Abstract
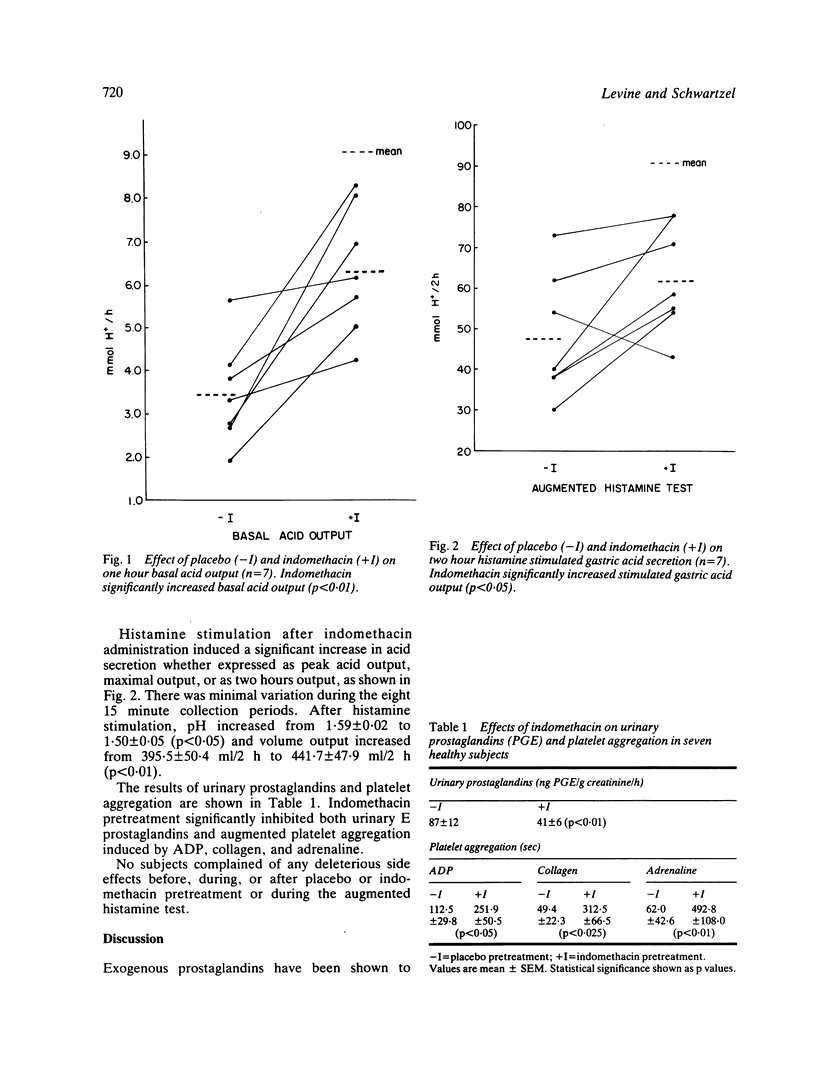
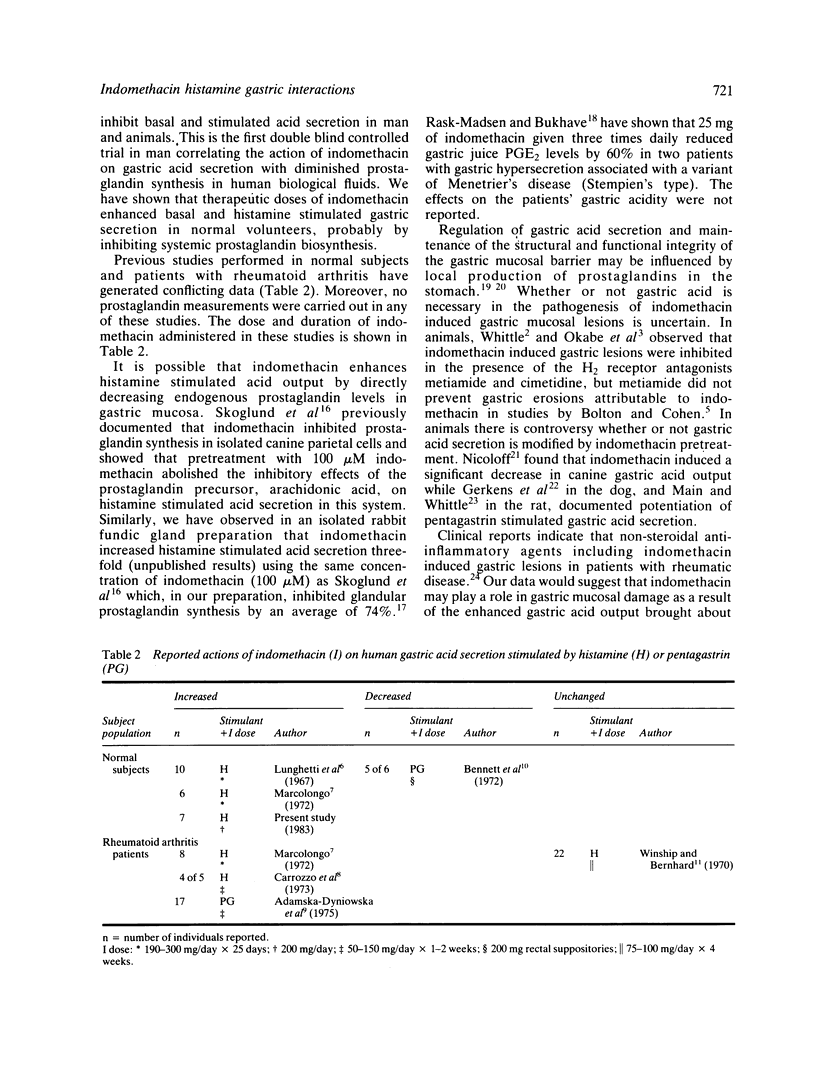
The effect of acute administration of indomethacin over 24 hours on basal and histamine stimulated gastric acid secretion was evaluated in seven normal male volunteers. Augmented histamine tests (0.015 mg/kg/h) infused with the antihistamine diphenhydramine hydrochloride (25 mg/h) were performed before and after pretreatment with indomethacin or matching placebo capsules. The dose of indomethacin was 75 mg (sustained release capsules) taken 12 and 24 hours before and 50 mg taken one hour before a two hour histamine infusion test. Indomethacin enhanced basal gastric secretion from 3.5 +/- 0.5 to 6.4 +/- 0.6 mmol/h (p less than 0.01) and histamine stimulated secretion from 48 +/- 6 to 62 +/- 5 mmol/2 h (p less than 0.05). Indomethacin significantly inhibited systemic prostaglandin biosynthesis as measured by urinary excretion (87 +/- 12 vs 41 +/- 6 ng PGE/g creatinine/h) and the drug increased platelet aggregation time two, five, and six fold, respectively, induced by ADP, collagen, and adrenaline. The data indicate that therapeutic doses of indomethacin augmented basal and secretagogue stimulated gastric acid secretion in control subjects. The enhancement of gastric acid secretion by indomethacin may be because of reduced levels of endogenous prostaglandins. Diminished prostaglandin biosynthesis may play a role in indomethacin induced gastric mucosal damage observed in patients receiving the drug.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamska-Dyniewska H., Bala T., Goch J. H., Kowalczyk L. Wpływ leczenia indometacyna na wydzielanie elektrolitów, białka całkowitego, mukoproteidów i kwasu sialowego w treści zoładkowej. Wiad Lek. 1975 Jul 1;28(13):1117–1121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett A., Stamford I. F., Unger W. G. Prostaglandin E2 and gastric acid secretion in man. J Physiol. 1973 Mar;229(2):349–360. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton J. P., Cohen M. M. The effect of prostaglandin E2, 15-methyl prostaglandin E2, and metiamide on established canine gastric mucosal barrier damage. Surgery. 1979 Mar;85(3):333–338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrozzo M., Panella C., Loizzi P. Tollerabilitá gastrica di un nuovo preparato antireumatico. Minerva Med. 1973 Jun 23;64(47):2507–2510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen P., Leyssac P. P. A specific radioimmunoassay for PGE2 using an antibody with high specificity and a sephadex LH-20 microcolumn for the separation of prostaglandins. Prostaglandins. 1976 Feb;11(2):399–420. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(76)90161-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dray F., Charbonnel B., Maclouf J. Radioimmunoassay of prostaglandins Falpha, E1 and E2 in human plasma. Eur J Clin Invest. 1975 Jul 29;5(4):311–318. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1975.tb00459.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerkens J. F., Shand D. G., Flexner C., Nies A. S., Oates J. A., Data J. L. Effect of indomethacin and aspirin on gastric blood flow and acid secretion. