Abstract
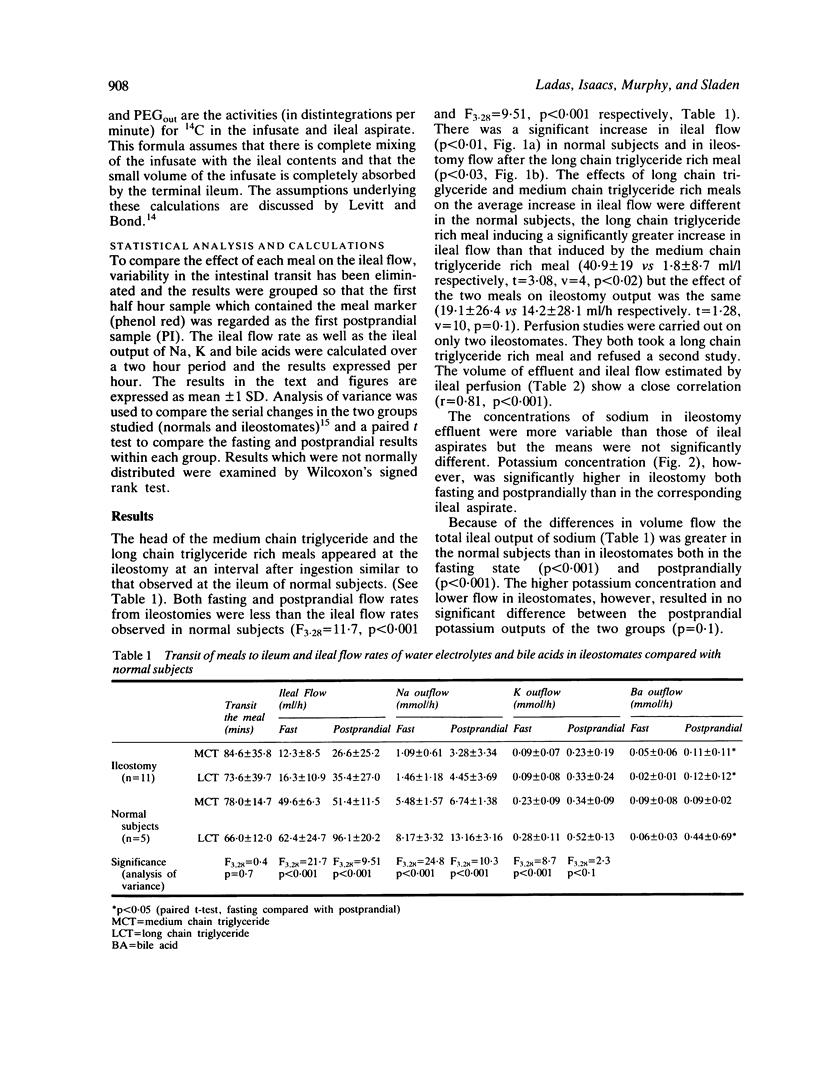
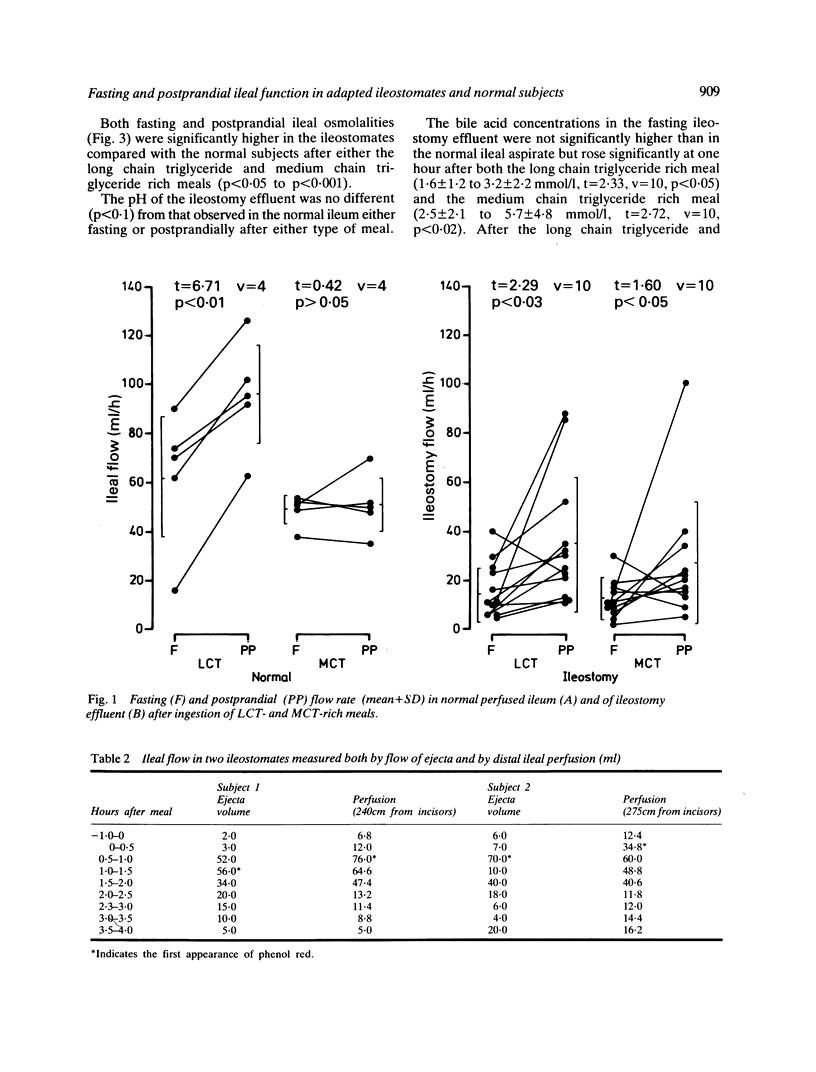
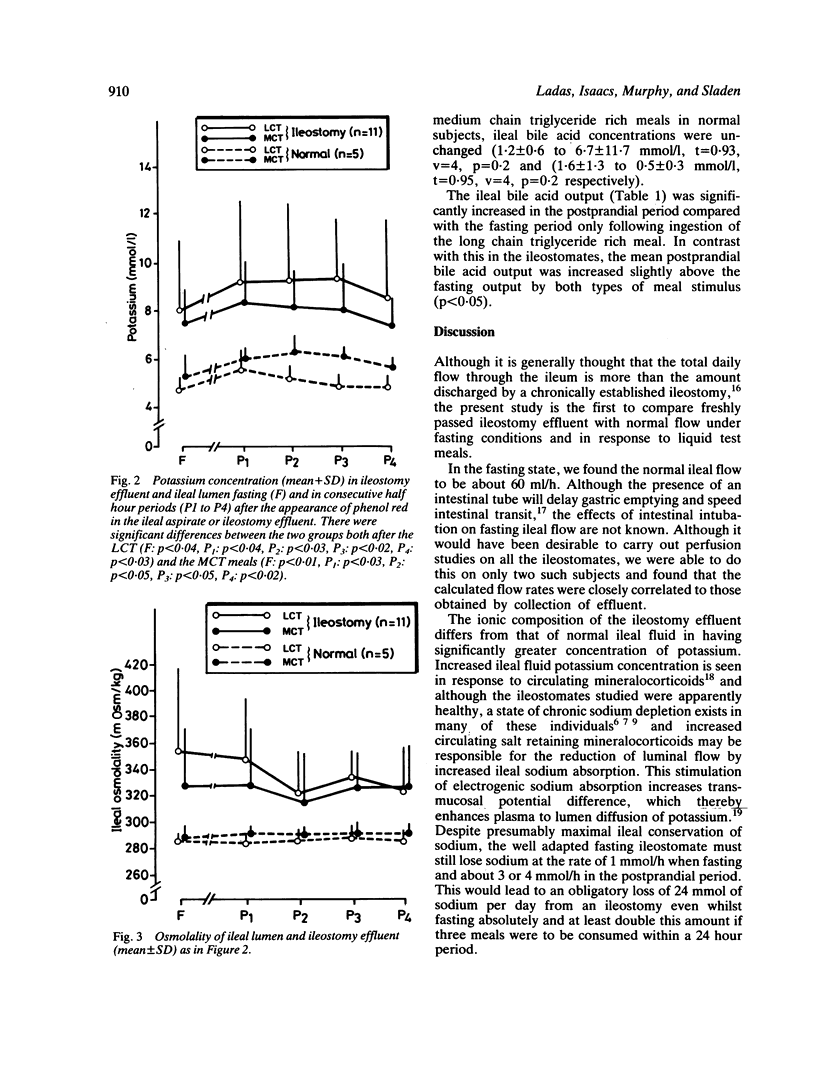
The output of 11 established ileostomies was compared with ileal flow measured by intestinal perfusion in five normal volunteers when fasting and during the ileal passage of test meals containing different proportions of medium chain triglyceride and long chain triglyceride. Oroileal transit of the meal was the same in the two groups, but ileostomy output was less than ileal flow of normal persons both fasting (16.3 +/- 10.9 vs 62.4 +/- 24.7 ml/h, p less than 0.001) and after the long chain triglyceride rich meal (35.4 27.0 vs 96.1 +/- 20.2 ml/h, p less than 0.001). After ingestion of the medium chain triglyceride rich meal, ideal flow failed to increase in normal subjects but in ileostomates the changes in flow after medium chain triglyceride and long chain triglyceride rich meals were not significantly different. The fasting ileostomy effluent composition differed from that of normal fasting ileal content in having a higher concentration of potassium (8.0 +/- 2.9 vs 4.7 +/- 0.6 mmol/1, p less than 0.04) and a higher osmolality (353 +/- 63 vs 287 +/- 5 mosm/kg, p less than 0.05). Sodium concentration tended to be lower in ileostomy effluent, but in contrast to previous reports, ileostomy effluent was of consistently alkaline pH (7.2 +/- 0.3). These concentrations were not significantly altered by either type of meal. The long chain triglyceride rich meal increased the ileal flow of bile acids in both normal subjects and ileostomates, whereas the medium chain triglyceride rich meal increased bile acid flow in ileostomates but not in normal subjects, possibly reflecting a different amount of the bile acids in the ileum of the ileostomate. In the adapted ileostomate, the low volume and high potassium concentration of fasting effluent suggest that sodium and water absorption are continuously stimulated by chronic salt depletion.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clarke A. M., Chirnside A., Hill G. L., Pope G., Stewart M. K. Chronic dehydration and sodium depletion in patients with established ileostomies. Lancet. 1967 Oct 7;2(7519):740–743. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)91945-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbach S. L., Nahas L., Weinstein L., Levitan R., Patterson J. F. Studies of intestinal microflora. IV. The microflora of ileostomy effluent: a unique microbial ecology. Gastroenterology. 