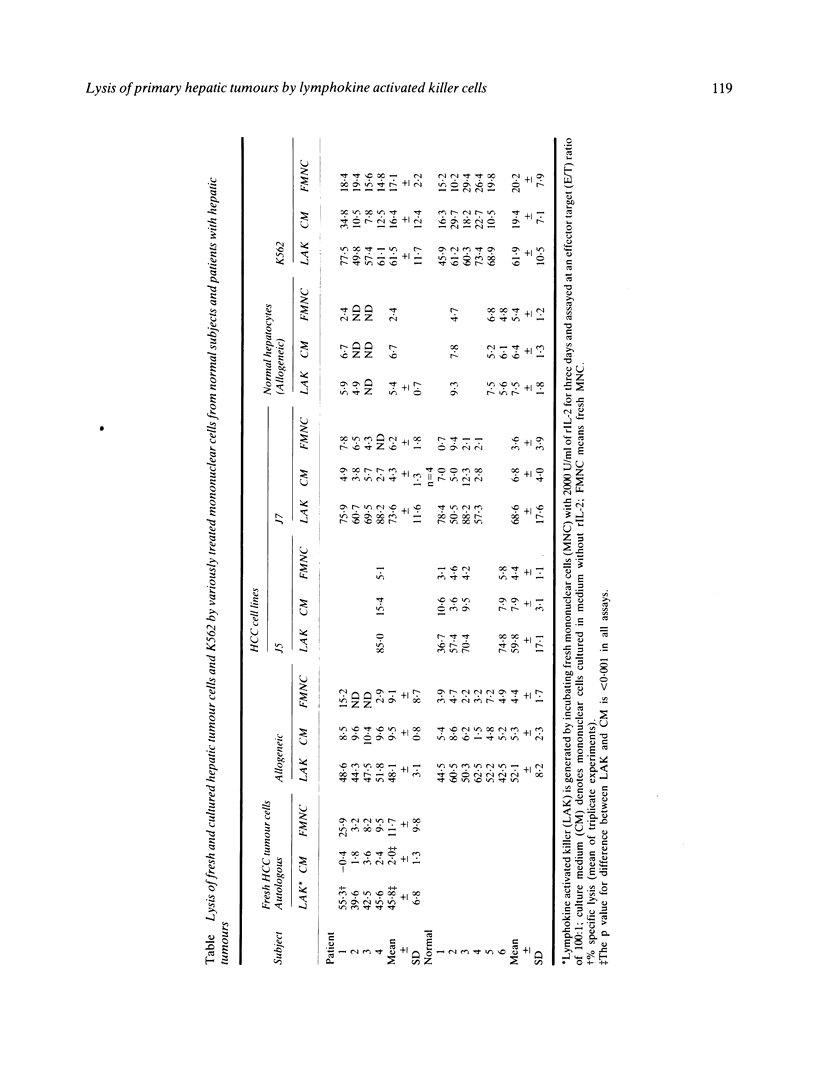
Abstract
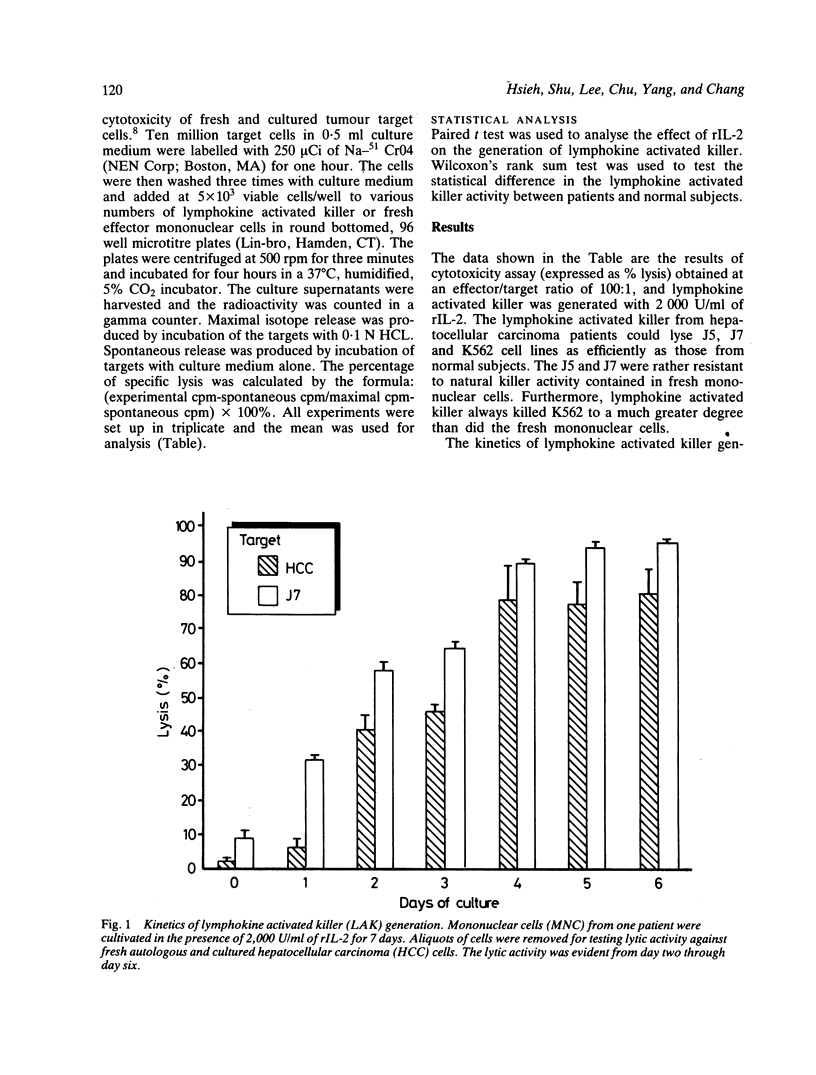
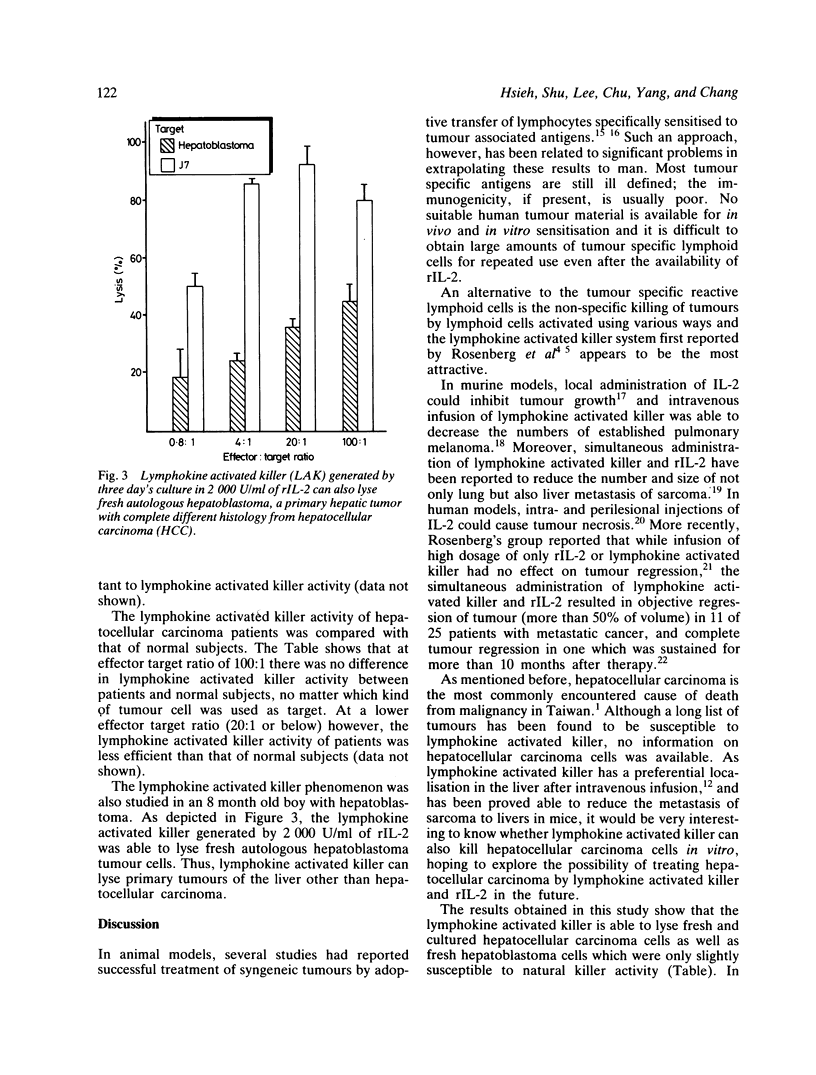
Lymphokine activated killer cell is a newly described lytic system against a variety of solid tumours and is distinct in several respects from the classic cytolytic T cell and the natural killer systems. This study was conducted to evaluate the lytic activity of lymphokine activated killer cells against fresh autologous and allogeneic, as well as cultured hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Lymphokine activated killer cell was generated by incubating peripheral blood mononuclear cells with various concentrations of recombinant IL-2 (rIL-2, Cetus, USA) for various periods of time. A four hour 51Cr release assay was used to measure cytotoxicity. The results show that fresh and cultured hepatocellular carcinoma cells were only slightly susceptible to natural killer cells. Normal hepatocytes were resistant to lymphokine activated killer-mediated lysis. Lymphokine activated killer cells could be generated from mononuclear cells of hepatocellular carcinoma patients and normal subjects with lytic activity against fresh autologous and allogeneic and cultured hepatocellular carcinoma cells, but lymphokine activated killer cells from the former was less efficient than that from the latter. It is concluded that the adoptive immunotherapy with combined rIL-2 and lymphokine activated killer may be worth trying in early cases of primary hepatocellular carcinoma.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beasley R. P., Hwang L. Y., Lin C. C., Chien C. S. Hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatitis B virus. A prospective study of 22 707 men in Taiwan. Lancet. 1981 Nov 21;2(8256):1129–1133. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90585-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheever M. A., Greenberg P. D., Fefer A. Specific adoptive therapy of established leukemia with syngeneic lymphocytes sequentially immunized in vivo and in vitro and nonspecifically expanded by culture with Interleukin 2. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1318–1322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennert G., Yogeeswaran G., Yamagata S. Cloned cell lines with natural killer activity. Specificity, function, and cell surface markers. J Exp Med. 1981 Mar 1;153(3):545–556. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.3.545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forni G., Giovarelli M., Santoni A. Lymphokine-activated tumor inhibition in vivo. I. The local administration of interleukin 2 triggers nonreactive lymphocytes from tumor-bearing mice to inhibit tumor growth. J Immunol. 1985 Feb;134(2):1305–1311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimm E. A., Mazumder A., Zhang H. Z., Rosenberg S. A. Lymphokine-activated killer cell phenomenon. Lysis of natural killer-resistant fresh solid tumor cells by interleukin 2-activated autologous human peripheral blood lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1982 Jun 1;155(6):1823–1841. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.6.1823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimm E. A., Ramsey K. M., Mazumder A., Wilson D. J., Djeu J. Y., Rosenberg S. A. Lymphokine-activated killer cell phenomenon. II. Precursor phenotype is serologically distinct from peripheral T lymphocytes, memory cytotoxic thymus-derived lymphocytes, and natural killer cells. J Exp Med. 1983 Mar 1;157(3):884–897. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.3.884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimm E. A., Robb R. J., Roth J. A., Neckers L. M., Lachman L. B., Wilson D. J., Rosenberg S. A. Lymphokine-activated killer cell phenomenon. III. Evidence that IL-2 is sufficient for direct activation of peripheral blood lymphocytes into lymphokine-activated killer cells. J Exp Med. 1983 Oct 1;158(4):1356–1361. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.4.1356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henney C. S., Kuribayashi K., Kern D. E., Gillis S. Interleukin-2 augments natural killer cell activity. Nature. 