Abstract
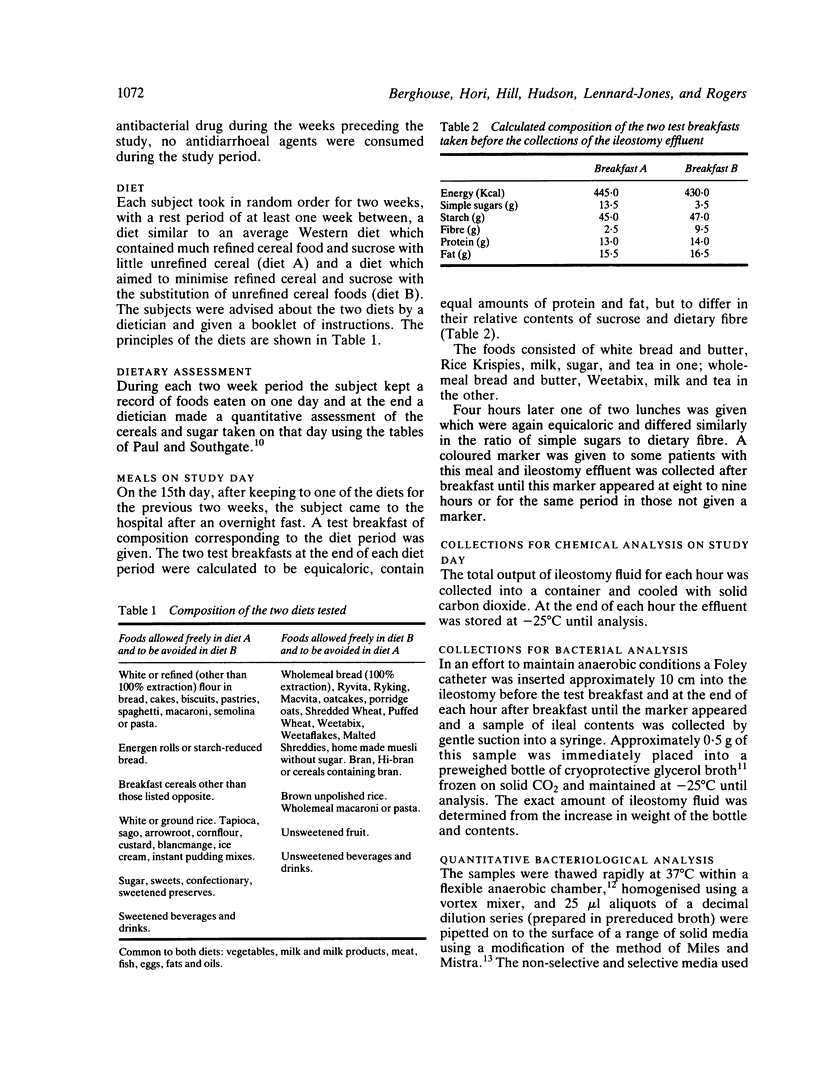
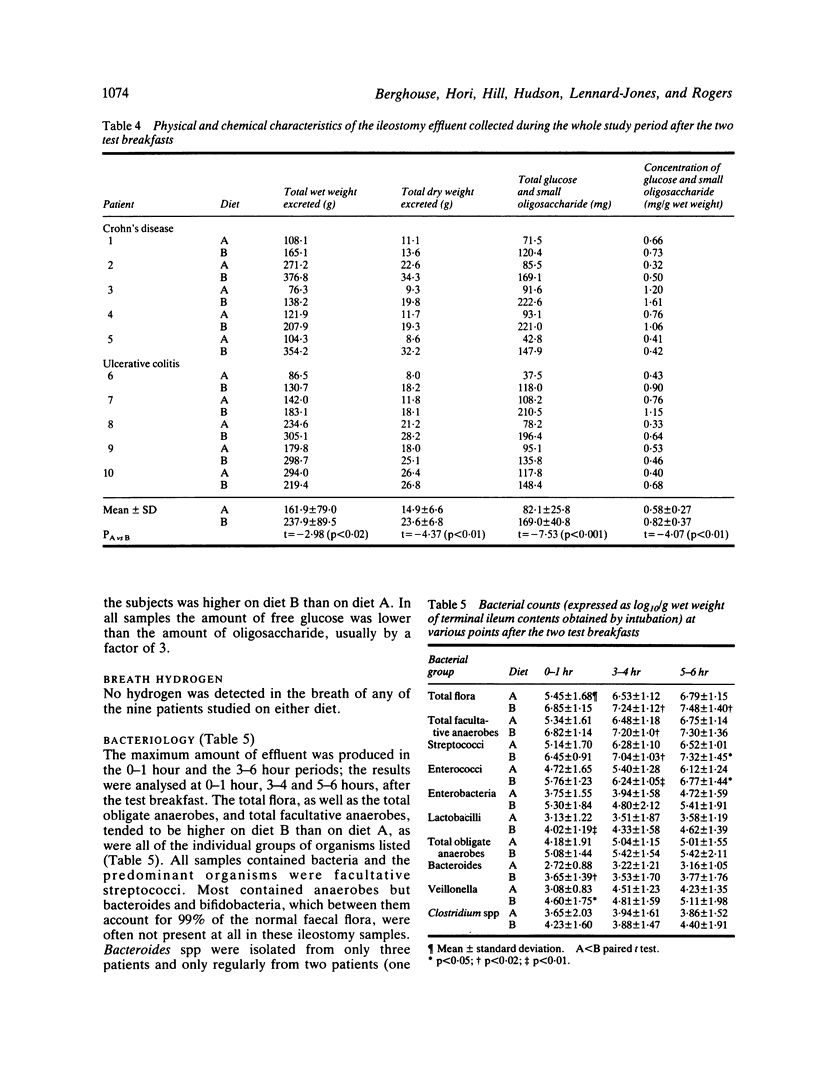
Dietary surveys have shown that patients with Crohn's disease tend to eat more sucrose than control subjects and this investigation was undertaken to determine whether a diet rich in refined carbohydrate affects the bacterial flora of the terminal ileum. Ileostomy effluent in five patients with Crohn's disease and five with ulcerative colitis after two weeks on a diet rich in sucrose and refined cereal has been compared with the same period on a diet low in sucrose and rich in unrefined cereal. Observations were made hourly for nine hours after equicaloric breakfasts representing the two diets. The amount of ileostomy effluent was greater on the unrefined carbohydrate diet both in terms of wet weight (238 +/- 89 g vs 162 +/- 79 g, p less than 0.02) and dry weight (23 X 6 +/- 6.8 g vs 14.9 +/- 6.6 g, p less than 0.01); surprisingly, the amount of glucose and oligosaccharide was also greater (169 +/- 41 mg vs 82 +/- 26 mg, p less than 0.001) in all 10 volunteers. The bacteriological flora per gram was also higher on the unrefined carbohydrate diet after the test meal (p less than 0.02 between three and six hours) as a result of a general increase in all organisms. The relative proportions of the organisms did not vary between the two diets. No differences were detected between patients with ulcerative colitis and those with Crohn's disease.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bingham S., Cummings J. H., McNeil N. I. Diet and health of people with an ileostomy. 1. Dietary assessment. Br J Nutr. 1982 May;47(3):399–406. doi: 10.1079/bjn19820051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borriello P., Hudson M., Hill M. Investigation of the gastrointestinal bacterial flora. Clin Gastroenterol. 1978 May;7(2):329–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowther J. S. Transport and storage of faeces for bacteriological examination. J Appl Bacteriol. 1971 Jun;34(2):477–483. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1971.tb02307.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnelly L. S., Hartman P. A. Gentamicin-based medium for the isolation of group D streptococci and application of the medium to water analysis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Mar;35(3):576–581. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.3.576-581.