Abstract
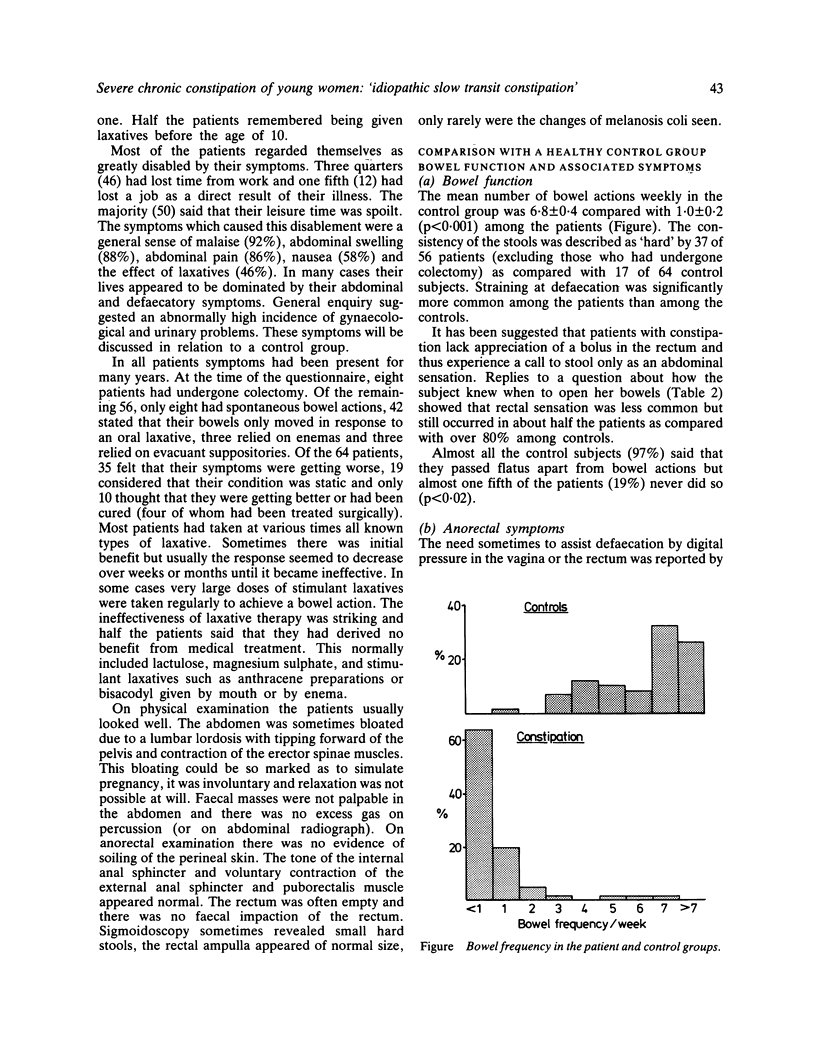
A series of 64 women complaining of severe constipation is described, in each of whom delayed elimination of markers from the colon was demonstrated but a barium enema was normal. All completed a detailed questionnaire and the responses are compared with those obtained in an age-matched series of healthy women with no bowel complaint. In each group 40 women also recorded in a manner suitable for analysis all food eaten over a period of seven days. The patients passed about one stool weekly with the aid of laxatives, and were greatly troubled by abdominal pain, bloating, malaise and nausea, to the extent that the symptoms were a major social disability and many lost time from work. Decreased bowel frequency and other symptoms were often first noticed around the age of puberty and slowly became worse until they were severe by the third decade. In a few, the symptoms began suddenly after an abdominal operation c-accident. Comparison with the control group showed no evidence that the patients had been underweight at any time or that they took less fibre; treatment with a bran supplement did not usually help them. The patients experienced rectal sensation before defaecation less often than the control subjects and they used digital pressure to assist defaecation more frequently. The women with constipation tended to have more painful and irregular menstrual periods, and there was an increased incidence of ovarian cystectomy and hysterectomy. Hesitancy in starting to pass urine was more common, as were some somatic symptoms such as cold hands or blackouts. Attention is drawn to this distinctive combination in young women of slow total gut transit time and a colon of normal width on barium enema, associated with abdominal, anorectal, gynaecological and somatic symptoms, as a disorder which can be disabling and particularly difficult to treat.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldi F., Ferrarini F., Corinaldesi R., Balestra R., Cassan M., Fenati G. P., Barbara L. Function of the internal anal sphincter and rectal sensitivity in idiopathic constipation. Digestion. 1982;24(1):14–22. doi: 10.1159/000198769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes P. R., Lennard-Jones J. E. Balloon expulsion from the rectum in constipation of different types. Gut. 1985 Oct;26(10):1049–1052. doi: 10.1136/gut.26.10.1049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bueno L., Fioramonti J., Ruckebusch Y., Frexinos J., Coulom P. Evaluation of colonic myoelectrical activity in health and functional disorders. Gut. 1980 Jun;21(6):480–485. doi: 10.1136/gut.21.6.480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONNELL A. M. The motility of the pelvic colon. II. Paradoxical motility in diarrhoea and constipation. Gut. 1962 Dec;3:342–348. doi: 10.1136/gut.3.4.342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connell A. M., Hilton C., Irvine G., Lennard-Jones J. E., Misiewicz J. J. Variation of bowel habit in two population samples. Br Med J. 1965 Nov 6;2(5470):1095–1099. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5470.1095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummings J. H. Constipation, dietary fibre and the control of large bowel function. Postgrad Med J. 1984 Nov;60(709):811–819. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.60.709.811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinoso V. P., Jr, Murthy S. N., Goldstein J., Rosner B. Basal motor activity of the distal colon: a reappraisal. Gastroenterology. 1983 Sep;85(3):637–642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frieri G., Parisi F., Corazziari E., Caprilli R. Colonic electromyography in chronic constipation. Gastroenterology. 1983 Apr;84(4):737–740. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fry I. K., Griffiths J. D., Smart P. J. Some observations on the movement of the pelvic floor and rectum with special reference to rectal prolapse. Br J Surg. 1966 Sep;53(9):784–787. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800530913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinton J. M., Lennard-Jones J. E., Young A. C. A ne method for studying gut transit times using radioopaque markers. Gut. 1969 Oct;10(10):842–847. doi: 10.1136/gut.10.10.842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnamurthy S., Schuffler M. D., Rohrmann C. A., Pope C. E., 2nd Severe idiopathic constipation is associated with a distinctive abnormality of the colonic myenteric plexus. Gastroenterology. 1985 Jan;88(1 Pt 1):26–34. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(85)80128-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marr J. W. Individual dietary surveys: purposes and methods. World Rev Nutr Diet. 1971;13:105–164. doi: 10.1159/000391884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meunier P., Marechal J. M., de Beaujeu M. J. Rectoanal pressures and rectal sensitivity studies in chronic childhood constipation. Gastroenterology. 1979 Aug;77(2):330–336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meunier P., Rochas A., Lambert R. Motor activity of the sigmoid colon in chronic constipation: comparative study with normal subjects. Gut. 1979 Dec;20(12):1095–1101. doi: 10.1136/gut.20.12.1095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston D. M., Hawley P. R., Lennard-Jones J. E., Todd I. P. Results of colectomy for severe idiopathic constipation in women (Arbuthnot Lane's disease). Br J Surg. 1984 Jul;71(7):547–552. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800710726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston D. M., Lennard-Jones J. E. Anismus in chronic constipation. Dig Dis Sci. 1985 May;30(5):413–418. doi: 10.1007/BF01318172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston D. M., Lennard-Jones J. E. Pelvic motility and response to intraluminal bisacodyl in slow-transit constipation. Dig Dis Sci. 1985 Apr;30(4):289–294. doi: 10.1007/BF01403835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston D. M., Lennard-Jones J. E., Thomas B. M. Towards a radiologic definition of idiopathic megacolon. Gastrointest Radiol. 1985;10(2):167–169. doi: 10.1007/BF01893094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandler R. S., Drossman D. A., Nathan H. P., McKee D. C. Symptom complaints and health care seeking behavior in subjects with bowel dysfunction. Gastroenterology. 1984 Aug;87(2):314–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagart R. E. The anal canal and rectum: their varying relationship and its effect on anal continence. Dis Colon Rectum. 1966 Nov-Dec;9(6):449–452. doi: 10.1007/BF02617443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WANGEL A. G., DELLER D. J. INTESTINAL MOTILITY IN MAN. 3. MECHANISMS OF CONSTIPATION AND DIARRHEA WITH PARTICULAR REFERENCE TO THE IRRITABLE COLON SYNDROME. Gastroenterology. 1965 Jan;48:69–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waller S. L., Misiewicz J. J. Colonic motility in constipation or diarrhoea. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1972;7(1):93–96. doi: 10.3109/00365527209180743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waller S. L., Misiewicz J. J., Kiley N. Effect of eating on motility of the pelvic colon in constipation or diarrhoea. Gut. 1972 Oct;13(10):805–811. doi: 10.1136/gut.13.10.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watier A., Devroede G., Duranceau A., Abdel-Rahman M., Duguay C., Forand M. D., Tétreault L., Arhan P., Lamarche J., Elhilali M. Constipation with colonic inertia. A manifestation of systemic disease? Dig Dis Sci. 1983 Nov;28(11):1025–1033. doi: 10.1007/BF01311732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead W. E., Winget C., Fedoravicius A. S., Wooley S., Blackwell B. Learned illness behavior in patients with irritable bowel syndrome and peptic ulcer. Dig Dis Sci. 1982 Mar;27(3):202–208. doi: 10.1007/BF01296915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOUNG C. M., HAGAN G. C., TUCKER R. E., FOSTER W. D. A comparison of dietary study methods. II. Dietary history vs. seven-day record vs. 24-hr. recall. J Am Diet Assoc. 1952 Mar;28(3):218–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


