Abstract
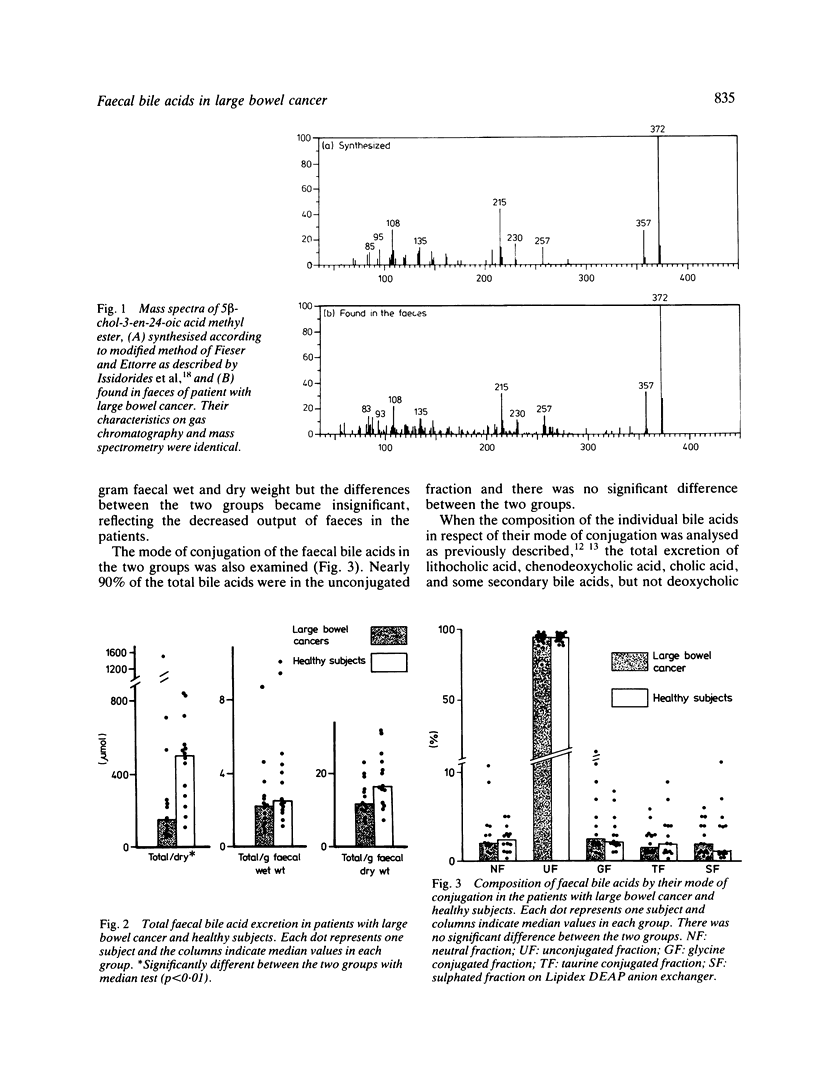
To study the possible role of bile acids in carcinogenesis of the large bowel faecal bile acid profiles were analysed in detail in 14 patients with large bowel cancer and compared with 14 matched healthy subjects. The total faecal bile acid excretion was lower in the patients (297.3 +/- 402.8 mumol/day) than in the healthy subjects (470.6 +/- 231.1 mumol/day) (p less than 0.01), although the difference became insignificant when these data were expressed as mumol per wet or dry faecal weight. The faecal profiles of individual bile acids and their conjugates were similar in both groups except that 5 beta-chol-3-en-24-oic acid, a bacterial metabolite of sulpholithocholic acid, was found in nine cancer patients (64%) compared with only two healthy subjects (14%) (p less than 0.01). The significance of 5 beta-chol-3-en-24-oic acid in carcinogenesis needs further prospective and experimental studies.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borriello S. P., Owen R. W. The metabolism of lithocholic acid and lithocholic acid-3-alpha-sulfate by human fecal bacteria. Lipids. 1982 Jul;17(7):477–482. doi: 10.1007/BF02535328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bremmelgaard A., Bremmelgaard A. Bacterial metabolization of taurolithocholic acid 3-alpha-sulfate. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1974 Aug;82(4):537–540. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1974.tb02363.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummings J. H., Wiggins H. S., Jenkins D. J., Houston H., Jivraj T., Drasar B. S., Hill M. J. Influence of diets high and low in animal fat on bowel habit, gastrointestinal transit time, fecal microflora, bile acid, and fat excretion. J Clin Invest. 1978 Apr;61(4):953–963. doi: 10.1172/JCI109020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENEROTH P. THIN-LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY OF BILE ACIDS. J Lipid Res. 1963 Jan;4:11–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haenszel W., Berg J. W., Segi M., Kurihara M., Locke F. B. Large-bowel cancer in Hawaiian Japanese. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 Dec;51(6):1765–1779. doi: 10.1093/jnci/51.6.1765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill M. J., Drasar B. S., Hawksworth G., Aries V., Crowther J. S., Williams R. E. Bacteria and aetiology of cancer of large bowel. Lancet. 1971 Jan 16;1(7690):95–100. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90837-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill M. J., Drasar B. S., Williams R. E., Meade T. W., Cox A. G., Simpson J. E., Morson B. C. Faecal bile-acids and clostridia in patients with cancer of the large bowel. Lancet. 1975 Mar 8;1(7906):535–539. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91556-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huijghebaert S. M., Mertens J. A., Eyssen H. J. Isolation of a bile salt sulfatase-producing Clostridium strain from rat intestinal microflora. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jan;43(1):185–192. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.1.185-192.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imperato T. J., Wong C. G., Chen L. J., Bolt R. J. Hydrolysis of lithocholate sulfate by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1977 Apr;130(1):545–547. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.1.545-547.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelsey M. I., Molina J. E., Huang S. K., Hwang K. K. The identification of microbial metabolites of sulfolithocholic acid. J Lipid Res. 1980 Aug;21(6):751–759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. A. Recent trends of large bowel cancer in Japan compared to United States and England and Wales. Int J Epidemiol. 