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1977 Dec;203(3):646–652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasuya Y., Urushidani T., Okabe S. Effects of various drugs and vagotomy on indomethacin-induced gastric ulcers in the rat. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1979 Aug;29(4):670–673. doi: 10.1254/jjp.29.670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y. H., Mollison K. W., Cheng W. D. The effects of anti-ulcer agents on indomethacin-induced gastric ulceration in the rat. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1971 Aug;192(2):370–377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine R. A., Schwartzel E. H., Jr, Bachman S., Talev J. N. Gastric cycle nucleotide concentration in health and disease. Response to secretagogues and role of circulating gastrin and intragastric acid secretion. Gastroenterology. 1977 Oct;73(4 Pt 1):737–745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Main I. H., Whittle B. J. Investigation of the vasodilator and antisecretory role of prostaglandins in the rat gastric mucosa by use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Br J Pharmacol. 1975 Feb;53(2):217–224. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1975.tb07351.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcolongo R. Effetti collaterali indesiderati dell'indometacin. Clin Ter. 1972 Feb 29;60(4):343–353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert A. Cytoprotection by prostaglandins. Gastroenterology. 1979 Oct;77(4 Pt 1):761–767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert A., Nezamis J. E., Lancaster C., Hanchar A. J. Cytoprotection by prostaglandins in rats. Prevention of gastric necrosis produced by alcohol, HCl, NaOH, hypertonic NaCl, and thermal injury. Gastroenterology. 1979 Sep;77(3):433–443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagel J., Colwell J. A., Crook L., Laimins M. Increased platelet aggregation in early diabetus mellitus. Ann Intern Med. 1975 Jun;82(6):733–738. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-82-6-733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silvoso G. R., Ivey K. J., Butt J. H., Lockard O. O., Holt S. D., Sisk C., Baskin W. N., Mackercher P. A., Hewett J. Incidence of gastric lesions in patients with rheumatic disease on chronic aspirin therapy. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Oct;91(4):517–520. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-4-517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skoglund M. L., Nies A. S., Gerber J. G. Inhibition of acid secretion in isolated canine parietal cells by prostaglandins. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Feb;220(2):371–374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittle B. J. Relationship between the prevention of rat gastric erosions and the inhibition of acid secretion by prostaglandins. Eur J Pharmacol. 1976 Dec;40(2):233–239. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(76)90057-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winship D. H., Bernhard G. C. Basal and histamine-stimulated human gastric acid secretion. Lack of effect of indomethacin in therapeutic doses. Gastroenterology. 1970 Jun;58(6):762–765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


