Abstract
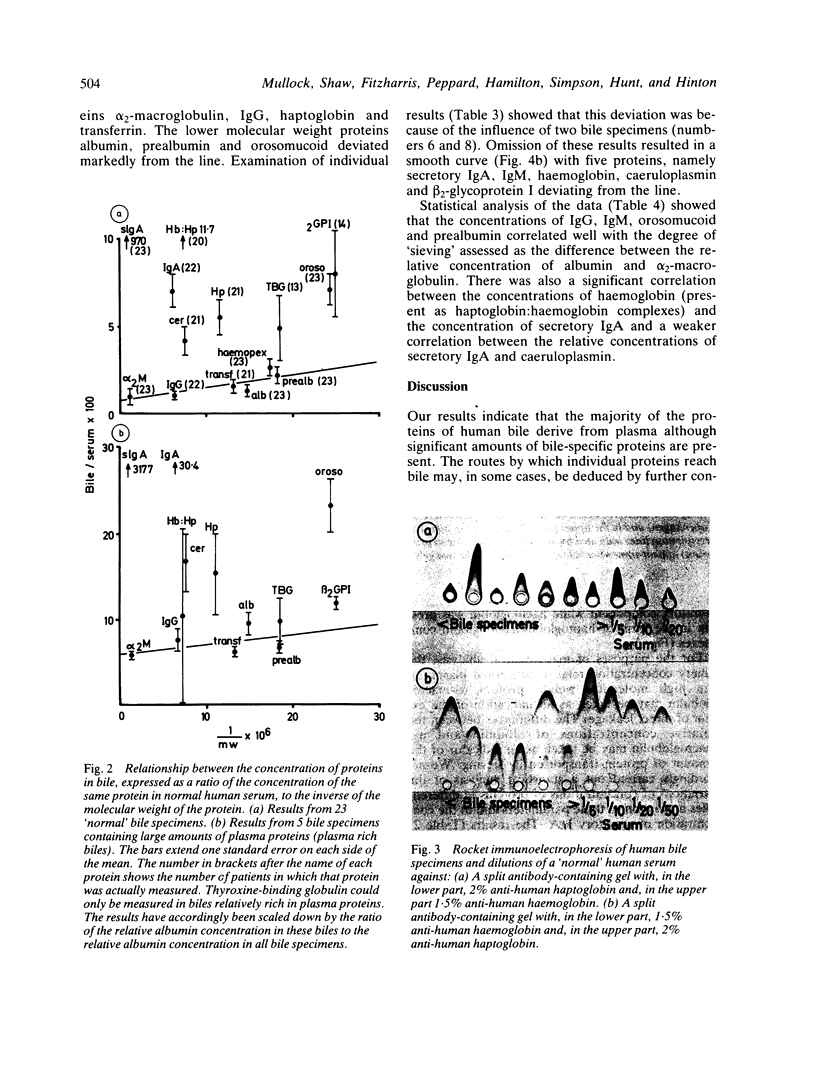
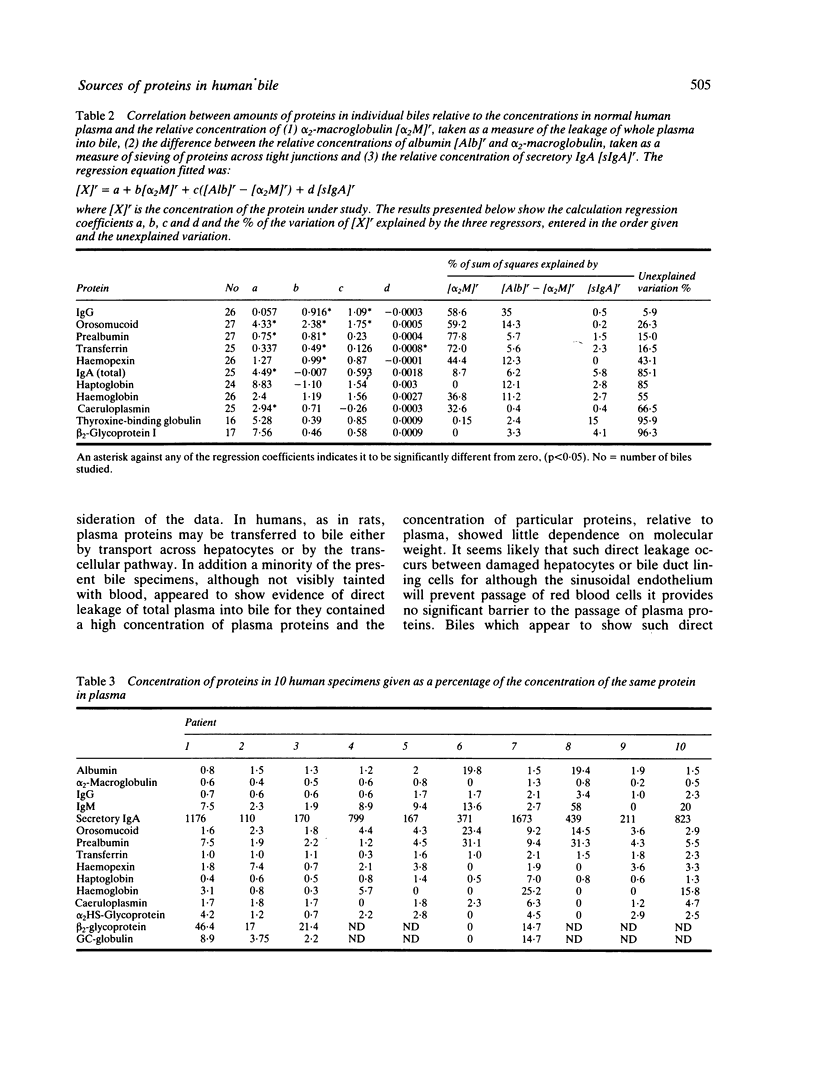
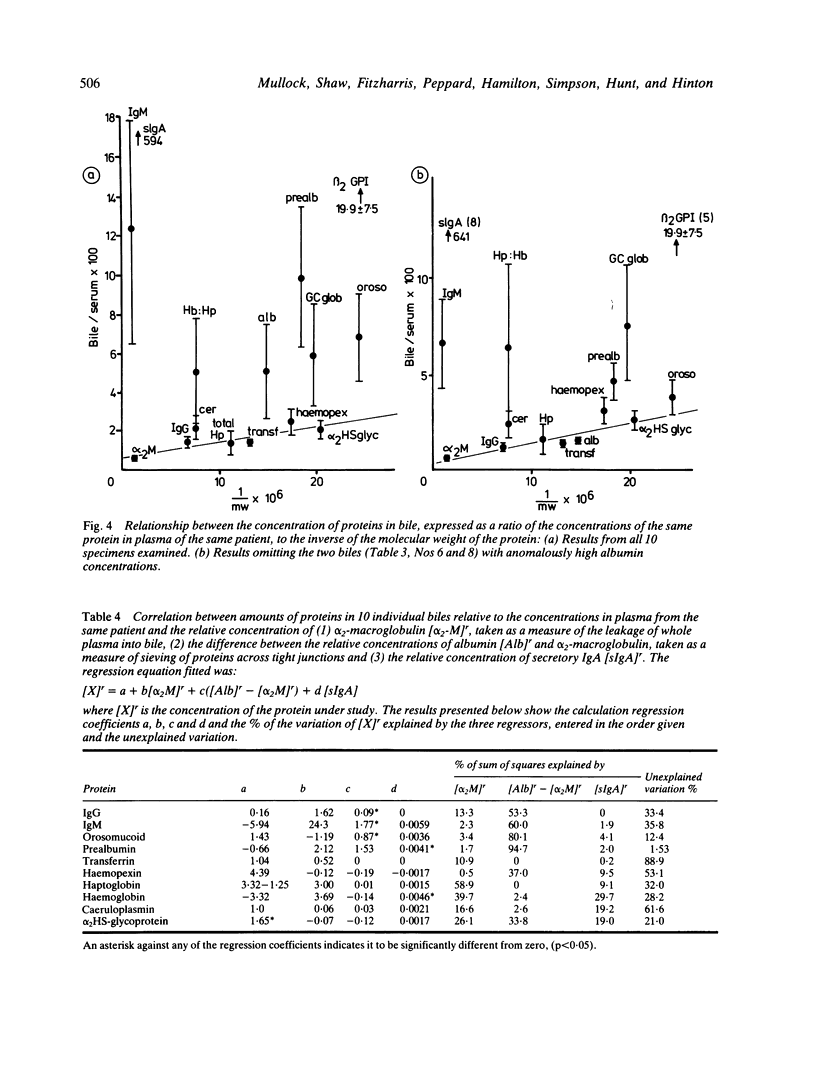
The proteins of 46 human bile specimens, collected by several different routes have been studied by crossed immunoelectrophoresis, by rocket immunoelectrophoresis and by radioimmunoassay. The results were analysed by plotting the variation in the bile: plasma ratio of particular proteins against molecular weight and by examination of the correlation between the concentrations of different proteins in the biles of different patients. Our results show that the majority of human bile proteins derive from plasma although bile specific proteins are always present. The majority of plasma proteins appear to enter bile by a 'sieving' mechanism which results in an inverse relationship between the bile: plasma ratio and the molecular weight. In addition there was a very high degree of correlation between the biliary concentrations of alpha 2-macroglobulin, IgG, haptoglobin, haemopexin, albumin, prealbumin, and orosomucoid. A number of other proteins namely thyroxine binding globulin, GC globulin and alpha 2HS-glycoprotein appeared in bile at concentrations greater than those expected if entry is by the sieving mechanism. These three proteins, however, are of rather low molecular weight and the reason for the lack of correlation appears to be individual variation in the 'pore size', presumably reflecting variation in the porosity of tight junction between hepatocytes. Although the majority of human bile proteins would appear to enter bile by a molecular weight-dependent pathway, four proteins, namely secretory IgA, IgM, haemoglobin and caeruloplasmin, showed significant deviation from the predicted relationship and probably enter bile at least partly by transport across cells. The concentration of beta 2-glycoprotein I was also much greater than expected from its molecular weight. The reason for this is not yet clear but may well reflect a very efficient and specific transport mechanism.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balant L., Fabre J. Clinical relevance of different electrophoretic methods for the analysis of urinary proteins. Curr Probl Clin Biochem. 1979;(9):216–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delacroix D. L., Dive C., Rambaud J. C., Vaerman J. P. IgA subclasses in various secretions and in serum. Immunology. 1982 Oct;47(2):383–385. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delacroix D. L., Furtado-Barreira G., de Hemptinne B., Goudswaard J., Dive C., Vaerman J. P. The liver in the IgA secretory immune system. Dogs, but not rats and rabbits, are suitable models for human studies. Hepatology. 