Abstract
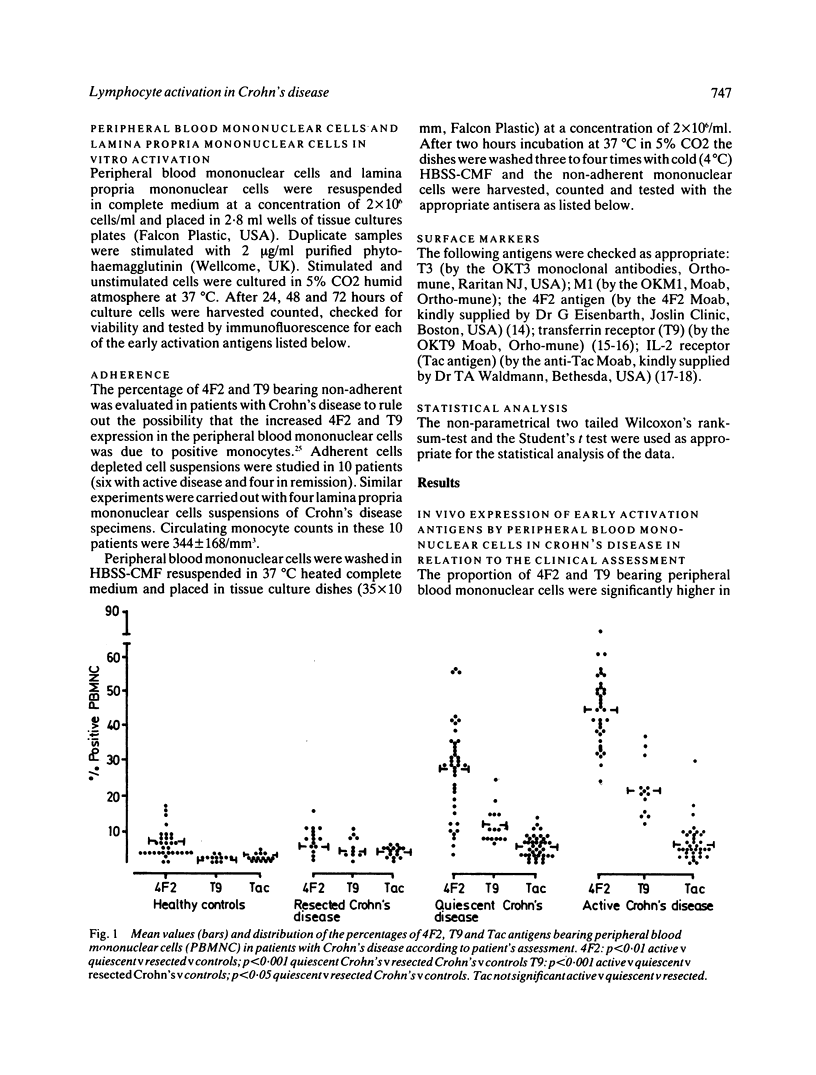
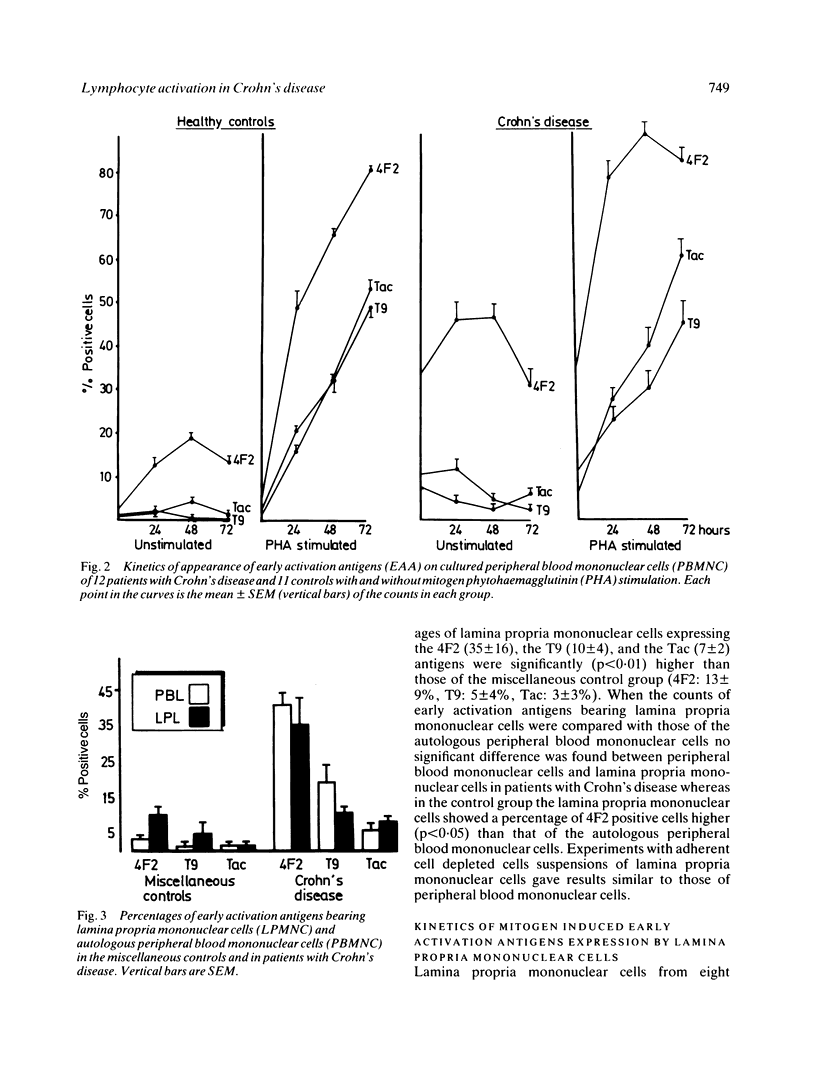
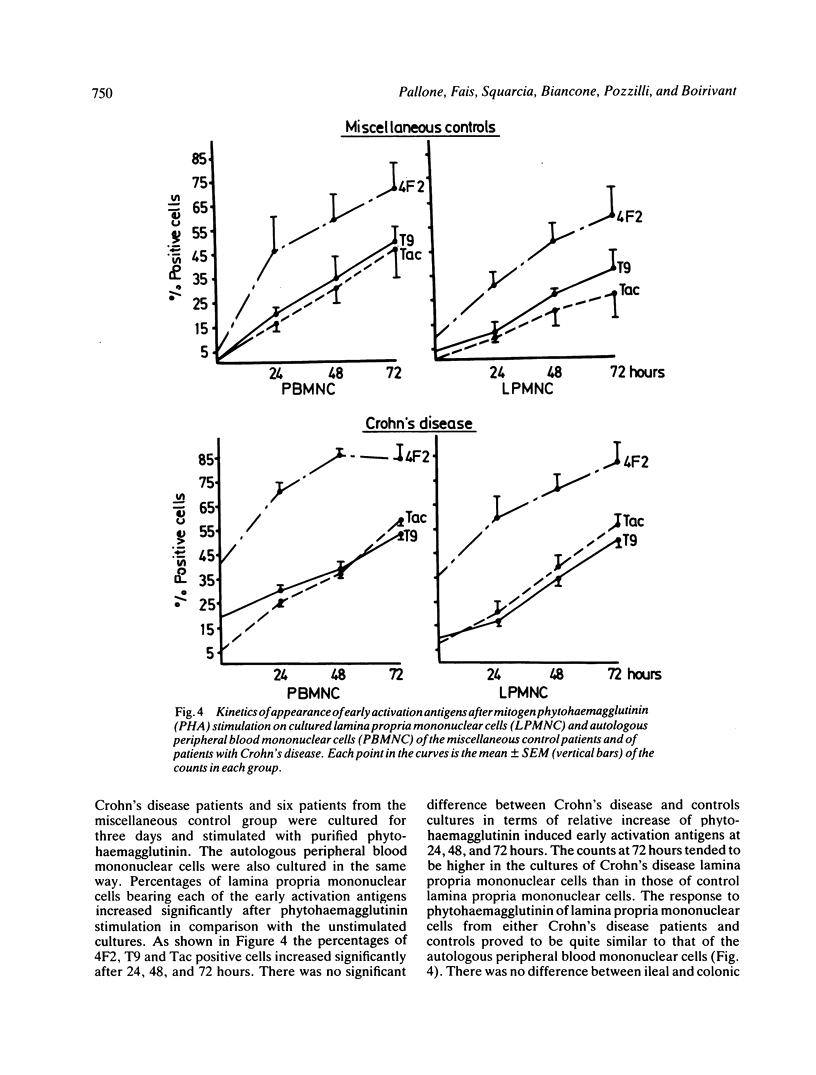
In the present study the state of activation of either peripheral blood and intestinal lamina propria mononuclear cells in Crohn's disease was defined by investigating the expression of early activation antigens (namely the 4F2 antigen, the transferrin receptor and the interleukin-2 receptor). The expression of 4F2 and T9 antigens was greatly increased--in the peripheral blood and in the intestinal lamina propria whereas the proportion of interleukin-2 receptor bearing cells was much less pronounced. The counts of early activation antigens bearing cells in the lamina propria were quite comparable with those of the autologous peripheral cells. In the peripheral blood counts of 4F2 and T9 positive cells were very high in patients with active Crohn's disease but patients with quiescent disease also had a significantly raised proportion of 4F2 and T9 bearing cells. Only in those patients with no evidence of macroscopic disease (namely those resected without recurrence) the counts of early activation antigens bearing cells were within the normal range. The in vitro mitogen induced expression of early activation antigens on either peripheral and intestinal mononuclear cells of patients with Crohn's disease proved to be both quantitatively and qualitatively similar to that of the controls showing the full expression of 4F2, transferrin receptor, and interleukin-2 receptor. While demonstrating that in Crohn's disease there was no intrinsic defect of generation and expression of growth factors receptors by peripheral and intestinal lymphocytes, these results showed that there was a divergence in the expression of early activation antigens in vivo and in vitro. This would indicate that in Crohn's disease there is an in vivo increased population of preactivated rather than fully activated lymphocytes consisting of 4F2 and T9 bearing cells. The high proportion of these cells in the peripheral blood and in the intestine suggests that a chronic immune activation is present in these patients outside as well as within the affected bowel.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auer I. O., Röder A., Fröhlich J. Immune status in Crohn's disease. VI. Immunoregulation evaluated by multiple, distinct T-suppressor cell assays of lymphocyte proliferation, and by enumeration of immunoregulatory T-lymphocyte subsets. Gastroenterology. 1984 Jun;86(6):1531–1543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bettens F., Kristensen F., Walker C., Schwuléra U., Bonnard G. D., de Weck A. L. Lymphokine regulation of activated (G1) lymphocytes. II. Glucocorticoid and anti-Tac-induced inhibition of human T lymphocyte proliferation. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):261–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bull D. M., Bookman M. A. Isolation and functional characterization of human intestinal mucosal lymphoid cells. J Clin Invest. 