Abstract
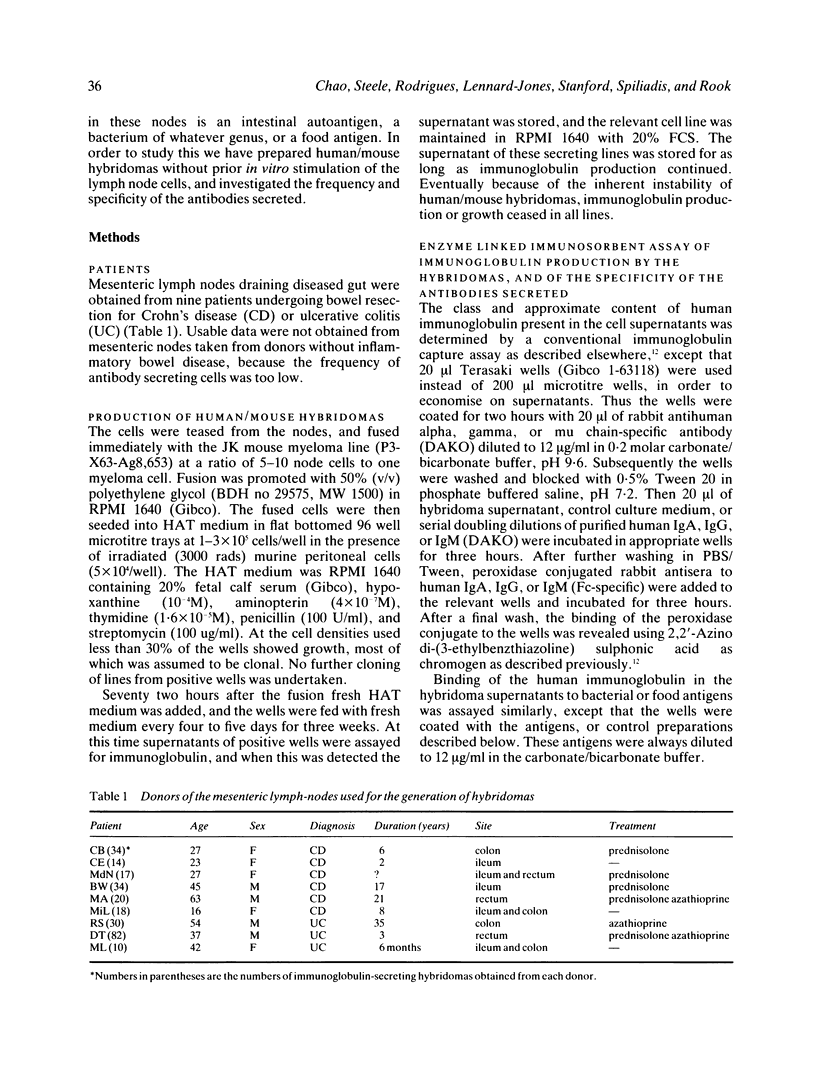
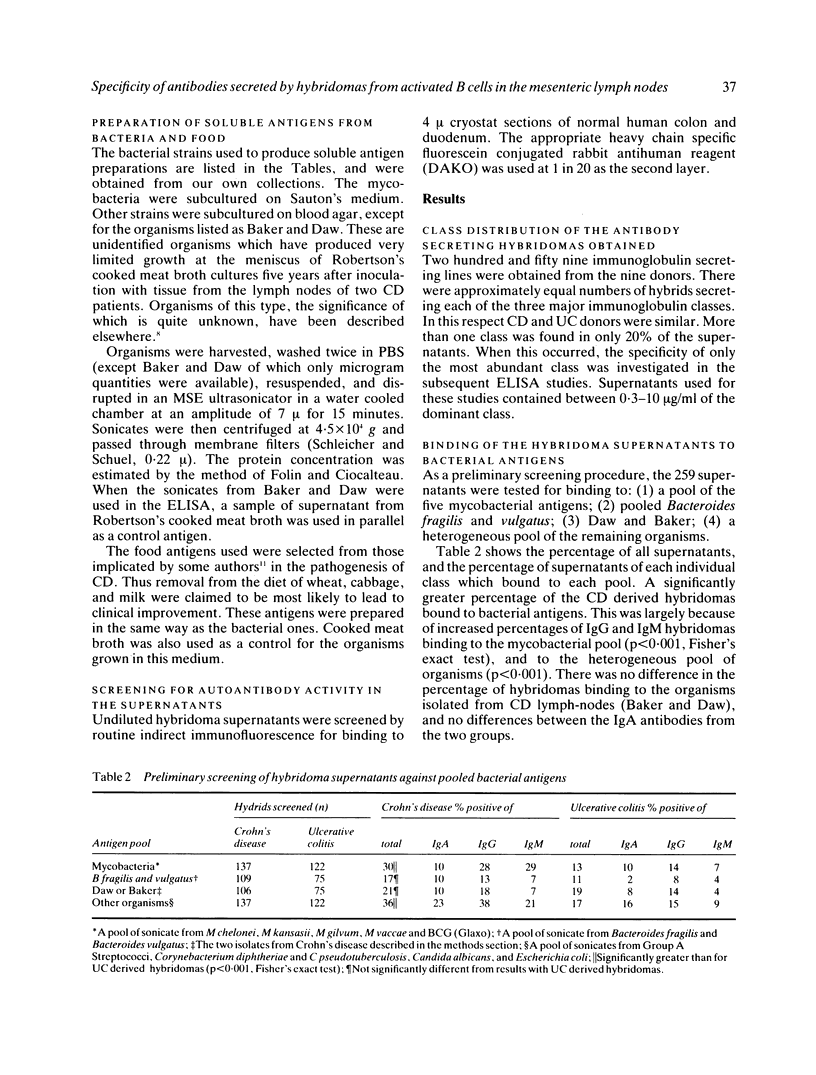
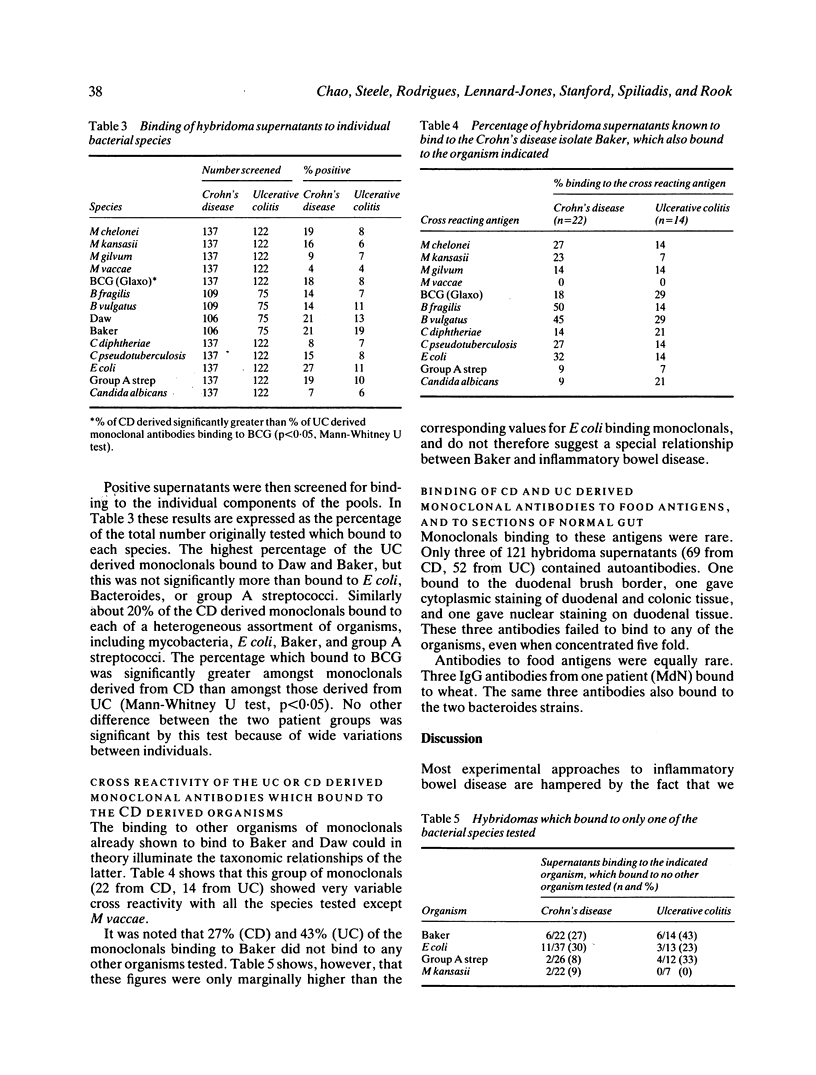
Hybridomas have been prepared from active B cells in lymphoid tissue draining lesions of Crohn's disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC), by fusion of fresh mesenteric lymph node suspensions with the murine JK myeloma. Two hundred and fifty nine immunoglobulin secreting hybridomas have been obtained from nine patients. The antibodies have been screened for binding to food antigens, sections of human gut, and bacteria including two unidentified acid fast isolates from CD lymph nodes. Autoantibodies, and antibodies to food antigens implicated by others in the aetiology of CD were rare, comprising 1.2%, and 2.5% respectively. Most donors yielded none of these. Thus neither food antigens nor autoantigens are major antigenic stimuli in nodes draining inflammatory bowel disease. On the other hand between 19% and 83% of supernatants from different donors bound to one or more bacterial genus. The mycobacteria and the CD isolates were amongst the genera to which most antibodies bound, though binding to E coli was more frequent. Significantly more CD than UC derived supernatants bound to BCG. As mycobacteria are not though to be part of the normal bowel flora, the high percentage of hybridomas secreting antibodies which bind to this genus is surprising.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aronson R. A., Cook S. L., Roche J. K. Sensitization to epithelial antigens in chronic mucosal inflammatory disease. I. Purification, characterization, and immune reactivity of murine epithelial cell-associated components (ECAC). J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):2796–2804. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auer I. O., Röder A., Wensinck F., van de Merwe J. P., Schmidt H. Selected bacterial antibodies in Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1983 Mar;18(2):217–223. doi: 10.3109/00365528309181586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bull D. M., Ignaczak T. F. Enterobacterial common antigen-induced lymphocyte reactivity in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 1973 Jan;64(1):43–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnham W. R., Lennard-Jones J. E., Stanford J. L., Bird R. G. Mycobacteria as a possible cause of inflammatory bowel disease. Lancet. 