1967 Dec;53(6):874–880. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill G. L., Goligher J. C., Smith A. H., Mair W. S. Long term changes in total body water, total exchangable sodium and total body potassium before and after ileostomy. Br J Surg. 1975 Jul;62(7):524–527. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800620706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacs P. E., Horth C. E., Turnberg L. A. The electrical potential difference across human ileostomy mucosa. Gastroenterology. 1976 Jan;70(1):52–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KANAGHINIS T., LUBRAN M., COGHILL N. F. THE COMPOSITION OF ILEOSTOMY FLUID. Gut. 1963 Dec;4:322–338. doi: 10.1136/gut.4.4.322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRAMER P., KEARNEY M. M., INGELFINGER F. J. The effect of specific foods and water loading on the ileal excreta of ileostomized human subjects. Gastroenterology. 1962 May;42:535–546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladas S. D., Isaacs P. E., Murphy G. M., Sladen G. E. Comparison of the effects of medium and long chain triglyceride containing liquid meals on gall bladder and small intestinal function in normal man. Gut. 1984 Apr;25(4):405–411. doi: 10.1136/gut.25.4.405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitan R., Goulston K. Water and electrolyte content of human ileostomy fluid after d-aldosterone administration. Gastroenterology. 1967 Mar;52(3):510–512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt M. D., Bond J. Use of the constant perfusion technique in the nonsteady state. Gastroenterology. 1977 Dec;73(6):1450–1453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miettinen T. A., Peltokallio P. Bile salt, fat, water, and vitamin B 12 excretion after ileostomy. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1971;6(6):543–552. doi: 10.3109/00365527109181671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss S., Gordon D., Forsling M. L., Peart W. S., James V. H., Roddis S. A. Water and electrolyte composition of urine and ileal fluid and its relationship to renin and aldosterone during dietary sodium deprivation in patients with ileostomies. Clin Sci (Lond) 1981 Oct;61(4):407–415. doi: 