Abstract
An endoscopic pressure sensor has been evaluated in the measurement of oesophageal variceal pressure and its response to drug ingestion. The variceal pressure showed a highly significant correlation with the splenic pulp pressure (r = 0.97) in six patients with liver disease of diverse aetiology and with hepatic venous wedge pressure (r = 0.92) in eight alcoholic cirrhotic men. Intraduodenal infusion of isosorbide dinitrate in the cirrhotics produced no change in wedge pressure or endoscopic variceal pressure despite profound falls in arterial systolic pressure. Thus isosorbide dinitrate appears to be of no value in treating portal hypertension. This study establishes the endoscopic pressure sensor as a valuable tool in screening drugs in this condition.
Full text
PDF
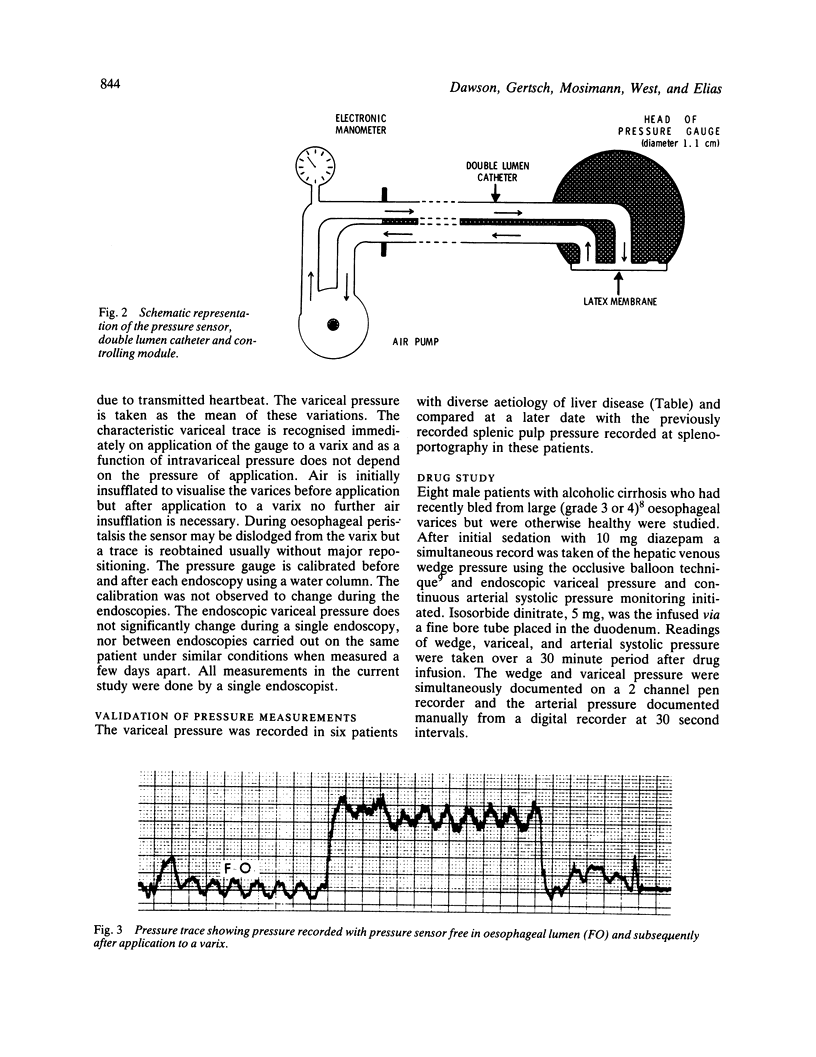
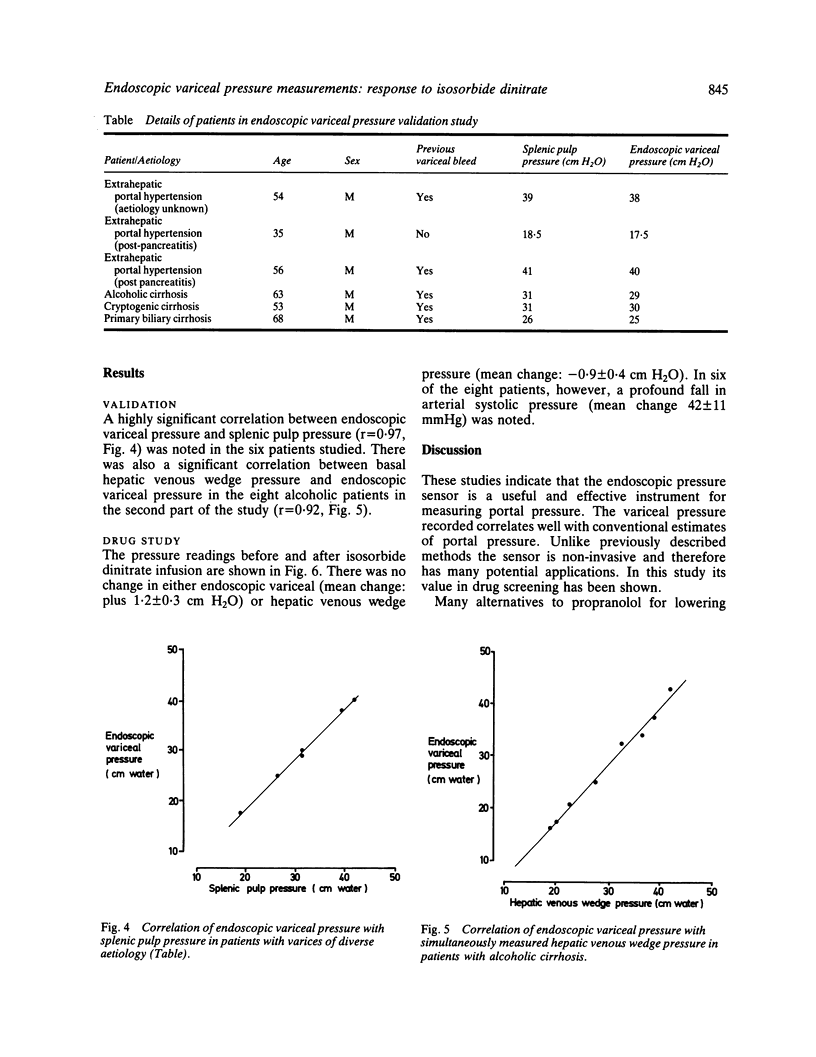
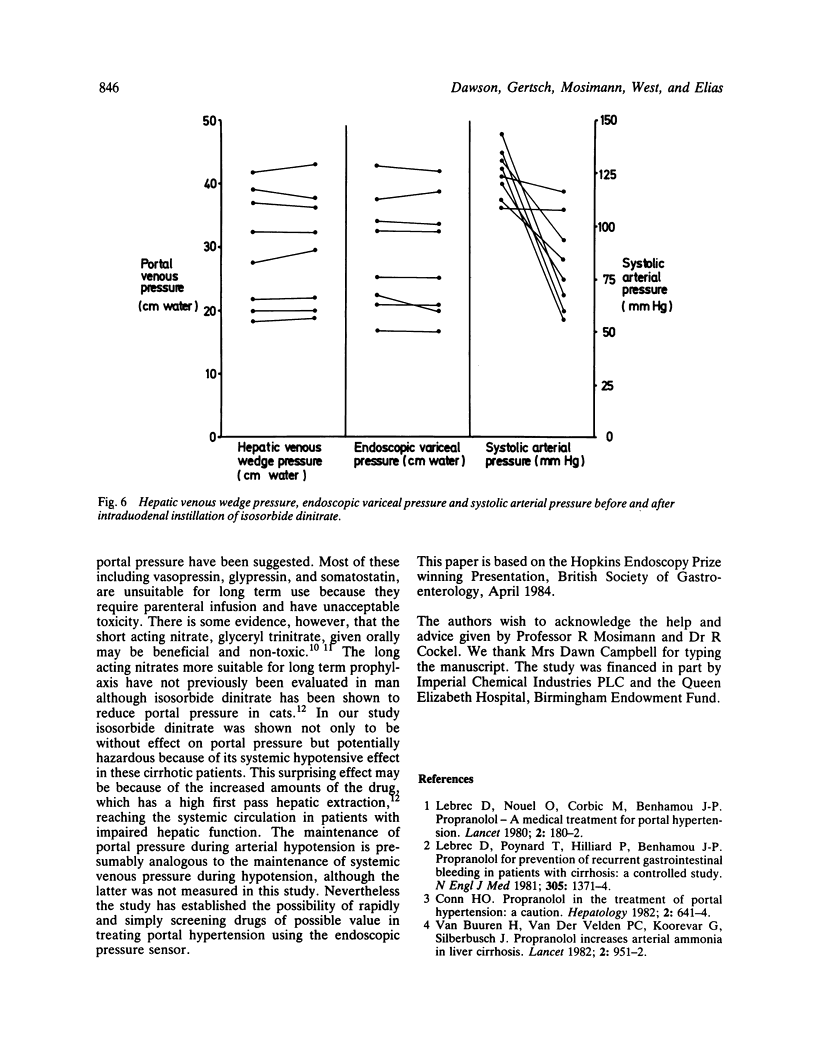

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burroughs A. K., Jenkins W. J., Sherlock S., Dunk A., Walt R. P., Osuafor T. O., Mackie S., Dick R. Controlled trial of propranolol for the prevention of recurrent variceal hemorrhage in patients with cirrhosis. N Engl J Med. 1983 Dec 22;309(25):1539–1542. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198312223092502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conn H. O. Propranolol in the treatment of portal hypertension: a caution. Hepatology. 