Abstract
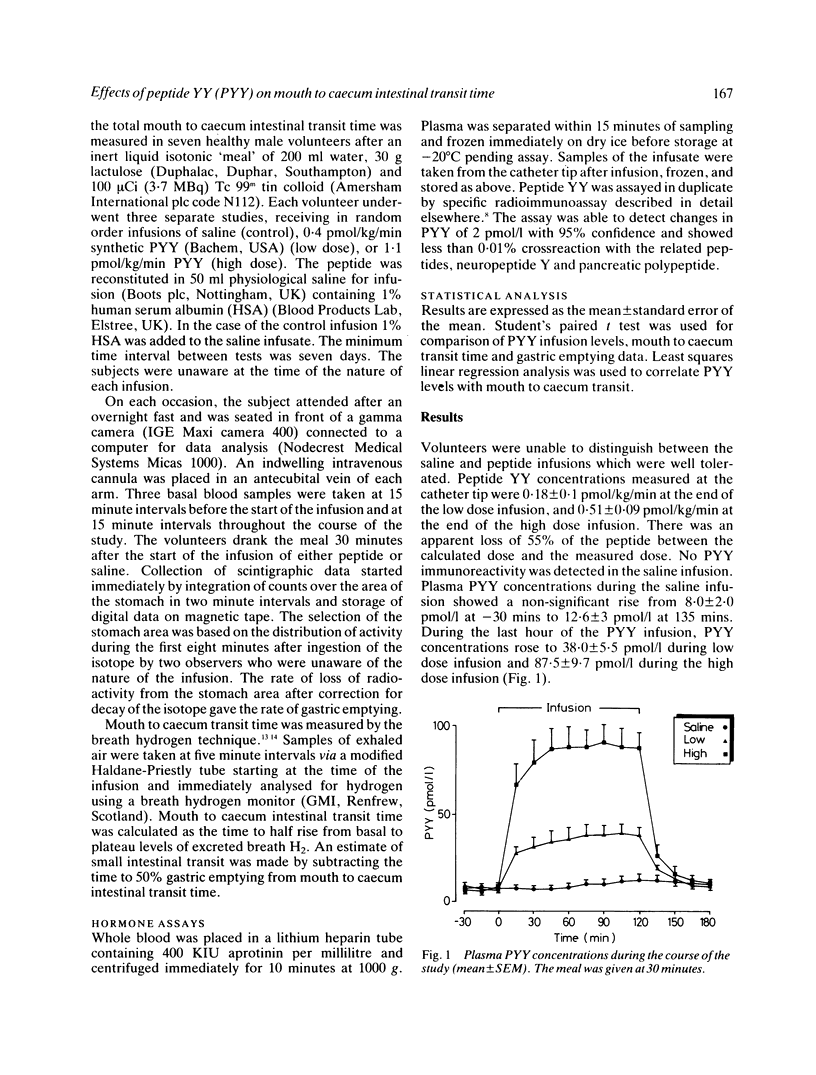
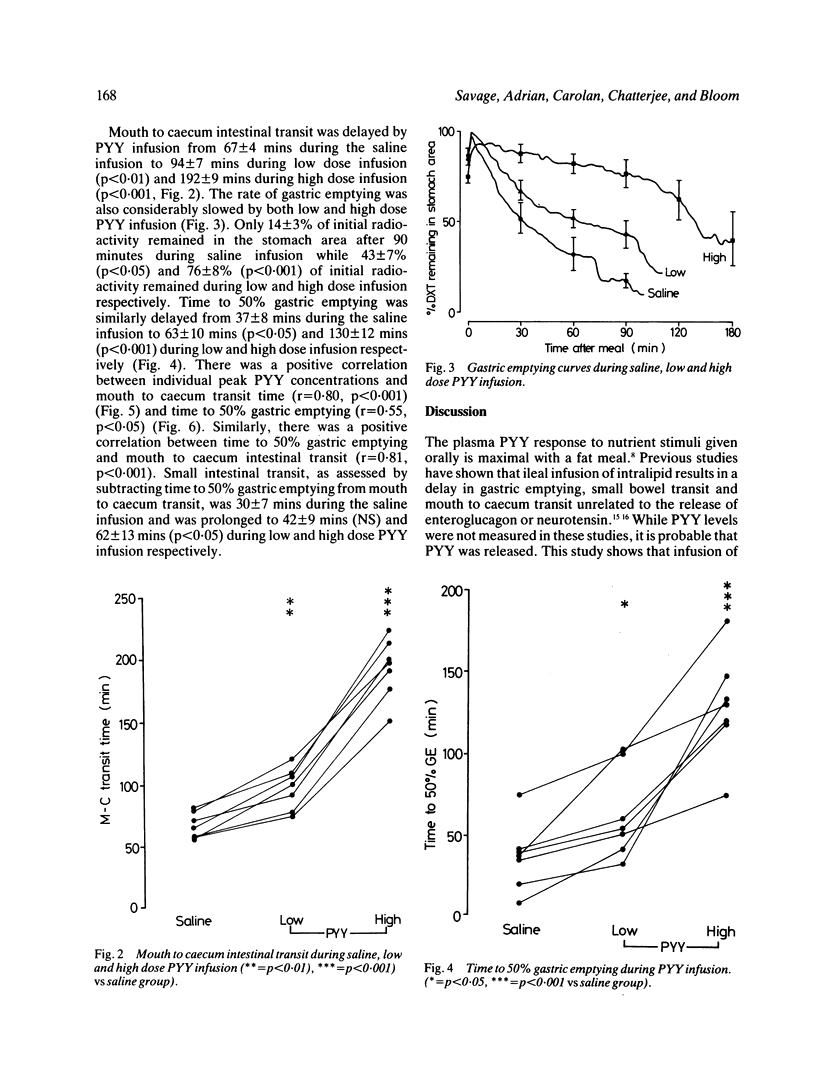
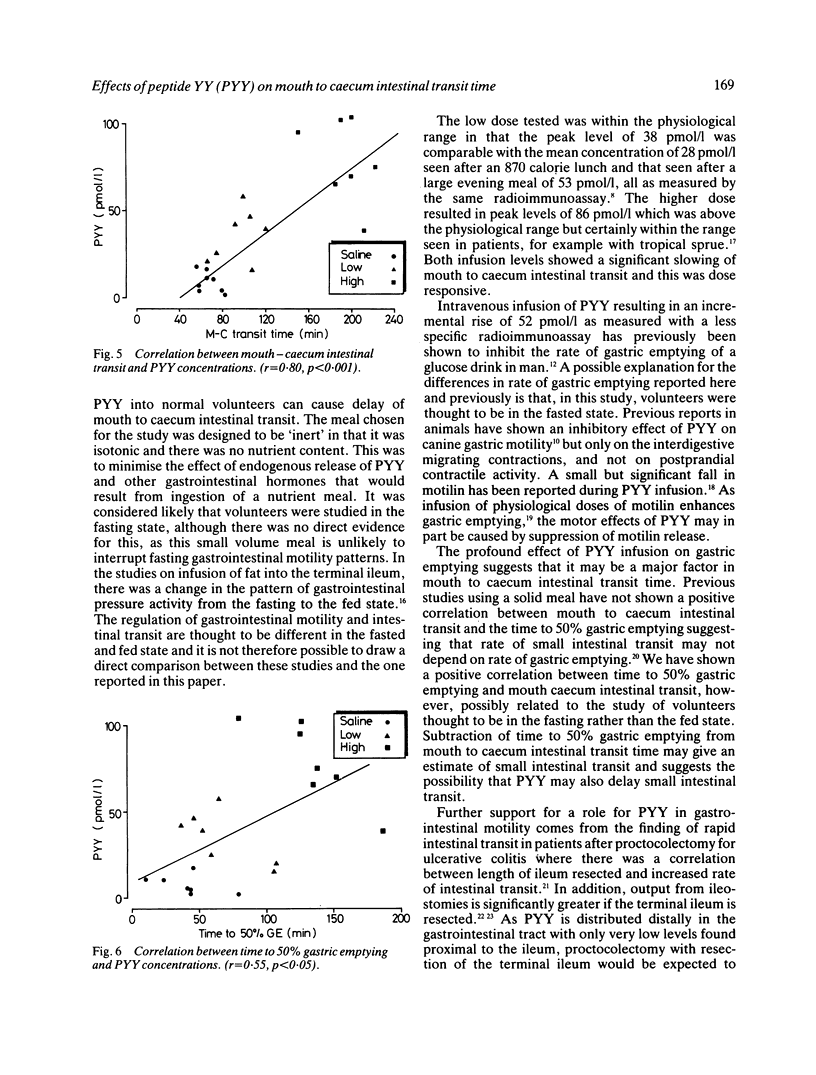
The effect of an infusion of two doses of peptide YY (PYY), a novel putative gastrointestinal hormone, has been assessed on mouth to caecum intestinal transit time and on the rate of gastric emptying after ingestion of an inert 200 ml liquid meal thought unlikely to interrupt fasting gastrointestinal motility patterns. A low dose of PYY was chosen to give plasma concentrations within the range seen postprandially in healthy subjects, while the high dose mimicked the raised levels seen in several malabsorptive conditions. During infusion of PYY at 0.18 pmol/kg/min plasma concentrations rose from a basal of 8 +/- 2 pmol/l to 38 +/- 5 pmol/l and at 0.51 pmol/kg/min to 87 +/- 10 pmol/l. Mouth to caecum transit time was delayed from 67 +/- 4 mins on the saline infusion day to 94 +/- 7 mins (p less than 0.01) on the low dose and 192 +/- 9 mins (p less than 0.001) on the high dose infusion day. Time to 50% gastric emptying was prolonged from 37 +/- 8 mins during saline infusion to 63 +/- 10 mins (p less than 0.05) during low and 130 +/- 12 mins (p less than 0.001) during high dose infusion. Thus the infusion of PYY shows a dose related inhibition of mouth to caecum intestinal transit time and of the rate of gastric emptying and suggests this novel hormonal peptide to be of importance in gastrointestinal physiology.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian T. E., Ferri G. L., Bacarese-Hamilton A. J., Fuessl H. S., Polak J. M., Bloom S. R. Human distribution and release of a putative new gut hormone, peptide YY. Gastroenterology. 1985 Nov;89(5):1070–1077. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(85)90211-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian T. E., Savage A. P., Bacarese-Hamilton A. J., Wolfe K., Besterman H. S., Bloom S. R. Peptide YY abnormalities in gastrointestinal diseases. Gastroenterology. 1986 Feb;90(2):379–384. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90936-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian T. E., Savage A. P., Sagor G. R., Allen J. M., Bacarese-Hamilton A. J., Tatemoto K., Polak J. M., Bloom S. R. Effect of peptide YY on gastric, pancreatic, and biliary function in humans. Gastroenterology. 1985 Sep;89(3):494–499. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(85)90442-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ali-Rachedi A., Varndell I. M., Adrian T. E., Gapp D. A., Van Noorden S., Bloom S. R., Polak J. M. Peptide YY (PYY) immunoreactivity is co-stored with glucagon-related immunoreactants in endocrine cells of the gut and pancreas. Histochemistry. 1984;80(5):487–491. doi: 10.1007/BF00495439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen J. M., Fitzpatrick M. L., Yeats J. C., Darcy K., Adrian T. E., Bloom S. R. Effects of peptide YY and neuropeptide Y on gastric emptying in man. Digestion. 1984;30(4):255–262. doi: 10.1159/000199117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond J. H., Jr, Levitt M. D., Prentiss R. Investigation of small bowel transit time in man utilizing pulmonary hydrogen (H2) measurements. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Apr;85(4):546–555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böttcher G., Sjölund K., Ekblad E., Håkanson R., Schwartz T. W., Sundler F. Coexistence of peptide YY and glicentin immunoreactivity in endocrine cells of the gut. Regul Pept. 1984 Jul;8(4):261–266. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(84)90034-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christofides N. D., Modlin I. M., Fitzpatrick M. L., Bloom S. R. Effect of motilin on the rate of gastric emptying and gut hormone release during breakfast. Gastroenterology. 1979 May;76(5 Pt 1):903–907. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbett C. L., Thomas S., Read N. W., Hobson N., Bergman I., Holdsworth C. D. Electrochemical detector for breath hydrogen determination: measurement of small bowel transit time in normal subjects and patients with the irritable bowel syndrome. Gut. 1981 Oct;22(10):836–840. doi: 10.1136/gut.22.10.836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Salhy M., Grimelius L., Wilander E., Ryberg B., Terenius L., Lundberg J. M., Tatemoto K. Immunocytochemical identification of polypeptide YY (PYY) cells in the human gastrointestinal tract. Histochemistry. 1983;77(1):15–23. doi: 10.1007/BF00496632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill G. L., Mair W. S., Goligher J. C. Cause and management of high volume output salt-depleting ileostomy. Br J Surg. 1975 Sep;62(9):720–726. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800620912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill G. L., Mair W. S., Goligher J. C. Impairment of 'ileostomy adaptation' in patients after ileal resection. Gut. 1974 Dec;15(12):982–987. doi: 10.1136/gut.15.12.982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Tatemoto K., Terenius L., Hellström P. M., Mutt V., Hökfelt T., Hamberger B. Localization of peptide YY (PYY) in gastrointestinal endocrine cells and effects on intestinal blood flow and motility. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(14):4471–4475. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.14.4471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neal D. E., Williams N. S., Barker M. C., King R. F. The effect of resection of the distal ileum on gastric emptying, small bowel transit and absorption after proctocolectomy. Br J Surg. 1984 Sep;71(9):666–670. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800710906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nygaard K. Resection of the small intestine in rats. IV. Adaptation of gastro-intestinal motility. Acta Chir Scand. 1967;133(5):407–416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read N. W., McFarlane A., Kinsman R. I., Bates T. E., Blackhall N. W., Farrar G. B., Hall J. C., Moss G., Morris A. P., O'Neill B. Effect of infusion of nutrient solutions into the ileum on gastrointestinal transit and plasma levels of neurotensin and enteroglucagon. Gastroenterology. 