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drasar B. S., Shiner M., McLeod G. M. Studies on the intestinal flora. I. The bacterial flora of the gastrointestinal tract in healthy and achlorhydric persons. Gastroenterology. 1969 Jan;56(1):71–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finegold S. M., Sutter V. L., Boyle J. D., Shimada K. The normal flora of ileostomy and transverse colostomy effluents. J Infect Dis. 1970 Nov;122(5):376–381. doi: 10.1093/infdis/122.5.376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbach S. L., Nahas L., Weinstein L., Levitan R., Patterson J. F. Studies of intestinal microflora. IV. The microflora of ileostomy effluent: a unique microbial ecology. Gastroenterology. 1967 Dec;53(6):874–880. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heaton K. W., Thornton J. R., Emmett P. M. Treatment of Crohn's disease with an unrefined-carbohydrate, fibre-rich diet. Br Med J. 1979 Sep 29;2(6193):764–766. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6193.764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasper H., Sommer H. Dietary fiber and nutrient intake in Crohn's disease. Am J Clin Nutr. 1979 Sep;32(9):1898–1901. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/32.9.1898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koransky J. R., Allen S. D., Dowell V. R., Jr Use of ethanol for selective isolation of sporeforming microorganisms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Apr;35(4):762–765. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.4.762-765.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martini G. A., Brandes J. W. Increased consumption of refined carbohydrates in patients with Crohn's disease. Klin Wochenschr. 1976 Apr 15;54(8):367–371. doi: 10.1007/BF01469792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayberry J. F., Rhodes J., Allan R., Newcombe R. G., Regan G. M., Chamberlain L. M., Wragg K. G. Diet in Crohn's disease two studies of current and previous habits in newly diagnosed patients. Dig Dis Sci. 1981 May;26(5):444–448. doi: 10.1007/BF01313588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayberry J. F., Rhodes J., Newcombe R. G. Breakfast and dietary aspects of Crohn's disease. Br Med J. 1978 Nov 18;2(6149):1401–1401. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6149.1401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayberry J. F., Rhodes J., Newcombe R. G. Increased sugar consumption in Crohn's disease. Digestion. 