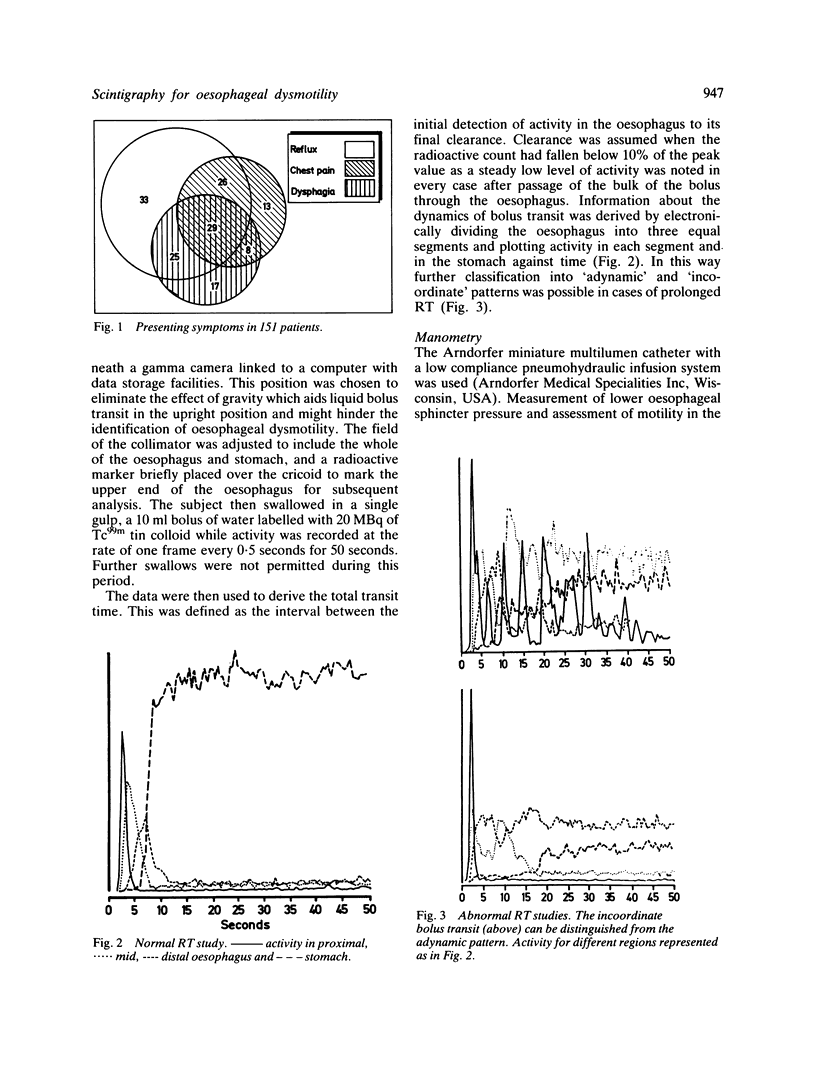
Abstract
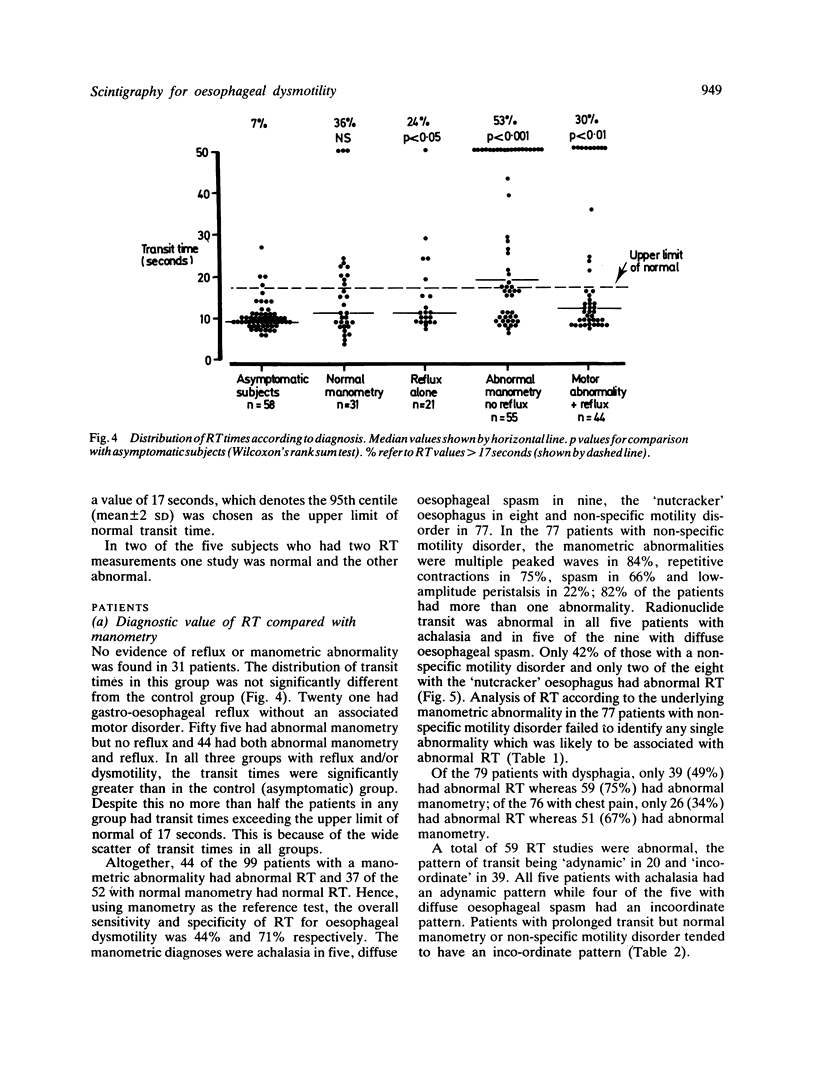
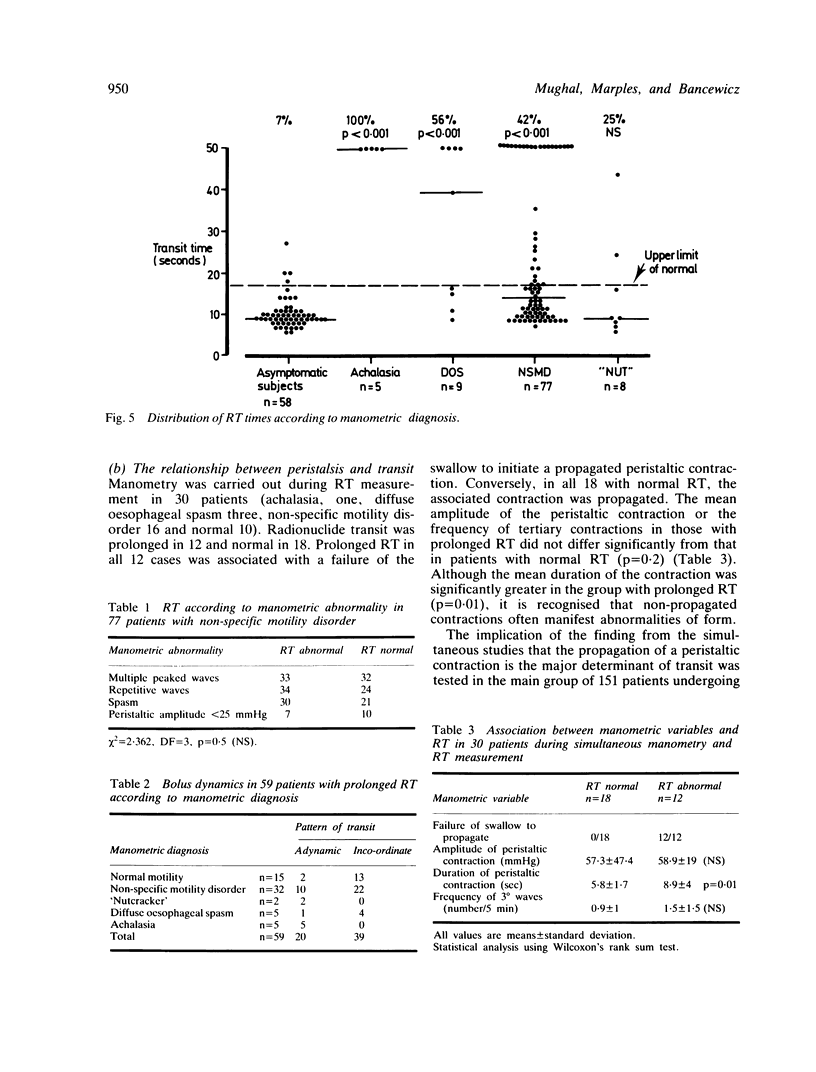
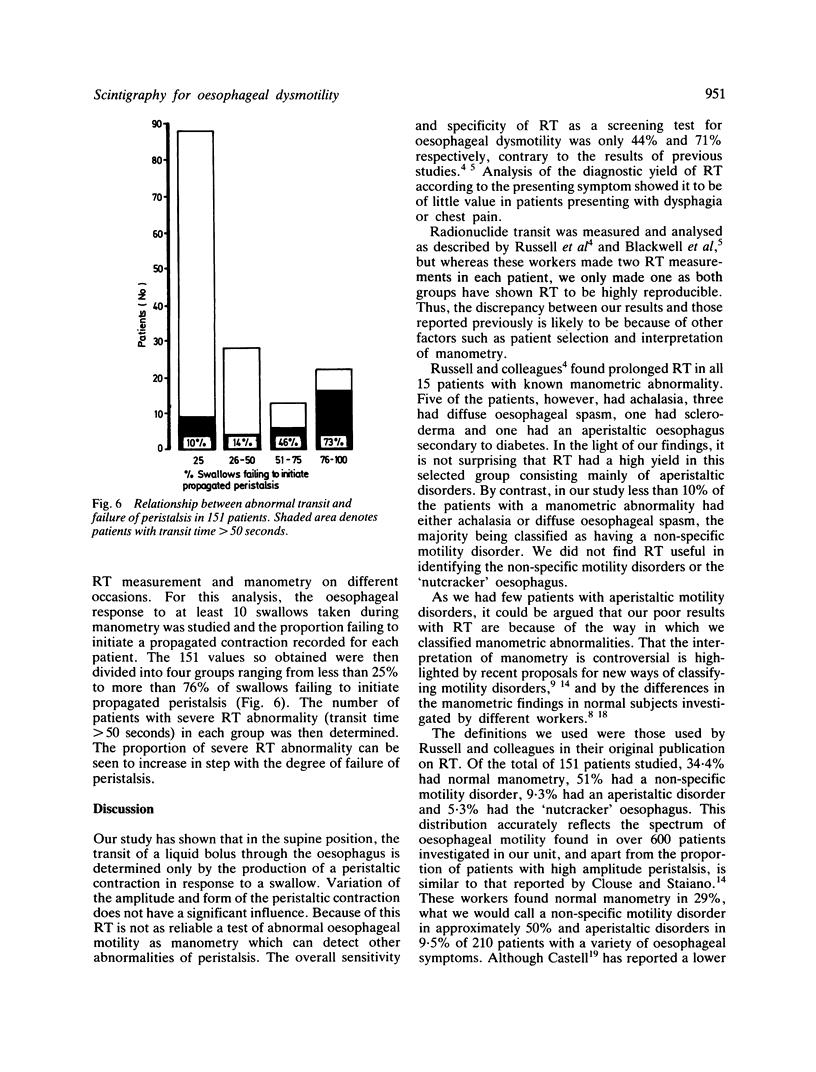
Computer analysed transit of a liquid bolus containing Tc99m (RT) was compared with manometry for the detection of oesophageal motility disorders in 151 patients with a variety of oesophageal symptoms. Manometry was abnormal in 99 of whom 44 had abnormal RT (sensitivity 44%); it was normal in 52 of whom 37 had normal RT (specificity 71%). The commonest manometric abnormalities were non-specific motility disorders characterised by abnormalities of peristaltic amplitude, waveform or baseline. Radionuclide transit was abnormal in only 32/77 (42%) of these. Achalasia, which is characterised by complete aperistalsis, was the least common diagnosis, but all five cases had abnormal RT. Simultaneous manometry and RT in 30 patients showed that the transit of a liquid bolus through the oesophagus is determined by the propagation rather than the form of the peristaltic contraction. Because non-specific motility disorders are common in clinical practice, RT is not a useful screening test for oesophageal dysmotility.