Abstract
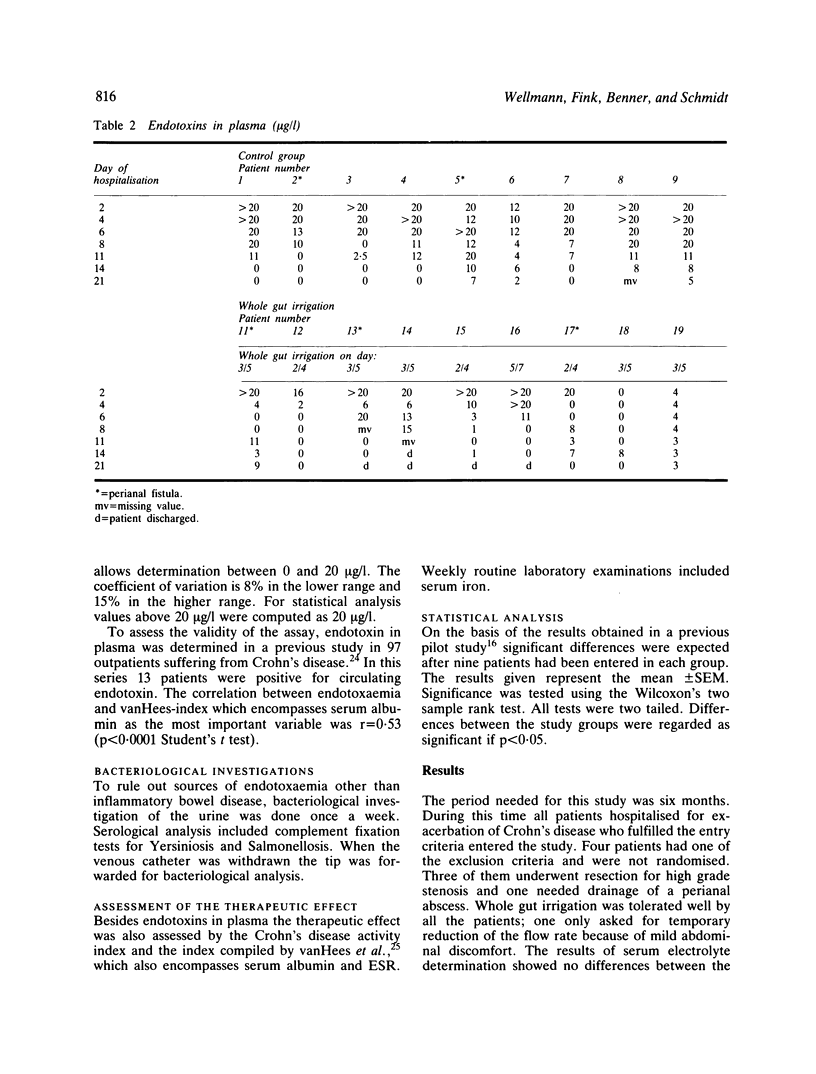
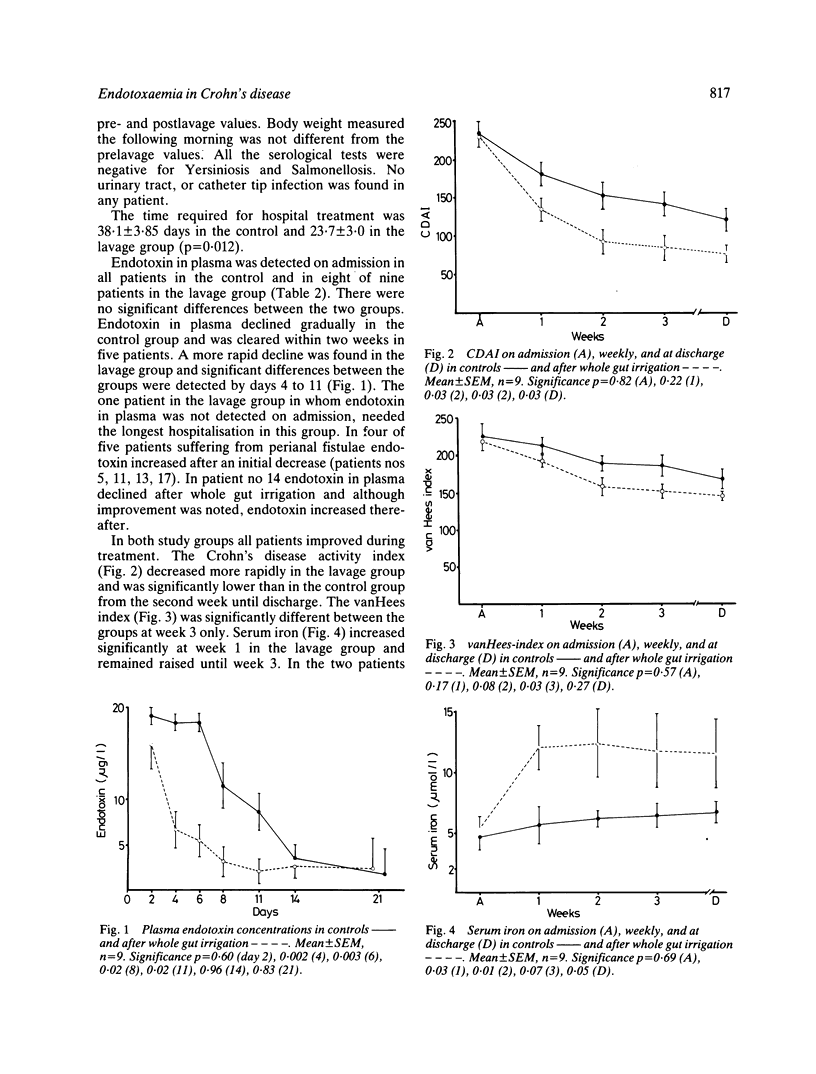
Endotoxins in plasma were monitored during treatment in 18 patients hospitalised for acute exacerbation of Crohn's disease: systemic endotoxaemia was found on admission in all but one. The patients were randomly divided into two groups: one receiving treatment with total parenteral nutrition and steroids. To decrease the absorbable endotoxin pool, the other group was additionally treated with whole gut irrigation and 5-aminosalicylic acid was added to the lavage fluid. In most of these patients endotoxaemia cleared after intestinal lavage and they needed shorter hospitalisation. Earlier improvement was also indicated by a faster decrease of the Crohn's disease activity index and vanHees index. In the group receiving conservative treatment alone, endotoxaemia was controlled within three weeks. We conclude that endotoxaemia occurs in most patients suffering from active Crohn's disease. Control of endotoxaemia after intestinal lavage suggests that systemic endotoxaemia is caused by absorption of endotoxins from the gut. Earlier improvement after whole gut irrigation indicates its beneficial effect in active Crohn's disease.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allan R., Steinberg D. M., Dixon K., Cooke W. T. Changes in the bidirectional sodium flux across the intestinal mucosa in Crohn's disease. Gut. 1975 Mar;16(3):201–204. doi: 10.1136/gut.16.3.201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambrose N. S., Johnson M., Burdon D. W., Keighley M. R. Incidence of pathogenic bacteria from mesenteric lymph nodes and ileal serosa during Crohn's disease surgery. Br J Surg. 1984 Aug;71(8):623–625. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800710821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen B. M., Solberg O. The endotoxin-liberating effect of antibiotics on meningococci in vitro. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1980 Aug;88(4):231–236. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1980.tb02633.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoki K. A study of endotoxemia in ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. I. Clinical study. Acta Med Okayama. 1978 Jun;32(2):147–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beeken W. L., Kanich R. E. Microbial flora of the upper small bowel in Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. 1973 Sep;65(3):390–397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein L. H., Frank M. S., Brandt L. J., Boley S. J. Healing of perineal Crohn's disease with metronidazole. Gastroenterology. 