1983 Nov-Dec;3(6):980–988. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840030616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delacroix D. L., Hodgson H. J., McPherson A., Dive C., Vaerman J. P. Selective transport of polymeric immunoglobulin A in bile. Quantitative relationships of monomeric and polymeric immunoglobulin A, immunoglobulin M, and other proteins in serum, bile, and saliva. J Clin Invest. 1982 Aug;70(2):230–241. doi: 10.1172/JCI110610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delacroix D. L., Jonard P., Dive C., Vaerman J. P. Serum IgM-bound secretory component (sIgM) in liver diseases: comparative molecular state of the secretory component in serum and bile. J Immunol. 1982 Jul;129(1):133–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delacroix D. L., Reynaert M., Pauwels S., Geubel A. P., Vaerman J. P. High serum levels of secretory IgA in liver disease: possible liver origin of the circulating secretory component. Dig Dis Sci. 1982 Apr;27(4):333–340. doi: 10.1007/BF01296753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dive C., Heremans J. F. Nature and origin of the proteins of bile. I. A comparative analysis of serum and bile proteins in man. Eur J Clin Invest. 1974 Aug;4(4):235–239. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1974.tb00398.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dive C., Nadalini R. A., Vaerman J. P., Heremans J. F. Origin and nature of the proteins of bile. II. A comparative analysis of serum, hepatic lymph and bile proteins in the dog. Eur J Clin Invest. 1974 Aug;4(4):241–246. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1974.tb00399.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dooley J. S., Potter B. J., Thomas H. C., Sherlock S. A comparative study of the biliary secretion of human dimeric and monomeric IgA in the rat and in man. Hepatology. 1982 May-Jun;2(3):323–327. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840020306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farris M. A., Chandy K. G., Ashdown K., Elias E., Burnett D. Serum secretory component: a potential marker of biliary obstruction. Clin Chim Acta. 1983 Sep 15;133(1):65–73. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(83)90021-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. G., Gyure L. A., Payne A. W. Comparative aspects of the transport of immunoglobulin A from blood to bile. Immunology. 1980 Dec;41(4):899–902. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinton R. H., Dobrota M., Mullock B. M. Haptoglobin-mediated transfer of haemoglobin from serum into bile. FEBS Lett. 1980 Apr 7;112(2):247–250. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80190-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Hsu P. L. Demonstration of IgA and secretory component in human hepatocytes. Gut. 1980 Nov;21(11):985–989. doi: 10.1136/gut.21.11.985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iscaki S., Buffet C., Briantais M. J., Geneste C., Etienne J. P., Pillot J. IgA sécrétoires sériques dans les maladies hépatiques et dans diverses situations physiologiques ou pathologiques humaines. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 1981 Mar;5(3):305–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John W. G., Mullock B. M., Hinton R. H. Proteins of guinea-pig bile: selective resorption in the gall bladder. Biosci Rep. 1983 Apr;3(4):389–394. doi: 10.1007/BF01122904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Layden T. J., Elias E., Boyer J. L. Bile formation in the rat: the role of the paracellular shunt pathway. J Clin Invest. 1978 Dec;62(6):1375–1385. doi: 10.1172/JCI109258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaître-Coelho I., Jackson G. D., Vaerman J. P. Rat bile as a convenient source of secretory IgA and free secretory component. Eur J Immunol. 1977 Aug;7(8):588–590. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830070818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullock B. M., Dobrota M., Hinton R. H. Sources of the proteins of rat bile. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Nov 1;543(4):497–507. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90304-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullock B. M., Hinton R. H., Dobrota M., Peppard J., Orlans E. Distribution of secretory component in hepatocytes and its mode of transfer into bile. Biochem J. 1980 Sep 15;190(3):819–826. doi: 10.1042/bj1900819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullock B. M., Hinton R. H. Mechanisms by which newly made glycoproteins are transferred from hepatocytes into bile. FEBS Lett. 1979 Oct 1;106(1):121–124. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80707-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullock B. M., Issa F. S., Hinton R. H. Bile 5'-nucleotidase in the serum of jaundiced rats. Clin Chim Acta. 1977 Aug 15;79(1):129–140. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(77)90470-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagura H., Smith P. D., Nakane P. K., Brown W. R. IGA in human bile and liver. J Immunol. 