Abstract
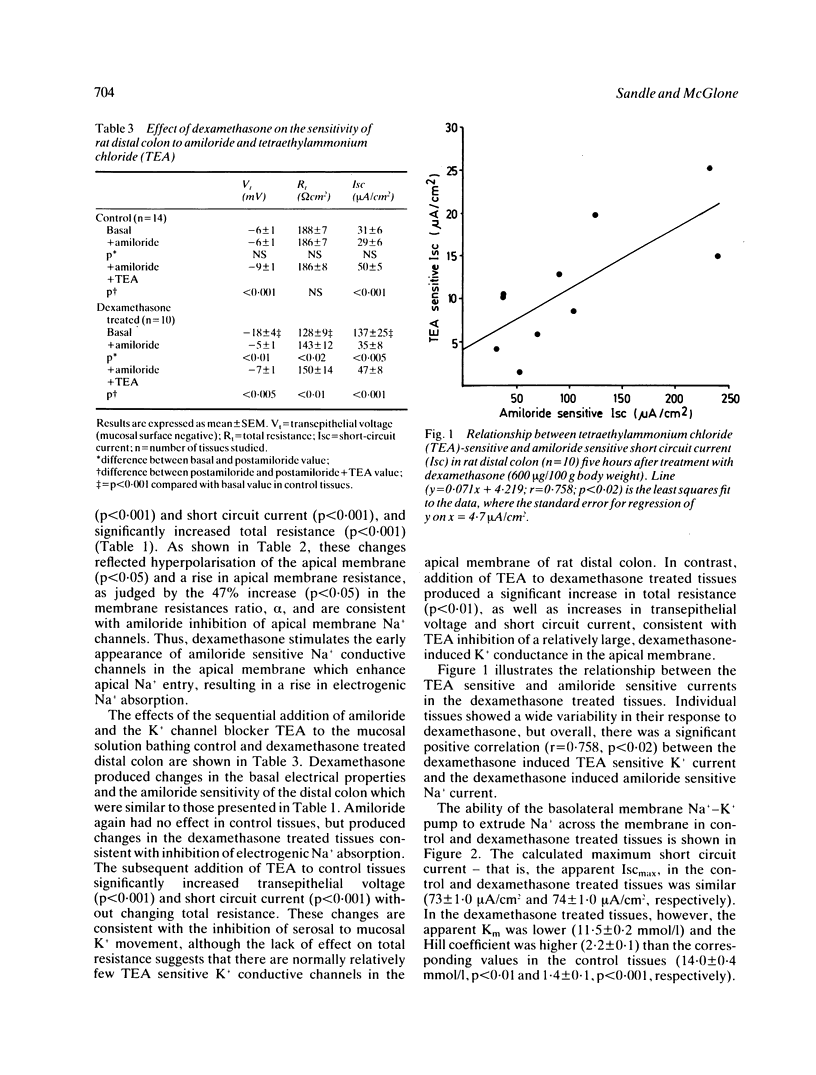
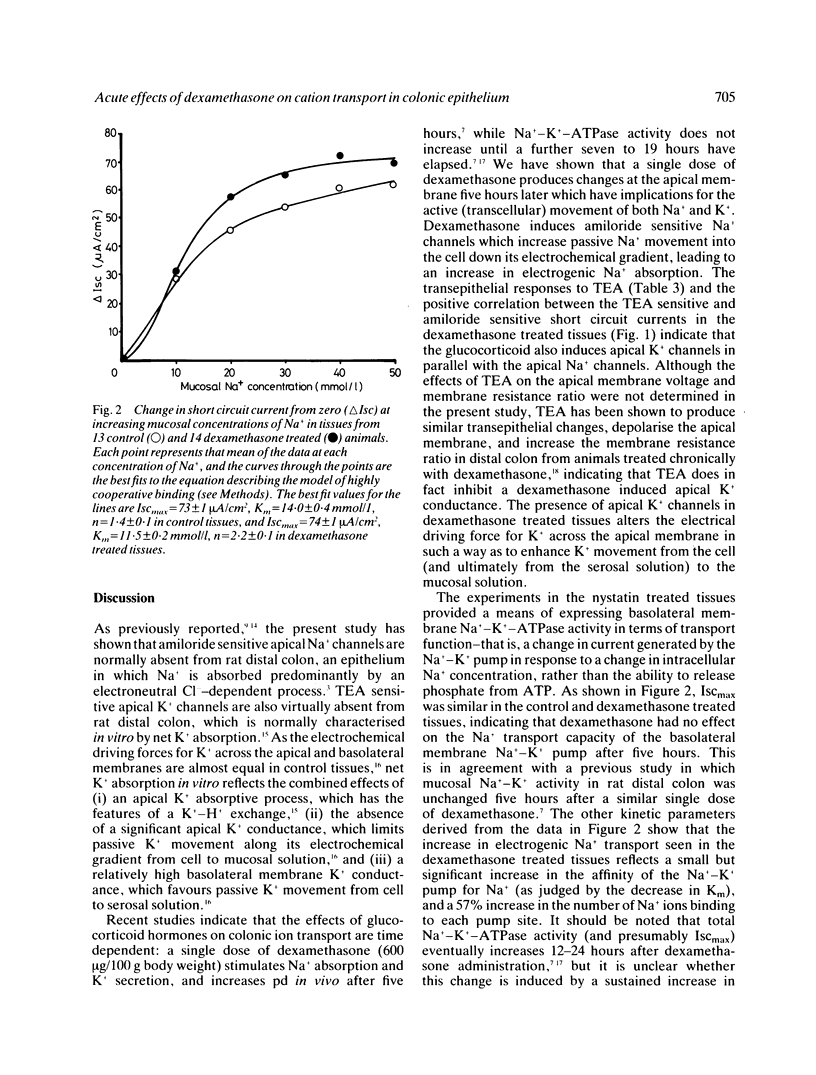
Single pharmacological doses of glucocorticoid hormones stimulate net Na+ and water absorption, K+ secretion and electrical potential difference in rat distal colon and human rectum after five hours. To determine the cellular basis of these effects, the Na+ and K+ transport properties of epithelial cell membranes in rat distal colon were studied in vitro five hours after in vivo treatment with dexamethasone 600 micrograms/100 g body weight. Compared with control tissues, dexamethasone increased transepithelial voltage 3.5-fold (p less than 0.001) and short circuit current 4.5-fold (p less than 0.001), and decreased total resistance by 20% (p less than 0.005). Measurements of cell membrane voltages obtained with intracellular microelectrodes indicated that the dexamethasone-induced rise in transepithelial voltage reflected a significant decrease (p less than 0.05) in apical membrane voltage, consistent with the induction of apical Na+ channels and the stimulation of electrogenic Na+ absorption. Apical addition of 10(-4) mol/l amiloride (a Na+ channel blocker) and then 30 mmol/l tetraethylammonium chloride (TEA; a K+ channel blocker) to control tissues had little or no effect on transepithelial electrical parameters, indicating the absence of significant apical Na+ and K+ conductances. In contrast, in dexamethasone treated tissues, amiloride and TEA produced electrical changes that were consistent with the inhibition of glucocorticoid-induced apical Na+ and K+ conductances. Kinetic studies of the basolateral membrane Na+-K+ pump revealed that five hours after administration, dexamethasone had no effect on the maximum capacity of the pump for Na+ transport, but significantly increased the affinity of the pump for Na+, and the number of Na+ ions binding to each pump site. Thus, the acute stimulatory effects of dexamethasone on distal colonic Na+ absorption and K+ secretion reflect increased apical membrane conductance to Na+ and K+, and an increase in the 'efficiency' of the basolateral membrane Na+-K+ pump.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bastl C. P., Barnett C. A., Schmidt T. J., Litwack G. Glucocorticoid stimulation of sodium absorption in colon epithelia is mediated by corticosteroid IB receptor. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 25;259(2):1186–1195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binder H. J. Effect of dexamethasone on electrolyte transport in the large intestine of the rat. Gastroenterology. 1978 Aug;75(2):212–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cass A., Finkelstein A., Krespi V. The ion permeability induced in thin lipid membranes by the polyene antibiotics nystatin and amphotericin B. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Jul;56(1):100–124. doi: 10.1085/jgp.56.1.100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clauss W., Dürr J., Skadhauge E., Hörnicke H. Effects of aldosterone and dexamethasone on apical membrane properties and Na-transport of rabbit distal colon in vitro. Pflugers Arch. 1985 Feb;403(2):186–192. doi: 10.1007/BF00584098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein F. O., Hayslett J. P. Role of medullary Na-K-ATPase in renal potassium adaption. Am J Physiol. 1975 Aug;229(2):524–528. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.229.2.524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster E. S., Hayslett J. P., Binder H. J. Mechanism of active potassium absorption and secretion in the rat colon. Am J Physiol. 1984 May;246(5 Pt 1):G611–G617. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1984.246.5.G611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster E. S., Zimmerman T. W., Hayslett J. P., Binder H. J. Corticosteroid alteration of active electrolyte transport in rat distal colon. Am J Physiol. 1983 Nov;245(5 Pt 1):G668–G675. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1983.245.5.G668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorkasky D., Cox M., Feldman G. M. Differential effects of corticosteroids on Na+ transport in rat distal colon in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1985 Apr;248(4 Pt 1):G424–G431. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1985.248.4.G424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. A., Wills N. K. Interaction between apical and basolateral membranes during sodium transport across tight epithelia. Soc Gen Physiol Ser. 1981;36:93–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marusic E. T., Hayslett J. P., Binder H. J. Corticosteroid-binding studies in cytosol of colonic mucosa of the rat. Am J Physiol. 1981 Jun;240(6):G417–G423. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1981.240.6.G417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pressley L., Funder J. W. Glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid receptors in gut mucosa. Endocrinology. 