1981 May 28;291(5813):335–338. doi: 10.1038/291335a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh K., Tilden A. B., Kumagai K., Balch C. M. Leu-11+ lymphocytes with natural killer (NK) activity are precursors of recombinant interleukin 2 (rIL 2)-induced activated killer (AK) cells. J Immunol. 1985 Feb;134(2):802–807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotze M. T., Line B. R., Mathisen D. J., Rosenberg S. A. The in vivo distribution of autologous human and murine lymphoid cells grown in T cell growth factor (TCGF): implications for the adoptive immunotherapy of tumors. J Immunol. 1980 Oct;125(4):1487–1493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotze M. T., Matory Y. L., Ettinghausen S. E., Rayner A. A., Sharrow S. O., Seipp C. A., Custer M. C., Rosenberg S. A. In vivo administration of purified human interleukin 2. II. Half life, immunologic effects, and expansion of peripheral lymphoid cells in vivo with recombinant IL 2. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2865–2875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazumder A., Rosenberg S. A. Successful immunotherapy of natural killer-resistant established pulmonary melanoma metastases by the intravenous adoptive transfer of syngeneic lymphocytes activated in vitro by interleukin 2. J Exp Med. 1984 Feb 1;159(2):495–507. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.2.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merluzzi V. J., Savage D. M., Mertelsmann R., Welte K. Generation of nonspecific murine cytotoxic T cells in vitro by purified human interleukin 2. Cell Immunol. 1984 Mar;84(1):74–84. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(84)90078-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulé J. J., Shu S., Schwarz S. L., Rosenberg S. A. Adoptive immunotherapy of established pulmonary metastases with LAK cells and recombinant interleukin-2. Science. 