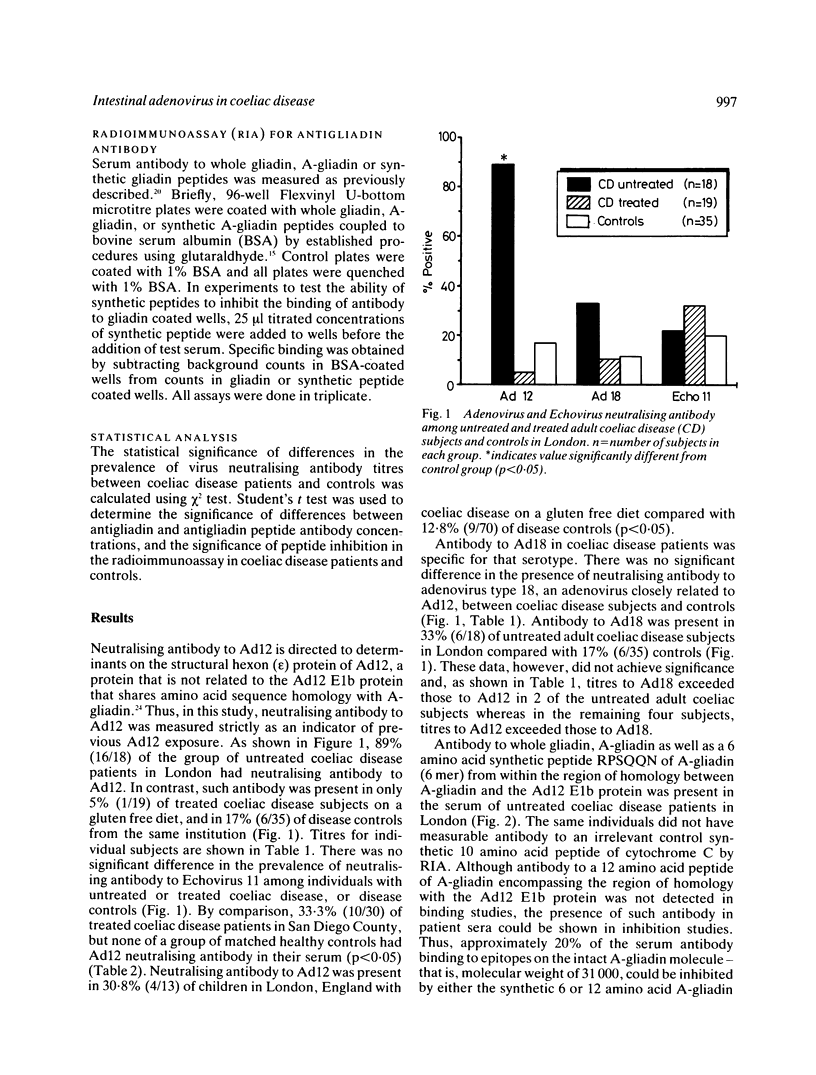
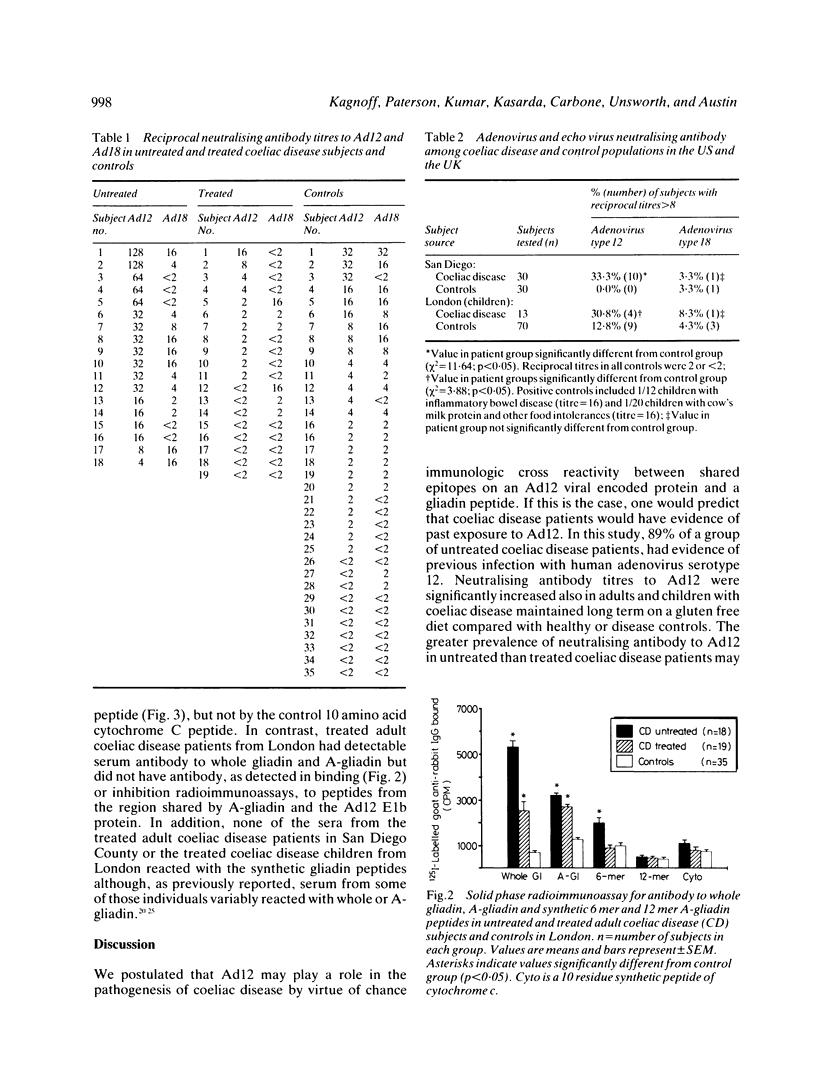
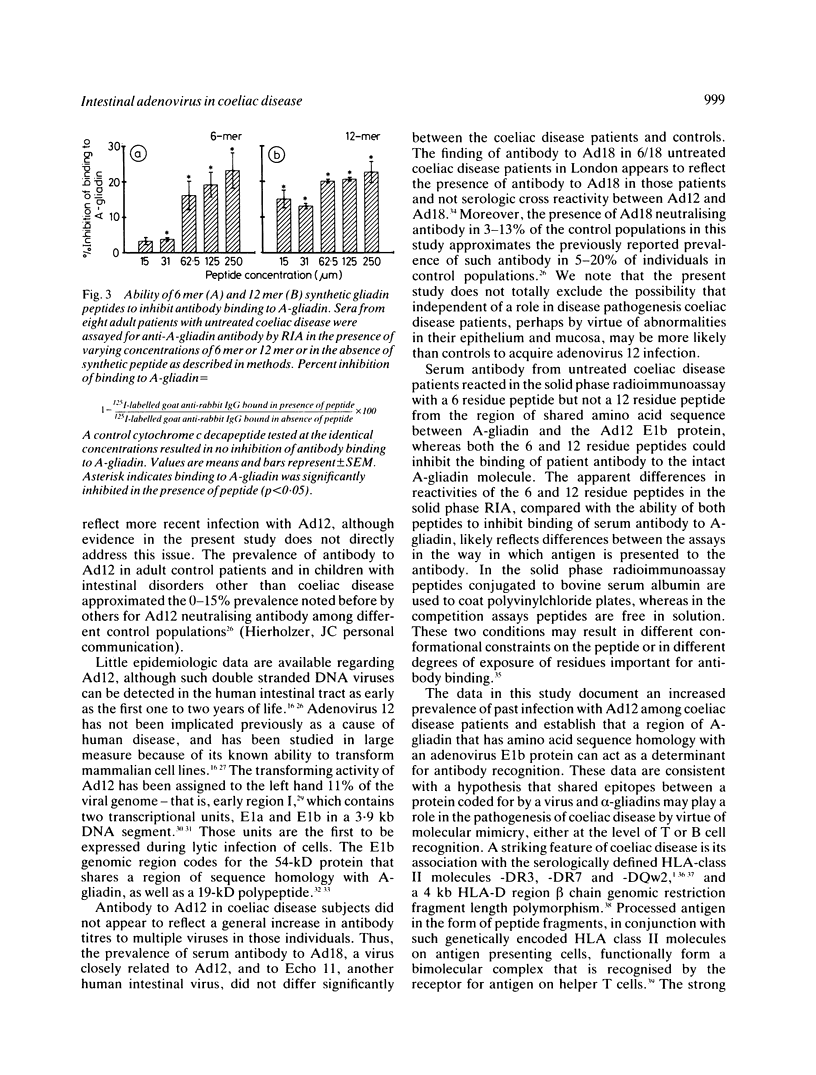
Abstract
We previously noted a region of amino acid sequence homology between A-gliadin, a major alpha-gliadin component known to activate coeliac disease, and the early region E1b protein of human adenovirus serotype 12 (Ad12), an adenovirus isolated from the human intestinal tract. In the present study sera from coeliac disease patients from the United Kingdom and the United States were assayed for neutralising antibody to Ad12 as evidence of past exposure to that virus and for antibody to synthetic peptides of A-gliadin from the region of shared sequence with the Ad12 E1b protein. Eighty nine per cent of untreated coeliac disease patients had evidence of previous Ad12 infection. There was also a significant increase in the prevalence of neutralising antibody to Ad12 among treated adults (33.3%) and children (30.8%) with coeliac disease compared with controls (0-12.8%) in the western USA and in London. There was no evidence for an increased prevalence of infection with a closely related adenovirus, adenovirus 18, or another enteric virus, Echovirus 11, among coeliac disease subjects. Additional studies documented that a region of A-gliadin that shares amino acid sequence homology with the adenovirus 12 E1b protein could be recognised as an antigenic determinant in active coeliac disease patients. Taken together, these data are compatible with the hypothesis that a viral protein may play a role in the pathogenesis of coeliac disease, perhaps by virtue of immunological cross reactivity between antigenic determinants shared by the viral protein and alpha-gliadins.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bos J. L., Polder L. J., Bernards R., Schrier P. I., van den Elsen P. J., van der Eb A. J., van Ormondt H. The 2.2 kb E1b mRNA of human Ad12 and Ad5 codes for two tumor antigens starting at different AUG triplets. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):121–131. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90366-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciclitira P. J., Evans D. J., Fagg N. L., Lennox E. S., Dowling R. H. Clinical testing of gliadin fractions in coeliac patients. Clin Sci (Lond) 1984 Mar;66(3):357–364. doi: 10.1042/cs0660357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corazza G. R., Tabacchi P., Frisoni M., Prati C., Gasbarrini G. DR and non-DR Ia allotypes are associated with susceptibility to coeliac disease. Gut. 1985 Nov;26(11):1210–1213. doi: 10.1136/gut.26.11.1210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Ambrosio E., Del Grosso N., Chicca A., Midulla M. Neutralizing antibodies against 33 human adenoviruses in normal children in Rome. J Hyg (Lond) 1982 Aug;89(1):155–161. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400070650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falchuk Z. M., Gebhard R. L., Sessoms C., Strober W. An in vitro model of gluten-sensitive enteropathy. Effect of gliadin on intestinal epithelial cells of patients with gluten-sensitive enteropathy in organ culture. J Clin Invest. 1974 Feb;53(2):487–500. doi: 10.1172/JCI107582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hierholzer J. C., Gamble W. C., Dowdle W. R. Reference equine antisera to 33 human adenovirus types: homologous and heterologous titers. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Jan;1(1):65–74. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.1.65-74.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howdle P. D., Ciclitira P. J., Simpson F. G., Losowsky M. S. Are all gliadins toxic in coeliac disease? An in vitro study of alpha, beta, gamma, and w gliadins. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1984 Jan;19(1):41–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell M. D., Austin R. K., Kelleher D., Nepom G. T., Kagnoff M. F. An HLA-D region restriction fragment length polymorphism associated with celiac disease. J Exp Med. 1986 Jul 1;164(1):333–338. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.1.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagnoff M. F., Austin R. K., Hubert J. J., Bernardin J. E., Kasarda D. D. Possible role for a human adenovirus in the pathogenesis of celiac disease. J Exp Med. 1984 Nov 1;160(5):1544–1557. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.5.1544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagnoff M. F., Austin R. K., Johnson H. C., Bernardin J. E., Dietler M. D., Kasarda D. D. Celiac sprue: correlation with murine T cell responses to wheat gliadin components. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2693–2697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasarda D. D., Okita T. W., Bernardin J. E., Baecker P. A., Nimmo C. C., Lew E. J., Dietler M. D., Greene F. C. Nucleic acid (cDNA) and amino acid sequences of alpha-type gliadins from wheat (Triticum aestivum). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4712–4716. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendall M. J., Schneider R., Cox P. S., Hawkins C. F. Gluten subfractions in coeliac disease. Lancet. 1972 Nov 18;2(7786):1065–1067. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)92344-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidd A. H., Cosgrove B. P., Brown R. A., Madeley C. R. Faecal adenoviruses from Glasgow babies. Studies on culture and identity. J Hyg (Lond) 1982 Jun;88(3):463–474. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400070327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura T., Sawada Y., Shinawawa M., Shimizu Y., Shiroki K., Shimojo H., Sugisaki H., Takanami M., Uemizu Y., Fujinaga K. Nucleotide sequence of the transforming early region E1b of adenovirus type 12 DNA: structure and gene organization, and comparison with those of adenovirus type 5 DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6571–6589. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levenson S. D., Austin R. K., Dietler M. D., Kasarda D. D., Kagnoff M. F. Specificity of antigliadin antibody in celiac disease. Gastroenterology. 1985 Jul;89(1):1–5. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(85)90737-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mearin M. L., Biemond I., Peña A. S., Polanco I., Vazquez C., Schreuder G. T., de Vries R. R., van Rood J. J. HLA-DR phenotypes in Spanish coeliac children: their contribution to the understanding of the genetics of the disease. Gut. 1983 Jun;24(6):532–537. doi: 10.1136/gut.24.6.532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrby E., Ankerst J. Biological characterization of structural components of Adenovirus type 12. J Gen Virol. 1969 Sep;5(2):183–194. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-5-2-183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perricaudet M., le Moullec J. M., Tiollais P., Pettersson U. Structure of two adenovirus type 12 transforming polypeptides and their evolutionary implications. Nature. 