1978 Sep 30;2(8092 Pt 1):693–696. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)92699-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman R. W., Cottone M., Selby W. S., Shepherd H. A., Sherlock S., Jewell D. P. Serum autoantibodies, ulcerative colitis and primary sclerosing cholangitis. Gut. 1986 Jan;27(1):86–91. doi: 10.1136/gut.27.1.86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiodini R. J., Van Kruiningen H. J., Thayer W. R., Merkal R. S., Coutu J. A. Possible role of mycobacteria in inflammatory bowel disease. I. An unclassified Mycobacterium species isolated from patients with Crohn's disease. Dig Dis Sci. 1984 Dec;29(12):1073–1079. doi: 10.1007/BF01317078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming B., Rook G. A. T-cell-dependent polyclonal activation by soluble mycobacterial extracts of B cells in peripheral blood mononuclear cell populations from leprosy patients and normal donors. Immunology. 1982 Dec;47(4):589–595. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helphingstine C. J., Hentges D. J., Campbell B. J., Butt J., Barrett J. T. Antibodies detectable by counterimmunoelectrophoresis against Bacteroides antigens in serum of patients with inflammatory bowel disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Mar;9(3):373–378. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.3.373-378.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibi T., Aiso S., Yoshida T., Watanabe M., Asakura H., Tsuru S., Tsuchiya M. Anti-colon antibody and lymphocytophilic antibody in ulcerative colitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Jul;49(1):75–80. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt P. S., Trotter S. Lymphoblastic response to autologous colon epithelial cells in ulcerative colitis in vitro. Gut. 1973 Nov;14(11):875–879. doi: 10.1136/gut.14.11.875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones V. A., Dickinson R. J., Workman E., Wilson A. J., Freeman A. H., Hunter J. O. Crohn's disease: maintenance of remission by diet. Lancet. 1985 Jul 27;2(8448):177–180. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91497-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews N., Mayberry J. F., Rhodes J., Neale L., Munro J., Wensinck F., Lawson G. H., Rowland A. C., Berkhoff G. A., Barthold S. W. Agglutinins to bacteria in Crohn's disease. Gut. 1980 May;21(5):376–380. doi: 10.1136/gut.21.5.376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai T., Das K. M. Detection of colonic antigen(s) in tissues from ulcerative colitis using purified colitis colon tissue-bound IgG (CCA-IgG). Gastroenterology. 1981 Sep;81(3):463–470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roche J. K., Fiocchi C., Youngman K. Sensitization to epithelial antigens in chronic mucosal inflammatory disease. Characterization of human intestinal mucosa-derived mononuclear cells reactive with purified epithelial cell-associated components in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1985 Feb;75(2):522–530. doi: 10.1172/JCI111728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shorter R. G., McGill D. B., Bahn R. C. Cytotoxicity of mononuclear cells for autologous colonic epithelial cells in colonic diseases. Gastroenterology. 1984 Jan;86(1):13–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabaqchali S., O'Donoghue D. P., Bettelheim K. A. Escherichia coli antibodies in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Gut. 1978 Feb;19(2):108–113. doi: 10.1136/gut.19.2.108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thayer W. R., Jr, Coutu J. A., Chiodini R. J., Van Kruiningen H. J., Merkal R. S. Possible role of mycobacteria in inflammatory bowel disease. II. Mycobacterial antibodies in Crohn's disease. Dig Dis Sci. 1984 Dec;29(12):1080–1085. doi: 10.1007/BF01317079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tvede M., Bondesen S., Nielsen O. H., Rasmussen S. N. Serum antibodies to Bacteroides species in chronic inflammatory bowel disease. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1983 Sep;18(6):783–789. doi: 10.3109/00365528309182095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WRIGHT R., TRUELOVE S. C. A CONTROLLED THERAPEUTIC TRIAL OF VARIOUS DIETS IN ULCERATIVE COLITIS. Br Med J. 1965 Jul 17;2(5454):138–141. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5454.138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



