Abstract
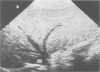
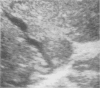
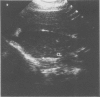
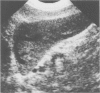
Ultrasonography, computed tomography and 99mTc liver scanning are all useful in diagnosis of patients with the Budd-Chiari syndrome. In a study to determine their comparative value characteristic findings were recorded in all nine patients at ultrasonography and in seven patients at computed tomography. In contrast 99mTc liver scan showed a characteristic pattern in only one of eight patients. In our experience intrahepatic venous abnormalities were seen better at ultrasonography than at computed tomography. In addition, abnormality in the direction of blood flow could be detected by pulsed Doppler examination. Ultrasonography is relatively inexpensive, readily accessible, does not require administration of radiation or contrast agents and therefore should be the primary non-invasive investigation of patients with Budd-Chiari syndrome, or those at risk of developing it.
Full text
PDF
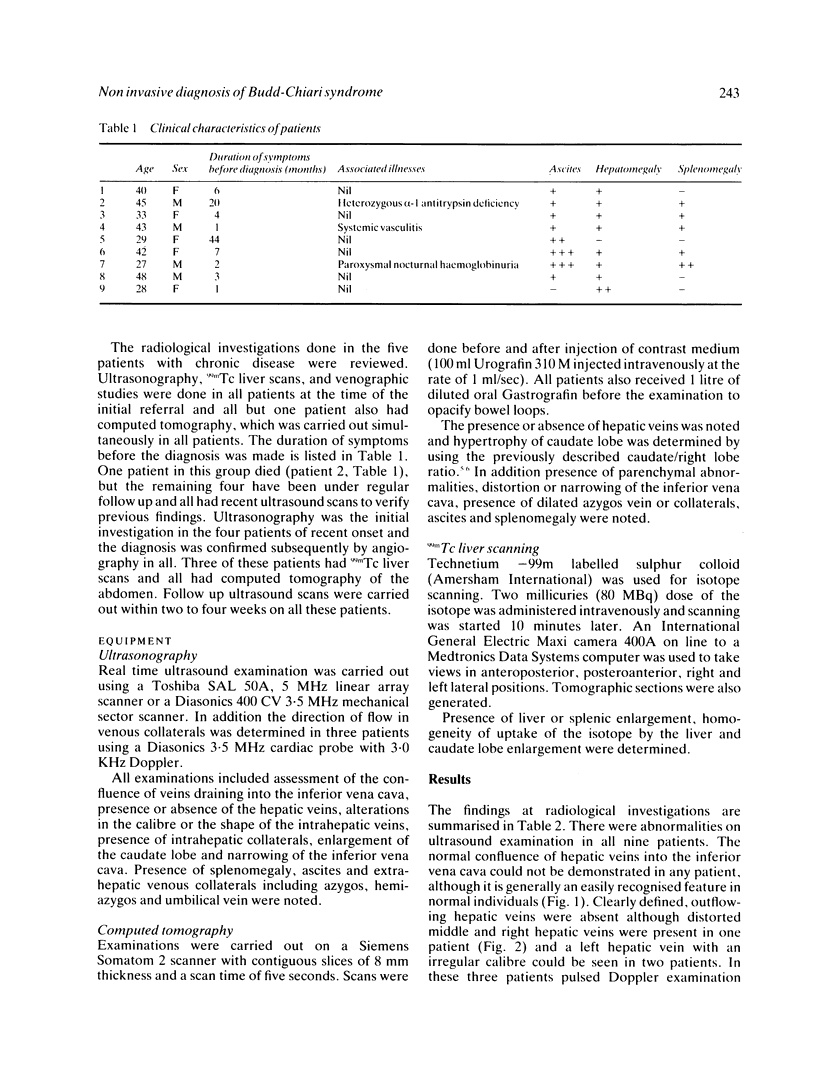
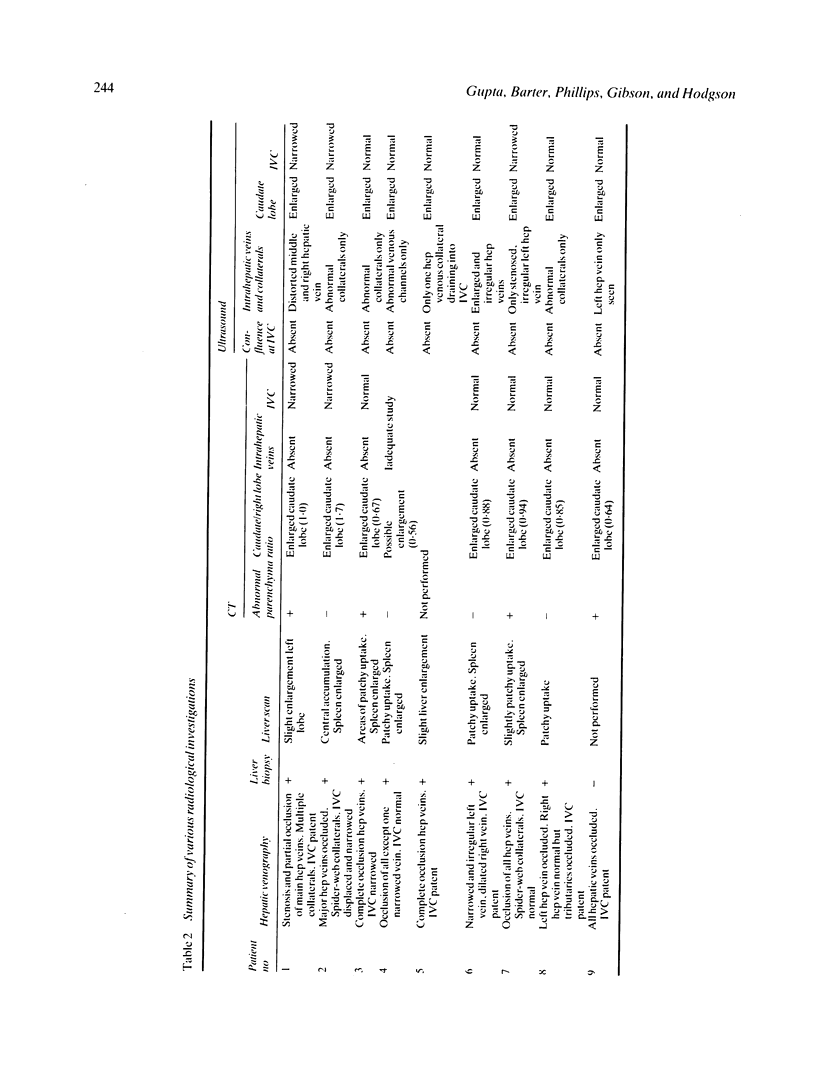
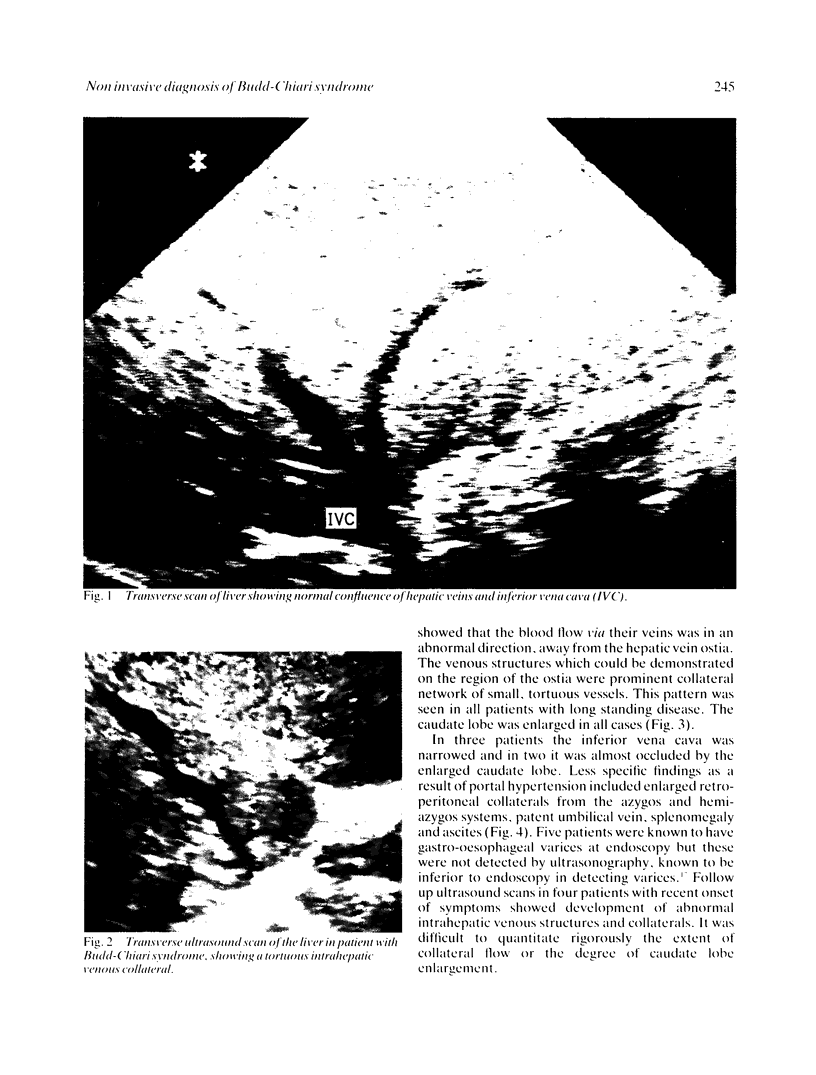

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baert A. L., Fevery J., Marchal G., Goddeeris P., Wilms G., Ponette E., De Groote J. Early diagnosis of Budd-Chiari syndrome by computed tomography and ultrasonography: report of five cases. Gastroenterology. 1983 Mar;84(3):587–595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clain D., Freston J., Kreel L., Sherlock S. Clinical diagnosis of the Budd-Chiari syndrome. A report of six cases. Am J Med. 1967 Oct;43(4):544–554. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(67)90178-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper R. A., Picker R. H., Fulton A. J., Lunzer M. R. The ultrasonic appearance of the liver in hepatic venous outflow obstruction (Budd-Chiari syndrome). J Clin Ultrasound. 