Abstract
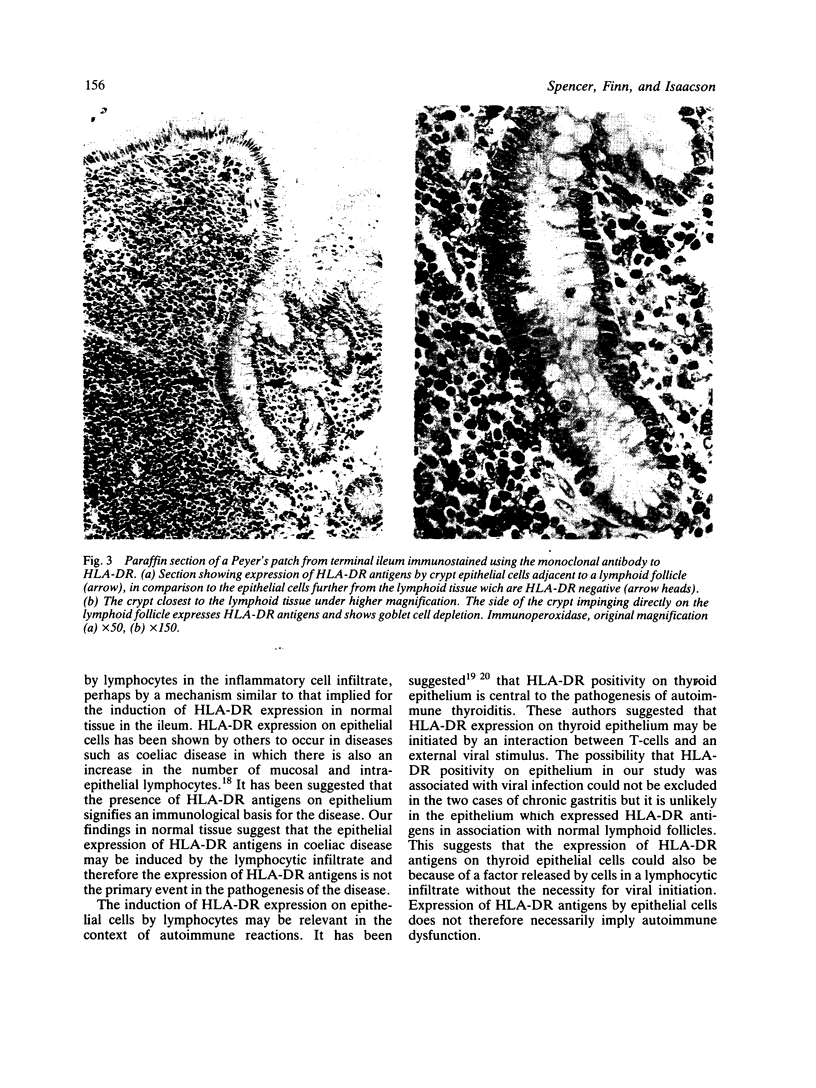
Mucosa from human stomach, terminal ileum, appendix, and colon was studied for epithelial HLA-DR expression using an immunoperoxidase technique with a monoclonal antibody that detects HLA-DR antigens in paraffin embedded tissues. Expression of HLA-DR by epithelial cells was studied with particular reference to the effect of adjacent lymphoid tissue or surrounding chronic inflammation. In the stomach, epithelial HLA-DR appeared to be induced by chronic inflammation. Where lymphoid nodules were present only that epithelium directly adjacent to the lymphoid tissue expressed HLA-DR. Expression was independent of cell type. Epithelium adjacent to normal lymphoid tissue in the terminal ileum, appendix, and colon also expressed HLA-DR, the relationship between expression and proximity to lymphoid tissue being remarkably precise. Expression of HLA-DR by gastrointestinal epithelium appears to be an effect of adjacent lymphocytes, whether part of an inflammatory response or normal tissue. This must be taken into account when assessing HLA-DR expression by gastrointestinal epithelium.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barclay A. N., Mason D. W. Induction of Ia antigen in rat epidermal cells and gut epithelium by immunological stimuli. J Exp Med. 1982 Dec 1;156(6):1665–1676. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.6.1665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottazzo G. F., Pujol-Borrell R., Hanafusa T., Feldmann M. Role of aberrant HLA-DR expression and antigen presentation in induction of endocrine autoimmunity. Lancet. 1983 Nov 12;2(8359):1115–1119. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90629-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran R. C., Gregory J. Effects of fixation and processing on immunohistochemical demonstration of immunoglobulin in paraffin sections of tonsil and bone marrow. J Clin Pathol. 1980 Nov;33(11):1047–1057. doi: 10.1136/jcp.33.11.1047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epenetos A. A., Bobrow L. G., Adams T. E., Collins C. M., Isaacson P. G., Bodmer W. F. A monoclonal antibody that detects HLA-D region antigen in routinely fixed, wax embedded sections of normal and neoplastic lymphoid tissues. J Clin Pathol. 1985 Jan;38(1):12–17. doi: 10.1136/jcp.38.1.12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsum U., Klareskog L., Peterson P. A. Distribution of Ia-antigen-like molecules on non-lymphoid tissues. Scand J Immunol. 1979;9(4):343–349. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1979.tb03172.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham R. C., Jr, Karnovsky M. J. The early stages of absorption of injected horseradish peroxidase in the proximal tubules of mouse kidney: ultrastructural cytochemistry by a new technique. J Histochem Cytochem. 