Abstract
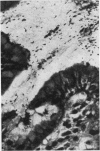
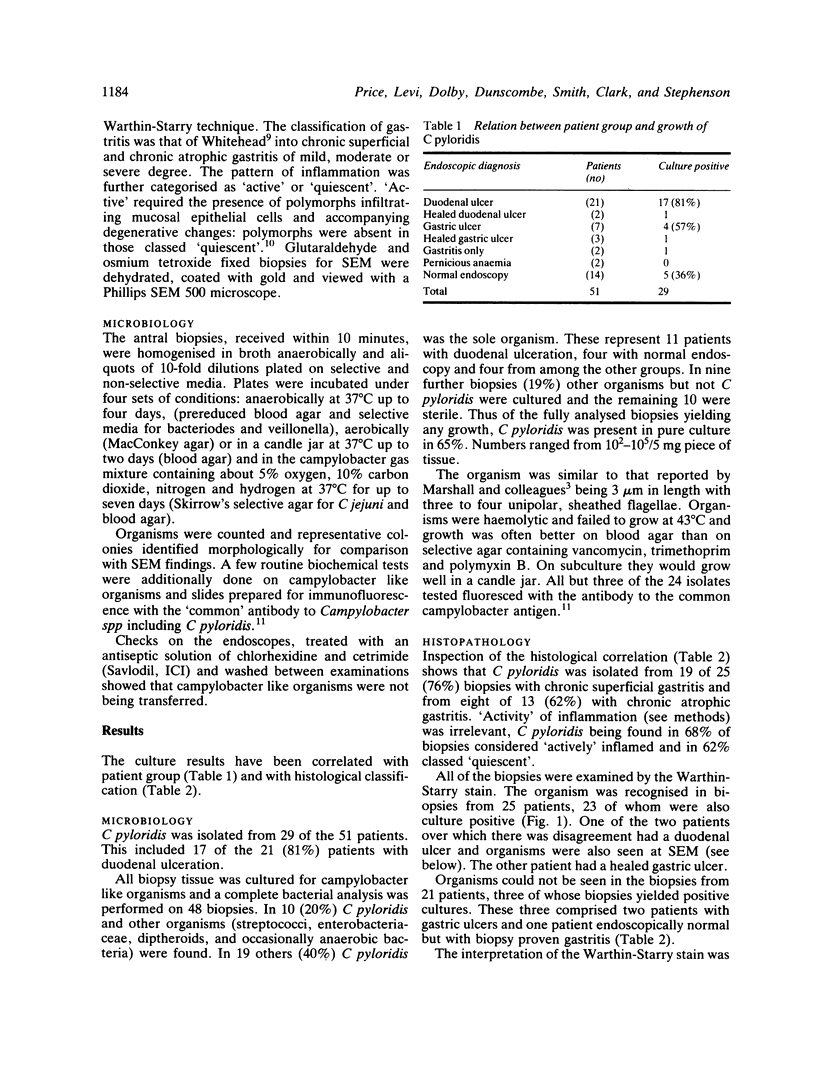
After the recent successful isolation of spiral organisms from the stomach this paper presents the bacteriological and pathological correlation of gastric antral biopsies from 51 patients endoscopied for upper gastrointestinal symptoms. Campylobacter pyloridis was cultured from 29 patients and seen by either silver staining of the biopsy or scanning electron microscopy in an additional three. The organism was cultured from 23 of the 33 (69%) patients with peptic ulcer disease and from within this group 17 (80%) of the 21 patients with duodenal ulceration. It was cultured only once from the 12 normal biopsies in the series but from 27 of the 38 (71%) biopsies showing gastritis. C pyloridis was also cultured from five out of seven of the 14 endoscopically normal patients, who despite this had biopsy evidence of gastritis. It was the sole organism cultured from 65% of the positive biopsies and scanning electron microscopy invariably revealed it deep to the surface mucus layer. C pyloridis persisted in the three patients with duodenal ulcers after treatment and healing. The findings support the hypothesis that C pyloridis is aetiologically related to gastritis and peptic ulceration though its precise role still remains to be defined.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cotton P. B., Price A. B., Tighe J. R., Beales J. S. Preliminary evaluation of "duodenitis" by endoscopy and biopsy. Br Med J. 1973 Aug 25;3(5877):430–433. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5877.430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gastric spiral bacteria. Lancet. 1984 Jul 14;2(8394):100–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gastric spiral bacteria. Lancet. 1984 Jul 14;2(8394):100–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. M., Lessells A. M., Eldridge J. Campylobacter like organisms on the gastric mucosa: culture, histological, and serological studies. J Clin Pathol. 1984 Sep;37(9):1002–1006. doi: 10.1136/jcp.37.9.1002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall B. J., Warren J. R. Unidentified curved bacilli in the stomach of patients with gastritis and peptic ulceration. Lancet. 1984 Jun 16;1(8390):1311–1315. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91816-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D. F., Hollanders D., May S. J., Ravenscroft M. M., Tweedle D. E., Miller J. P. Difference in relapse rates of duodenal ulcer after healing with cimetidine or tripotassium dicitrato bismuthate. Lancet. 1981 Jan 3;1(8210):7–10. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90114-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean A. J., Harrison P. M., Ioannides-Demos L. L., Byrne A. J., McCarthy P., Dudley F. J. Microbes, peptic ulcer, and relapse rates with different drugs. Lancet. 1984 Sep 1;2(8401):525–526. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92607-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNulty C. A., Watson D. M. Spiral bacteria of the gastric antrum. Lancet. 1984 May 12;1(8385):1068–1069. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91469-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price A. B., Dolby J. M., Dunscombe P. R., Stirling J. Detection of campylobacter by immunofluorescence in stools and rectal biopsies of patients with diarrhoea. J Clin Pathol. 1984 Sep;37(9):1007–1013. doi: 10.1136/jcp.37.9.1007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rollason T. P., Stone J., Rhodes J. M. Spiral organisms in endoscopic biopsies of the human stomach. J Clin Pathol. 1984 Jan;37(1):23–26. doi: 10.1136/jcp.37.1.23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unidentified curved bacilli on gastric epithelium in active chronic gastritis. Lancet. 1983 Jun 4;1(8336):1273–1275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]