1975 Sep;97(3):588–596. doi: 10.1210/endo-97-3-588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez H. J., Sinha S. K., Starling J., Klahr S. Regulation of renal Na+-K+-ATPase in the rat by adrenal steroids. Am J Physiol. 1981 Aug;241(2):F186–F195. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.241.2.F186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandle G. I., Foster E. S., Lewis S. A., Binder H. J., Hayslett J. P. The electrical basis for enhanced potassium secretion in rat distal colon during dietary potassium loading. Pflugers Arch. 1985 Apr;403(4):433–439. doi: 10.1007/BF00589258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandle G. I., Hayslett J. P., Binder H. J. Effect of chronic hyperaldosteronism on the electrophysiology of rat distal colon. Pflugers Arch. 1984 May;401(1):22–26. doi: 10.1007/BF00581528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandle G. I., Hayslett J. P., Binder H. J. Effect of glucocorticoids on rectal transport in normal subjects and patients with ulcerative colitis. Gut. 1986 Mar;27(3):309–316. doi: 10.1136/gut.27.3.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Will P. C., Cortright R. N., DeLisle R. C., Douglas J. G., Hopfer U. Regulation of amiloride-sensitive electrogenic sodium transport in the rat colon by steroid hormones. Am J Physiol. 1985 Jan;248(1 Pt 1):G124–G132. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1985.248.1.G124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Will P. C., DeLisle R. C., Cortright R. N., Hopfer U. Induction of amiloride-sensitive sodium transport in the intestines by adrenal steroids. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1981;372:64–78. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1981.tb15458.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Will P. C., Lebowitz J. L., Hopfer U. Induction of amiloride-sensitive sodium transport in the rat colon by mineralocorticoids. Am J Physiol. 1980 Apr;238(4):F261–F268. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1980.238.4.F261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wills N. K., Lewis S. A., Eaton D. C. Active and passive properties of rabbit descending colon: a microelectrode and nystatin study. J Membr Biol. 1979 Mar 28;45(1-2):81–108. doi: 10.1007/BF01869296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