1982 Sep-Oct;2(5):641–644. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840020518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenway C. V. Effects of sodium nitroprusside, isosorbide dinitrate, isoproterenol, phentolamine and prazosin on hepatic venous responses to sympathetic nerve stimulation in the cat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1979 Apr;209(1):56–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groszmann R. J., Glickman M., Blei A. T., Storer E., Conn H. O. Wedged and free hepatic venous pressure measured with a balloon catheter. Gastroenterology. 1979 Feb;76(2):253–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groszmann R. J., Kravetz D., Bosch J., Glickman M., Bruix J., Bredfeldt J., Conn H. O., Rodes J., Storer E. H. Nitroglycerin improves the hemodynamic response to vasopressin in portal hypertension. Hepatology. 1982 Nov-Dec;2(6):757–762. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840020602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebrec D., Nouel O., Corbic M., Benhamou J. P. Propranolol--a medical treatment for portal hypertension? Lancet. 1980 Jul 26;2(8187):180–182. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)90063-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebrec D., Poynard T., Hillon P., Benhamou J. P. Propranolol for prevention of recurrent gastrointestinal bleeding in patients with cirrhosis: a controlled study. N Engl J Med. 1981 Dec 3;305(23):1371–1374. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198112033052302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosimann R. Mesure de la pression des varices oesophagiennes par voie endoscopique non sanglante. Helv Chir Acta. 1981 Apr;48(1-2):261–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarver D., Walt R. P., Dunk A. A., Jenkins W. J., Sherlock S. Precipitation of hepatic encephalopathy by propranolol in cirrhosis. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 Aug 27;287(6392):585–585. doi: 10.1136/bmj.287.6392.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor T., Chasseaud L. F., Doyle E., Darragh A., O'Kelly D. A., Fitzgerald D. Pharmacokinetics of isosorbide dinitrate after intravenous infusion in human subjects. Biopharm Drug Dispos. 1980 Jan-Mar;1(3):149–156. doi: 10.1002/bdd.2510010310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Buuren H. R., van der Velden P. C., Koorevaar G., Silberbusch J. Propranolol increases arterial ammonia in liver cirrhosis. Lancet. 1982 Oct 30;2(8305):951–952. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)90158-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