1980 Nov 13;288(5787):174–176. doi: 10.1038/288174a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. H. T-lymphocyte recognition of antigen in association with gene products of the major histocompatibility complex. Annu Rev Immunol. 1985;3:237–261. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.03.040185.001321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shale D. J., Johnston D. G., Hall R., Roberts D. F. Coeliac disease in monozygotic twins. Postgrad Med J. 1982 Dec;58(686):797–798. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.58.686.797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosi R., Vismara D., Tanigaki N., Ferrara G. B., Cicimarra F., Buffolano W., Follo D., Auricchio S. Evidence that celiac disease is primarily associated with a DC locus allelic specificity. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1983 Sep;28(3):395–404. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(83)90106-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vargosko A. J., Kim H. W., Parrott R. H., Jeffries B. C., Wong D., Chanock R. M. Recovery and identification of adenovirus in infections of infants and children. Bacteriol Rev. 1965 Dec;29(4):487–495. doi: 10.1128/br.29.4.487-495.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOYCHIK J. H., BOUNDY J. A., DIMLER R. J. Starch gel electrophoresis of wheat gluten proteins with concentrated urea. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961 Sep;94:477–482. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(61)90075-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J. B., Austin R. K., Schanfield M. S., Kagnoff M. F. Gluten-sensitive enteropathy. Immunoglobulin G heavy-chain (Gm) allotypes and the immune response to wheat gliadin. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):96–101. doi: 10.1172/JCI110988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M. C., Fraser N. W., Darnell J. E., Jr Mapping of RNA initiation sites by high doses of uv irradiation: evidence for three independent promoters within the left 11% of the Ad-2 genome. Virology. 1979 Apr 15;94(1):175–184. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90447-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


