann P., Hein J. Altersveräderungen des Pankreasgangsystems und ihre Rückwirkungen auf das Parenchym. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histol. 1976 Aug 23;371(2):145–152. doi: 10.1007/BF00444930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz-Moormann P., Otte C. A., Ihm P., Schmidt G. Vergleichende röntgenologische und morphologische Untersuchungen am menschlichen Pankreas. 3. Morphometrische Untersuchungen am Ductus pancreaticus major. Z Gastroenterol. 1979 Apr;17(4):256–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz-Moormann P., Riedel R., Ihm P. Morphometrische Untersuchung der Kaliberschwankungen am normalen Ductus pancreaticus major. Z Gastroenterol. 1981 Jun;19(6):299–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz-Moormann P., Thoma W., Hein J., Ihm P. Vergleichende röntgenologische und morphologische Untersuchungen am menschlichen Pankreas. 2. Morphometrische Untersuchungen am Gangsystem des menschlichen Pankreas. Anat Anz. 1977;141(5):507–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tympner F., Rösch W., Lutz H., Koch H. Diagnostische Methoden bei chronischer Pankreatitis. Stellenwert von endoskopisch retrograder Pankreatikographie, volumenverlustkorrigiertem Sekretin. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1978 May 12;103(19):805–805. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1104514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]