1976 Jun;5(2):187–194. doi: 10.1093/ije/5.2.187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskovitz M., White C., Barnett R. N., Stevens S., Russell E., Vargo D., Floch M. H. Diet, fecal bile acids, and neutral sterols in carcinoma of the colon. Dig Dis Sci. 1979 Oct;24(10):746–751. doi: 10.1007/BF01317206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mower H. F., Ray R. M., Shoff R., Stemmermann G. N., Nomura A., Glober G. A., Kamiyama S., Shimada A., Yamakawa H. Fecal bile acids in two Japanese populations with different colon cancer risks. Cancer Res. 1979 Feb;39(2 Pt 1):328–331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudd D. G., McKelvey S. T., Norwood W., Elmore D. T., Roy A. D. Faecal bile acid concentration of patients with carcinoma or increased risk of carcinoma in the large bowel. Gut. 1980 Jul;21(7):587–590. doi: 10.1136/gut.21.7.587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray W. R., Backwood A., Trotter J. M., Calman K. C., MacKay C. Faecal bile acids and clostridia in the aetiology of colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. 1980 Jun;41(6):923–928. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1980.170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORMAN A., PALMER R. H. METABOLITES OF LITHOCHOLIC ACID-24-C-14 IN HUMAN BILE AND FECES. J Lab Clin Med. 1964 Jun;63:986–1001. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narisawa T., Magadia N. E., Weisburger J. H., Wynder E. L. Promoting effect of bile acids on colon carcinogenesis after intrarectal instillation of N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine in rats. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1974 Oct;53(4):1093–1097. doi: 10.1093/jnci/53.4.1093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. H., Bolt M. G. Bile acid sulfates. I. Synthesis of lithocholic acid sulfates and their identification in human bile. J Lipid Res. 1971 Nov;12(6):671–679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perogambros A., Legakis N. J. Faecal bile acids in patients with colon cancer. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg B. 1982 Aug;176(4):346–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy B. S., Wynder E. L. Metabolic epidemiology of colon cancer. Fecal bile acids and neutral sterols in colon cancer patients and patients with adenomatous polyps. Cancer. 1977 Jun;39(6):2533–2539. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197706)39:6<2533::aid-cncr2820390634>3.0.co;2-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setchell K. D., Lawson A. M., Tanida N., Sjövall J. General methods for the analysis of metabolic profiles of bile acids and related compounds in feces. J Lipid Res. 1983 Aug;24(8):1085–1100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman S. J., Andrews A. W. Bile acids: co-mutagenic activity in the Salmonella-mammalian-microsome mutagenicity test: brief communication. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1977 Nov;59(5):1557–1559. doi: 10.1093/jnci/59.5.1557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takano S., Matsushima M., Ertürk E., Bryan G. T. Early induction of rat colonic epithelial ornithine and S-adenosyl-L-methionine decarboxylase activities by N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine or bile salts. Cancer Res. 1981 Feb;41(2):624–628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanida N., Hikasa Y., Hosomi M., Satomi M., Oohama I., Shimoyama T. Fecal bile acid analysis in healthy Japanese subjects using a lipophilic anion exchanger, capillary column gas chromatography and mass spectrometry. Gastroenterol Jpn. 1981;16(4):363–371. doi: 10.1007/BF02774469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanida N., Hikasa Y., Shimoyama T., Setchell K. D. Comparison of faecal bile acid profiles between patients with adenomatous polyps of the large bowel and healthy subjects in Japan. Gut. 1984 Aug;25(8):824–832. doi: 10.1136/gut.25.8.824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tserng K. Y., Klein P. D. Synthesis of sulfate esters of lithocholic acid, glycolithocholic acid, and taurolithocholic acid with sulfur trioxide-triethylamine. J Lipid Res. 1977 Jul;18(4):491–495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wynder E. L., Reddy B. S. Diet and cancer of the colon. Curr Concepts Nutr. 1977;6:55–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wynder E. L., Reddy B. S. Metabolic epidemiology of colorectal cancer. Cancer. 1974 Sep;34(3):suppl–suppl:806. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197409)34:3+<801::aid-cncr2820340703>3.0.co;2-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