1984 Sep 28;225(4669):1487–1489. doi: 10.1126/science.6332379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizza G., Severini G., Menniti D., De Vinci C., Corrado F. Tumour regression after intralesional injection of interleukin 2 (IL-2) in bladder cancer. Preliminary report. Int J Cancer. 1984 Sep 15;34(3):359–367. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910340312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S. A., Grimm E. A., McGrogan M., Doyle M., Kawasaki E., Koths K., Mark D. F. Biological activity of recombinant human interleukin-2 produced in Escherichia coli. Science. 1984 Mar 30;223(4643):1412–1414. doi: 10.1126/science.6367046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S. A., Lotze M. T., Muul L. M., Leitman S., Chang A. E., Ettinghausen S. E., Matory Y. L., Skibber J. M., Shiloni E., Vetto J. T. Observations on the systemic administration of autologous lymphokine-activated killer cells and recombinant interleukin-2 to patients with metastatic cancer. N Engl J Med. 1985 Dec 5;313(23):1485–1492. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198512053132327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S. A., Terry W. D. Passive immunotherapy of cancer in animals and man. Adv Cancer Res. 1977;25:323–388. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60637-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teh H. S., Yu M. Activation of nonspecific killer cells by interleukin 2-containing supernatants. J Immunol. 1983 Oct;131(4):1827–1833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tong M. J., Sun S. C., Schaeffer B. T., Chang N. K., Lo K. J., Peters R. L. Hepatitis-associated antigen and hepatocellular carcinoma in Taiwan. Ann Intern Med. 1971 Nov;75(5):687–691. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-75-5-687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yron I., Wood T. A., Jr, Spiess P. J., Rosenberg S. A. In vitro growth of murine T cells. V. The isolation and growth of lymphoid cells infiltrating syngeneic solid tumors. J Immunol. 1980 Jul;125(1):238–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