1981 Feb;126(2):587–595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlans E., Peppard J. V., Payne A. W., Fitzharris B. M., Mullock B. M., Hinton R. H., Hall J. G. Comparative aspects of the hepatobiliary transport of IgA. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1983 Jun 30;409:411–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1983.tb26886.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier G., Briantais M. J., Buffet C., Pillot J., Etienne J. P. Serum and intestinal secretory IgA in alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver. Gut. 1982 Jun;23(6):475–480. doi: 10.1136/gut.23.6.475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peppard J. V., Jackson L. E., Hall J. G. The occurrence of secretory IgM in the bile of rats. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Sep;53(3):623–626. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peppard J. V. Quantitative estimation of IgA in rats: a comparison of two methods. J Immunol Methods. 1979;31(1-2):129–139. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90293-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schousboe I. Characterization of the interaction between beta 2-glycoprotein I and mitochondria, platelets, liposomes and bile acids. Int J Biochem. 1983;15(12):1393–1401. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(83)90070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Socken D. J., Underdown B. J. Comparison of human, bovine and rabbit secretory component-immunoglobulin interactions. Immunochemistry. 1978 Jul;15(7):499–506. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90080-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svenberg T. Carcinoembryonic antigen-like substances of human bile. Isolation and partial characterization. Int J Cancer. 1976 May 15;17(5):588–596. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910170506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. A., Carter R., Stokes R. P., Geddes A. M., Goodall J. A. Serum immunoglobulins, complement component levels and autoantibodies in liver disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Jul;14(3):335–346. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wurm H., Beubler E., Polz E., Holasek A., Kostner G. Studies on the possible function of beta 2-glycoprotein-I: influence in the triglyceride metabolism in the rat. Metabolism. 1982 May;31(5):484–486. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(82)90238-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]