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benjamin S. B., Gerhardt D. C., Castell D. O. High amplitude, peristaltic esophageal contractions associated with chest pain and/or dysphagia. Gastroenterology. 1979 Sep;77(3):478–483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin S. B., Richter J. E., Cordova C. M., Knuff T. E., Castell D. O. Prospective manometric evaluation with pharmacologic provocation of patients with suspected esophageal motility dysfunction. Gastroenterology. 1983 May;84(5 Pt 1):893–901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell J. N., Hannan W. J., Adam R. D., Heading R. C. Radionuclide transit studies in the detection of oesophageal dysmotility. Gut. 1983 May;24(5):421–426. doi: 10.1136/gut.24.5.421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bombeck C. T., Battle W. S., Nyhuss L. M. Spasm in the differential diagnosis of gastroesophageal reflux. Arch Surg. 1972 Apr;104(4):477–483. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1972.04180040091016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castell D. O. Esophageal motility disorders: the specter of the spectrum. Dig Dis Sci. 1985 Feb;30(2):188–189. doi: 10.1007/BF01308210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clouse R. E., Staiano A. Contraction abnormalities of the esophageal body in patients referred to manometry. A new approach to manometric classification. Dig Dis Sci. 1983 Sep;28(9):784–791. doi: 10.1007/BF01296900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMarino A. J., Jr Characteristics of lower esophageal sphincter function in symptomatic diffuse esophageal spasm. Gastroenterology. 1974 Jan;66(1):1–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duranceau A. C., Devroede G., LaFontaine E., Jamieson G. G. Esophageal motility in asymptomatic volunteers. Surg Clin North Am. 1983 Aug;63(4):777–786. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6109(16)43079-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. S., Cohen S. Disorders of the lower esophageal sphincter. Annu Rev Med. 1975;26:373–390. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.26.020175.002105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. S., Malmud L. S., Applegate G., Rock E., Lorber S. H. Effect of bolus composition on esophageal transit: concise communication. J Nucl Med. 1982 Oct;23(10):878–882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrington J. P., Burns T. W., Balart L. A. Chest pain and dysphagia in patients with prolonged peristaltic contractile duration of the esophagus. Dig Dis Sci. 1984 Feb;29(2):134–140. doi: 10.1007/BF01317054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. F., Demeester T. R. Twenty-four-hour pH monitoring of the distal esophagus. A quantitative measure of gastroesophageal reflux. Am J Gastroenterol. 1974 Oct;62(4):325–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjellén G., Svedberg J. B., Tibbling L. Solid bolus transit by esophageal scintigraphy in patients with dysphagia and normal manometry and radiography. Dig Dis Sci. 1984 Jan;29(1):1–5. doi: 10.1007/BF01296854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen A. M., Schlegel J. F. Motility disturbances caused by esophagitis. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1965 Nov;50(5):607–612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pope C. E., 2nd Esophageal motility--who needs it? Gastroenterology. 1978 Jun;74(6):1337–1338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell C. O., Hill L. D., Holmes E. R., 3rd, Hull D. A., Gannon R., Pope C. E., 2nd Radionuclide transit: a sensitive screening test for esophageal dysfunction. Gastroenterology. 1981 May;80(5 Pt 1):887–892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