10.1042/cs0610407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips S. F., Giller J. The contribution of the colon to electrolyte and water conservation in man. J Lab Clin Med. 1973 May;81(5):733–746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read N. W., Al Janabi M. N., Bates T. E., Barber D. C. Effect of gastrointestinal intubation on the passage of a solid meal through the stomach and small intestine in humans. Gastroenterology. 1983 Jun;84(6):1568–1572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHEDL H. P., CLIFTON J. A. Small intestinal absorption of steroids. Gastroenterology. 1961 Nov;41:491–499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMIDDY F. G., GREGORY S. D., SMITH I. B., GOLIGHER J. C. Faecal loss of fluid, electrolytes, and nitrogen in colitis before and after ileostomy. Lancet. 1960 Jan 2;1(7114):14–19. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(60)92717-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sowers J. R., Martin V. I., Beck F. W. Effects of dietary sodium on circadian rhythm and physiological responses of 18-hydroxycorticosterone. Clin Sci (Lond) 1983 Mar;64(3):295–301. doi: 10.1042/cs0640295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiller R. C., Trotman I. F., Higgins B. E., Ghatei M. A., Grimble G. K., Lee Y. C., Bloom S. R., Misiewicz J. J., Silk D. B. The ileal brake--inhibition of jejunal motility after ileal fat perfusion in man. Gut. 1984 Apr;25(4):365–374. doi: 10.1136/gut.25.4.365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TALALAY P. Enzymic analysis of steroid hormones. Methods Biochem Anal. 1960;8:119–143. doi: 10.1002/9780470110249.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnberg L. A., Morris A. I., Hawker P. C., Herman K. J., Shields R. A., Horth C. E. Intracellular electrolyte depletion in patients with ileostomies. Gut. 1978 Jun;19(6):563–568. doi: 10.1136/gut.19.6.563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnberg L. A. Potassium transport in the human small bowel. Gut. 1971 Oct;12(10):811–818. doi: 10.1136/gut.12.10.811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright H. K., Cleveland J. C., Tilson M. D., Herskovic T. Morphology and absorptive capacity of the ileum after ileostomy in man. Am J Surg. 1969 Feb;117(2):242–245. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(69)90310-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