1977 May;59(5):966–974. doi: 10.1172/JCI108719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burmester G. R., Jahn B., Gramatzki M., Zacher J., Kalden J. R. Activated T cells in vivo and in vitro: divergence in expression of Tac and Ia antigens in the nonblastoid small T cells of inflammation and normal T cells activated in vitro. J Immunol. 1984 Sep;133(3):1230–1234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotner T., Williams J. M., Christenson L., Shapiro H. M., Strom T. B., Strominger J. Simultaneous flow cytometric analysis of human T cell activation antigen expression and DNA content. J Exp Med. 1983 Feb 1;157(2):461–472. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.2.461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebert E. C., Wright S. H., Lipshutz W. H., Hauptman S. P. T-cell abnormalities in inflammatory bowel disease are mediated by interleukin 2. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1984 Nov;33(2):232–244. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(84)90078-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fais S., Pallone F., Squarcia O., Boirivant M., Pozzilli P. T cell early activation antigens expressed by peripheral lymphocytes in Crohn's disease. J Clin Lab Immunol. 1985 Feb;16(2):75–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson A. Why study T cell subsets in Crohn's disease? Gut. 1983 Aug;24(8):687–691. doi: 10.1136/gut.24.8.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiocchi C., Hilfiker M. L., Youngman K. R., Doerder N. C., Finke J. H. Interleukin 2 activity of human intestinal mucosa mononuclear cells. Decreased levels in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 1984 Apr;86(4):734–742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiocchi C., Youngman K. R., Farmer R. G. Immunoregulatory function of human intestinal mucosa lymphoid cells: evidence for enhanced suppressor cell activity in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut. 1983 Aug;24(8):692–701. doi: 10.1136/gut.24.8.692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goding J. W., Burns G. F. Monoclonal antibody OKT-9 recognizes the receptor for transferrin on human acute lymphocytic leukemia cells. J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):1256–1258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin J. S., Bankhurst A. D., Messner R. P. Suppression of human T-cell mitogenesis by prostaglandin. Existence of a prostaglandin-producing suppressor cell. J Exp Med. 1977 Dec 1;146(6):1719–1734. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.6.1719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hafler D. A., Fox D. A., Manning M. E., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L., Weiner H. L. In vivo activated T lymphocytes in the peripheral blood and cerebrospinal fluid of patients with multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med. 1985 May 30;312(22):1405–1411. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198505303122201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey R. F., Bradshaw J. M. A simple index of Crohn's-disease activity. Lancet. 1980 Mar 8;1(8167):514–514. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)92767-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes B. F., Hemler M. E., Mann D. L., Eisenbarth G. S., Shelhamer J., Mostowski H. S., Thomas C. A., Strominger J. L., Fauci A. S. Characterization of a monoclonal antibody (4F2) that binds to human monocytes and to a subset of activated lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1409–1414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes B. F., Hemler M., Cotner T., Mann D. L., Eisenbarth G. S., Strominger J. L., Fauci A. S. Characterization of a monoclonal antibody (5E9) that defines a human cell surface antigen of cell activation. J Immunol. 1981 Jul;127(1):347–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. A., Morris M. A., Haynes B. F., Eisenbarth G. S. Increased circulating Ia-antigen-bearing T cells in type I diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1982 Apr 1;306(13):785–788. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198204013061305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James S. P., Neckers L. M., Graeff A. S., Cossman J., Balch C. M., Strober W. Suppression of immunoglobulin synthesis by lymphocyte subpopulations in patients with Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. 1984 Jun;86(6):1510–1518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard W. J., Depper J. M., Uchiyama T., Smith K. A., Waldmann T. A., Greene W. C. A monoclonal antibody that appears to recognize the receptor for human T-cell growth factor; partial characterization of the receptor. Nature. 1982 Nov 18;300(5889):267–269. doi: 10.1038/300267a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipkowitz S., Greene W. C., Rubin A. L., Novogrodsky A., Stenzel K. H. Expression of receptors for interleukin 2: Role in the commitment of T lymphocytes to proliferate. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):31–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mee A. S., Szawatakowski M., Jewell D. P. Monocytes in inflammatory bowel disease: phagocytosis and intracellular killing. J Clin Pathol. 1980 Oct;33(10):921–925. doi: 10.1136/jcp.33.10.921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittler R. S., Rao P. E., Talle M. A., Look R., Goldstein G. Cell membrane perturbation of resting T cells and thymocytes causes display of activation antigens. J Exp Med. 1983 Jul 1;158(1):99–111. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.1.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallone F., Montano S., Fais S., Boirivant M., Signore A., Pozzilli P. Studies of peripheral blood lymphocytes in Crohn's disease. Circulating activated T cells. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1983 Nov;18(8):1003–1008. doi: 10.3109/00365528309181833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallone F., Squarcia O., Fais S., Boirivant M., Biancone L., Tonietti G. T cell differentiation antigens expressed by peripheral blood lymphocytes in Crohn's disease. Boll Ist Sieroter Milan. 1985;64(5):394–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raedler A., Fraenkel S., Klose G., Seyfarth K., Thiele H. G. Involvement of the immune system in the pathogenesis of Crohn's disease. Expression of the T9 antigen on peripheral immunocytes correlates with the severity of the disease. Gastroenterology. 