1966 Apr;14(4):291–302. doi: 10.1177/14.4.291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanafusa T., Pujol-Borrell R., Chiovato L., Russell R. C., Doniach D., Bottazzo G. F. Aberrant expression of HLA-DR antigen on thyrocytes in Graves' disease: relevance for autoimmunity. Lancet. 1983 Nov 12;2(8359):1111–1115. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90628-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch M. R., Wietzerbin J., Pierres M., Goridis C. Expression of Ia antigens by cultured astrocytes treated with gamma-interferon. Neurosci Lett. 1983 Oct 31;41(1-2):199–204. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(83)90247-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayrhofer G., Pugh C. W., Barclay A. N. The distribution, ontogeny and origin in the rat of Ia-positive cells with dendritic morphology and of Ia antigen in epithelia, with special reference to the intestine. Eur J Immunol. 1983 Feb;13(2):112–122. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830130206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen R. L., Jones A. L. Epithelial cell specialization within human Peyer's patches: an ultrastructural study of intestinal lymphoid follicles. Gastroenterology. 1974 Feb;66(2):189–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pober J. S., Collins T., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Cotran R. S., Gitlin J. D., Fiers W., Clayberger C., Krensky A. M., Burakoff S. J., Reiss C. S. Lymphocytes recognize human vascular endothelial and dermal fibroblast Ia antigens induced by recombinant immune interferon. Nature. 1983 Oct 20;305(5936):726–729. doi: 10.1038/305726a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott H., Solheim B. G., Brandtzaeg P., Thorsby E. HLA-DR-like antigens in the epithelium of the human small intestine. Scand J Immunol. 1980;12(1):77–82. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1980.tb00043.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer J., Finn T., Isaacson P. G. Gut associated lymphoid tissue: a morphological and immunocytochemical study of the human appendix. Gut. 1985 Jul;26(7):672–679. doi: 10.1136/gut.26.7.672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steeg P. S., Moore R. N., Johnson H. M., Oppenheim J. J. Regulation of murine macrophage Ia antigen expression by a lymphokine with immune interferon activity. J Exp Med. 1982 Dec 1;156(6):1780–1793. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.6.1780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorsby E., Berle E., Nousiainen H. HLA-D region molecules restrict proliferative T cell responses to antigen. Immunol Rev. 1982;66:39–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00433.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R. The regulatory role of macrophages in antigenic stimulation. Part Two: symbiotic relationship between lymphocytes and macrophages. Adv Immunol. 1981;31:1–136. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60919-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]