Abstract
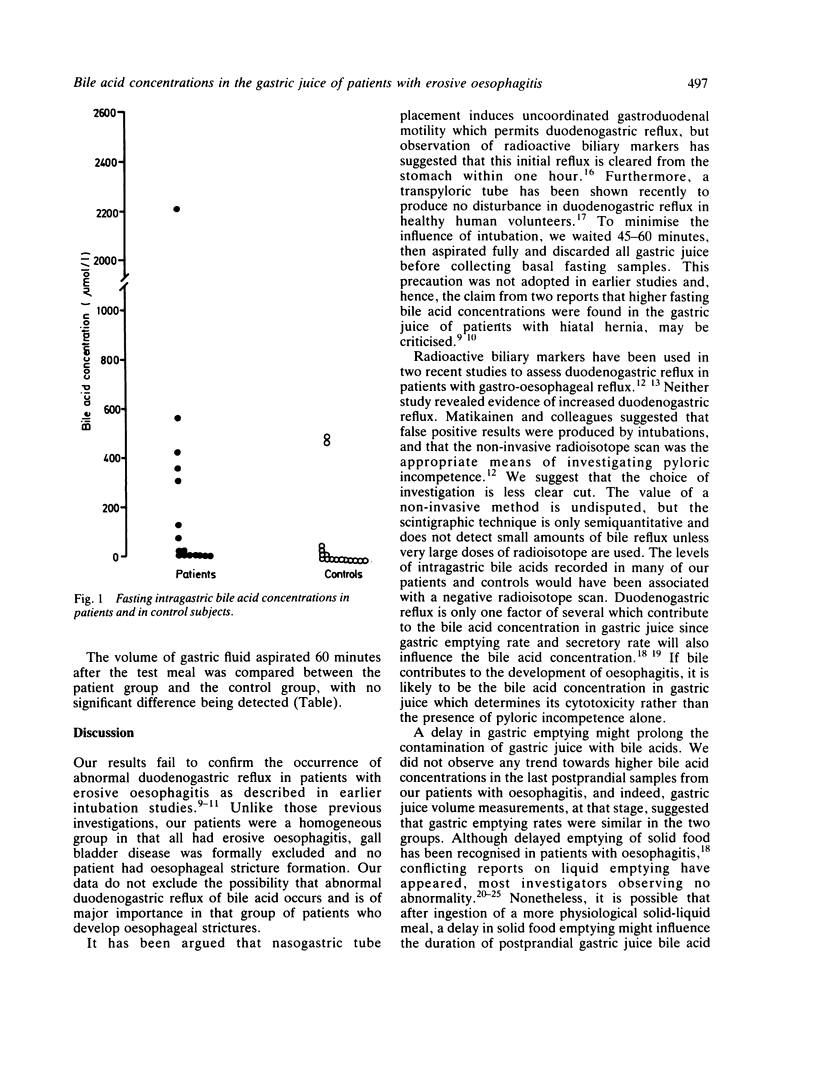
Intragastric total bile acid concentrations were measured before and after a corn oil test meal in 16 patients with erosive oesophagitis and symptoms of gastro-oesophageal reflux. Sixteen age and sex matched control subjects were also studied. No significant difference was detected between fasting or postprandial gastric bile acid concentrations in patients and in control subjects although a wide range of bile acid concentrations was detected among individuals in both groups. Gastric juice pH was less than 3.5 in seven patients when intragastric bile acid concentrations were greater than 200 mumol/l. These results do not support a role for abnormal duodenogastric reflux in the pathogenesis of erosive oesophagitis. The detection of acid reflux in such patients during intra-oesophageal pH monitoring, however, does not exclude the presence of bile acids which may contribute to the cytotoxic potential of gastric juice.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldi F., Corinaldesi R., Ferrarini F., Stanghellini V., Miglioli M., Barbara L. Gastric secretion and emptying of liquids in reflex esophagitis. Dig Dis Sci. 1981 Oct;26(10):886–889. doi: 10.1007/BF01309491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bateson M. C., Hopwood D., Milne G., Bouchier I. A. Oesophageal epithelial ultrastructure after incubation with gastrointestinal fluids and their components. J Pathol. 1981 Jan;133(1):33–51. doi: 10.1002/path.1711330105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behar J., Ramsby G. Gastric emptying and antral motility in reflux esophagitis. Effect of oral metoclopramide. Gastroenterology. 1978 Feb;74(2 Pt 1):253–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branicki F. J., Evans D. F., Ogilvie A. L., Atkinson M., Hardcastle J. D. Ambulatory monitoring of oesophageal pH in reflux oesophagitis using a portable radiotelemetry system. Gut. 1982 Nov;23(11):992–998. doi: 10.1136/gut.23.11.992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CASTEN D. F., BERNHANG A., NACH R. J., SPINZIA J. A physiological basis for the surgical treatment of sliding esophageal hiatal hernia. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1963 Jul;117:87–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins B. J., Watt P. C., O'Reilly T., McFarland R. J., Love A. H. Measurement of total bile acids in gastric juice. J Clin Pathol. 1984 Mar;37(3):313–316. doi: 10.1136/jcp.37.3.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crumplin M. K., Stol D. W., Murphy G. M., Collis J. L. The pattern of bile salt reflux and acid secretion in sliding hiatal hernia. Br J Surg. 1974 Aug;61(8):611–616. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800610806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csendes A., Henriquez A. Gastric emptying in patients with reflux esophagitis or benign strictures of the esophagus secondary to reflux compared to controls. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1978;13(2):205–207. doi: 10.3109/00365527809181749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donovan I. A., Harding L. K., Keighley M. R., Griffin D. W., Collis J. L. Abnormalities of gastric emptying and pyloric reflux in uncomplicated hiatus hernia. Br J Surg. 1977 Dec;64(12):847–848. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800641203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fausa O., Skålhegg B. A. Quantitative determination of bile acids and their conjugates using thin-layer chromatography and a purified 3alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1974;9(3):249–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillison E. W., De Castro V. A., Nyhus L. M., Kusakari K., Bombeck C. T. The significance of bile in reflux esophagitis. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1972 Mar;134(3):419–424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harmon J. W., Johnson L. F., Maydonovitch C. L. Effects of acid and bile salts on the rabbit esophageal mucosa. Dig Dis Sci. 1981 Jan;26(1):65–72. doi: 10.1007/BF01307977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R. D., Mugashe F. L., Jeejeebhoy K. N., Szczpanski M. M., Cullen J., Marryatt G., Boszko A. Synergism of acid and bile salts in the production of experimental esophagitis. Can J Surg. 1973 Jan;16(1):12–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. F., Demeester T. R., Haggitt R. C. Esophageal epithelial response to gastroesophageal reflux. A quantitative study. Am J Dig Dis. 1978 Jun;23(6):498–509. doi: 10.1007/BF01072693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. F., Demeester T. R. Twenty-four-hour pH monitoring of the distal esophagus. A quantitative measure of gastroesophageal reflux. Am J Gastroenterol. 1974 Oct;62(4):325–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye M. D., Showalter J. P. Pyloric incompetence in patients with symptomatic gastroesophageal reflux. J Lab Clin Med. 1974 Feb;83(2):198–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kivilaakso E., Fromm D., Silen W. Effect of bile salts and related compounds on esophageal mucosa. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1981;67:119–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krog M., Gustavsson S., Jung B. Studies on oesophagitis--no evidence for pyloric incompetence as a primary etiological factor. a scintigraphic study with 99Tcm-Solco-HIDA. Acta Chir Scand. 1982;148(5):439–442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matikainen M., Taavitsainen M., Kalima T. V. Duodenogastric reflux in patients with heartburn and oesophagitis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1981;16(2):253–255. doi: 10.3109/00365528109181964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCallum R. W., Berkowitz D. M., Lerner E. Gastric emptying in patients with gastroesophageal reflux. Gastroenterology. 1981 Feb;80(2):285–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Lissner S. A., Fimmel C. J., Will N., Müller-Duysing W., Heinzel F., Blum A. L. Effect of gastric and transpyloric tubes on gastric emptying and duodenogastric reflux. Gastroenterology. 1982 Dec;83(6):1276–1279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrini C. A., DeMeester T. R., Wernly J. A., Johnson L. F., Skinner D. B. Alkaline gastroesophageal reflux. Am J Surg. 1978 Feb;135(2):177–184. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(78)90093-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REDO S. F., BARNES W. A., DE LA SIERRA A. O. Perfusion of the canine esophagus with secretions of the upper gastro-intestinal tract. Ann Surg. 1959 Apr;149(4):556–564. doi: 10.1097/00000658-195904000-00017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stol D. W., Murphy G. M., Collis J. L. Duodeno-gastric reflux and acid secretion in patients with symptomatic hiatal hermia. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1974;9(1):97–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velasco N., Hill L. D., Gannan R. M., Pope C. E., 2nd Gastric emptying and gastroesophageal reflux. Effects of surgery and correlation with esophageal motor function. Am J Surg. 1982 Jul;144(1):58–62. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(82)90602-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