1980;20(5):323–326. doi: 10.1159/000198454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metz G., Gassull M. A., Leeds A. R., Blendis L. M., Jenkins D. J. A simple method of measuring breath hydrogen in carbohydrate malabsorption by end-expiratory sampling. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1976 Mar;50(3):237–240. doi: 10.1042/cs0500237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller B., Fervers F., Rohbeck R., Strohmeyer G. Zuckerkonsum bei Patienten mit Morbus Crohn. Verh Dtsch Ges Inn Med. 1976;82(Pt 1):922–924. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROGOSA M. A selective medium for the isolation and enumeration of the veillonella from the oral cavity. J Bacteriol. 1956 Oct;72(4):533–536. doi: 10.1128/jb.72.4.533-536.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silkoff K., Hallak A., Yegena L., Rozen P., Mayberry J. F., Rhodes J., Newcombe R. G. Consumption of refined carbohydrate by patients with Crohn's disease in Tel-Aviv-Yafo. Postgrad Med J. 1980 Dec;56(662):842–846. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.56.662.842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephen A. M., Cummings J. H. Mechanism of action of dietary fibre in the human colon. Nature. 1980 Mar 20;284(5753):283–284. doi: 10.1038/284283a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephen A. M., Cummings J. H. The microbial contribution to human faecal mass. J Med Microbiol. 1980 Feb;13(1):45–56. doi: 10.1099/00222615-13-1-45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutter V. L., Sugihara P. T., Finegold S. M. Rifampin-blood-agar as a selective medium for the isolation of certain anaerobic bacteria. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Nov;22(5):777–780. doi: 10.1128/am.22.5.777-780.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornton J. R., Emmett P. M., Heaton K. W. Diet and Crohn's disease: characteristics of the pre-illness diet. Br Med J. 1979 Sep 29;2(6193):762–764. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6193.762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wensinck F., Custers-van Lieshout, Poppelaars-Kustermans P. A., Schröder A. M. The faecal flora of patients with Crohn's disease. J Hyg (Lond) 1981 Aug;87(1):1–12. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400069187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