1985 Apr;88(4):978–983. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(85)80017-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raedler A., Fraenkel S., Klose G., Thiele H. G. Elevated numbers of peripheral T cells in inflammatory bowel diseases displaying T9 antigen and Fc alpha receptors. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Jun;60(3):518–524. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappaport R. S., Dodge G. R. Prostaglandin E inhibits the production of human interleukin 2. J Exp Med. 1982 Mar 1;155(3):943–948. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.3.943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb R. J., Munck A., Smith K. A. T cell growth factor receptors. Quantitation, specificity, and biological relevance. J Exp Med. 1981 Nov 1;154(5):1455–1474. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.5.1455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selby W. S., Janossy G., Bofill M., Jewell D. P. Intestinal lymphocyte subpopulations in inflammatory bowel disease: an analysis by immunohistological and cell isolation techniques. Gut. 1984 Jan;25(1):32–40. doi: 10.1136/gut.25.1.32. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selby W. S., Jewell D. P. T lymphocyte subsets in inflammatory bowel disease: peripheral blood. Gut. 1983 Feb;24(2):99–105. doi: 10.1136/gut.24.2.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchiyama T., Broder S., Waldmann T. A. A monoclonal antibody (anti-Tac) reactive with activated and functionally mature human T cells. I. Production of anti-Tac monoclonal antibody and distribution of Tac (+) cells. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1393–1397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Victorino R. M., Hodgson H. J. Spontaneous suppressor cell function in inflammatory bowel disease. Dig Dis Sci. 1981 Sep;26(9):801–806. doi: 10.1007/BF01309612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker C., Kristensen F., Bettens F., deWeck A. L. Lymphokine regulation of activated (G1) lymphocytes. I. Prostaglandin E2-induced inhibition of interleukin 2 production. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1770–1773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu D. T., Winchester R. J., Fu S. M., Gibofsky A., Ko H. S., Kunkel H. G. Peripheral blood Ia-positive T cells. Increases in certain diseases and after immunization. J Exp Med. 1980 Jan 1;151(1):91–100. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.1.91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan S. Z., Hanauer S. B., Kluskens L. F., Kraft S. C. Circulating lymphocyte subpopulations in Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. 1983 Dec;85(6):1313–1318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zifroni A., Treves A. J., Sachar D. B., Rachmilewitz D. Prostanoid synthesis by cultured intestinal epithelial and mononuclear cells in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut. 1983 Jul;24(7):659–664. doi: 10.1136/gut.24.7.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