1984 Feb;86(2):274–280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read N. W., Miles C. A., Fisher D., Holgate A. M., Kime N. D., Mitchell M. A., Reeve A. M., Roche T. B., Walker M. Transit of a meal through the stomach, small intestine, and colon in normal subjects and its role in the pathogenesis of diarrhea. Gastroenterology. 1980 Dec;79(6):1276–1282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage A. P., Gornacz G. E., Adrian T. E., Ghatei M. A., Goodlad R. A., Wright N. A., Bloom S. R. Is raised plasma peptide YY after intestinal resection in the rat responsible for the trophic response? Gut. 1985 Dec;26(12):1353–1358. doi: 10.1136/gut.26.12.1353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiller R. C., Trotman I. F., Higgins B. E., Ghatei M. A., Grimble G. K., Lee Y. C., Bloom S. R., Misiewicz J. J., Silk D. B. The ileal brake--inhibition of jejunal motility after ileal fat perfusion in man. Gut. 1984 Apr;25(4):365–374. doi: 10.1136/gut.25.4.365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki T., Nakaya M., Itoh Z., Tatemoto K., Mutt V. Inhibition of interdigestive contractile activity in the stomach by peptide YY in Heidenhain pouch dogs. Gastroenterology. 1983 Jul;85(1):114–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatemoto K., Carlquist M., Mutt V. Neuropeptide Y--a novel brain peptide with structural similarities to peptide YY and pancreatic polypeptide. Nature. 1982 Apr 15;296(5858):659–660. doi: 10.1038/296659a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatemoto K. Isolation and characterization of peptide YY (PYY), a candidate gut hormone that inhibits pancreatic exocrine secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(8):2514–2518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.8.2514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatemoto K., Mutt V. Isolation of two novel candidate hormones using a chemical method for finding naturally occurring polypeptides. Nature. 1980 Jun 5;285(5764):417–418. doi: 10.1038/285417a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