1982 Jan;10(1):35–36. doi: 10.1002/jcu.1870100108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garty I., Horovitz I., Keynan A. The use of gallium-67 liver imaging for the early diagnosis of Budd-Chiari syndrome. J Nucl Med. 1984 Mar;25(3):320–322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta S., Cuss F. M., Crofton M. E., Baron J. H., Hodgson H. J. Budd-Chiari syndrome and alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency. Hepatogastroenterology. 1985 Oct;32(5):253–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harbin W. P., Robert N. J., Ferrucci J. T., Jr Diagnosis of cirrhosis based on regional changes in hepatic morphology: a radiological and pathological analysis. Radiology. 1980 May;135(2):273–283. doi: 10.1148/radiology.135.2.7367613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maguire R., Doppman J. L. Angiographic abnormalities in partial Budd-Chiari syndrome. Radiology. 1977 Mar;122(3):629–635. doi: 10.1148/122.3.629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makuuchi M., Hasegawa H., Yamazaki S., Moriyama N., Takayasu K., Okazaki M. Primary Budd-Chiari syndrome: ultrasonic demonstration. Radiology. 1984 Sep;152(3):775–779. doi: 10.1148/radiology.152.3.6087405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meindok H., Langer B. Liver scan in Budd-Chiari syndrome. J Nucl Med. 1976 May;17(5):365–368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell M. C., Boitnott J. K., Kaufman S., Cameron J. L., Maddrey W. C. Budd-Chiari syndrome: etiology, diagnosis and management. Medicine (Baltimore) 1982 Jul;61(4):199–218. doi: 10.1097/00005792-198207000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura H., Tanaka T., Hori S., Yoshioka H., Kuroda C. Partial Budd-Chiari syndrome. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1982 Aug;6(4):833–835. doi: 10.1097/00004728-198208000-00037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi P., Sposito M., Simonetti G., Sposato S., Cusumano G. CT diagnosis of Budd-Chiari syndrome. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1981 Jun;5(3):366–369. doi: 10.1097/00004728-198106000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossleigh M. A., Uren R. F., Morris J. G. Radionuclide liver scan. A screening test for the Budd-Chiari syndrome. Med J Aust. 1984 Feb 18;140(4):234–236. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1984.tb104007.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saint-Marc Girardin M. F., Zafrani E. S., Prigent A., Larde D., Chauffour J., Dhumeaux D. Unilobar small hepatic vein obstruction: possible role of progestogen given as oral contraceptive. Gastroenterology. 1983 Mar;84(3):630–635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staab E. V., Hartman R. C., Parrott J. A. Liver imaging in the diagnosis of hepatic venous thrombosis in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Radiology. 1975 Nov;117(2):341–348. doi: 10.1148/117.2.341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi J., Takada A., Hasumura Y., Matsuda Y., Ikegami P. Budd-Chiari syndrome associated with obstruction of the inferior vena cava. A report of seven cases. Am J Med. 1971 Jul;51(1):11–20. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(71)90319-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tavill A. S., Wood E. J., Kreel L., Jones E. A., Gregory M., Sherlock S. The Budd-Chiari syndrome: correlation between hepatic scintigraphy and the clinical, radiological, and pathological findings in nineteen cases of hepatic venous outflow obstruction. Gastroenterology. 1975 Mar;68(3):509–518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thijs L. G., Heidendal G. A., Huijgens P. C., Mol J. J., Verkuyl M. The use of nuclear medicine procedures in the diagnosis of Budd-Chiari syndrome. Clin Nucl Med. 1978 Oct;3(10):389–392. doi: 10.1097/00003072-197810000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang P. J., Glazer G. M., Bowerman R. A. Budd-Chiari syndrome: computed tomographic and ultrasonographic findings. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1983 Feb;7(1):148–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]