1980 Aug;79(2):357–365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Best W. R., Becktel J. M., Singleton J. W., Kern F., Jr Development of a Crohn's disease activity index. National Cooperative Crohn's Disease Study. Gastroenterology. 1976 Mar;70(3):439–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Miller R. A., Lacher J., Singleton J. W. Patients with active Crohn's disease have elevated serum antibodies to antigens of seven enteric bacterial pathogens. Gastroenterology. 1984 Oct;87(4):888–894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradfield J. W. Control of spillover. The importance of Kupffer-cell function in clinical medicine. Lancet. 1974 Oct 12;2(7885):883–886. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91213-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt L. J., Bernstein L. H., Boley S. J., Frank M. S. Metronidazole therapy for perineal Crohn's disease: a follow-up study. Gastroenterology. 1982 Aug;83(2):383–387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campieri M., Lanfranchi G. A., Bazzocchi G., Brignola C., Sarti F., Franzin G., Battocchia A., Labo G., Dal Monte P. R. Treatment of ulcerative colitis with high-dose 5-aminosalicylic acid enemas. Lancet. 1981 Aug 8;2(8241):270–271. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90523-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colin R., Grancher T., Lemeland J. F., Hecketsweiler P., Galmiche J. P., Le Grix A., Geffroy Y. Recherche d'une endotoxinémie dans les entéro-colites inflammatoires cryptogénétiques. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 1979 Jan;3(1):15–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Wolff S. M. Molecular basis of fever in humans. Am J Med. 1982 May;72(5):799–819. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(82)90548-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink P. C., Grunert J. H. Endotoxemia in intensive care patients: a longitudinal study with the limulus amebocyte lysate test. Klin Wochenschr. 1984 Oct 15;62(20):986–991. doi: 10.1007/BF01728429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink P. C., Lehr L., Urbaschek R. M., Kozak J. Limulus amebocyte lysate test for endotoxemia: investigations with a femtogram sensitive spectrophotometric assay. Klin Wochenschr. 1981 Mar 2;59(5):213–218. doi: 10.1007/BF01476578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper P. H., Lee E. C., Kettlewell M. G., Bennett M. K., Jewell D. P. Role of the faecal stream in the maintenance of Crohn's colitis. Gut. 1985 Mar;26(3):279–284. doi: 10.1136/gut.26.3.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris R. I., Stone P. C., Evans G. R., Stuart J. Endotoxaemia as a cause of fever in immunosuppressed patients. J Clin Pathol. 1984 Apr;37(4):467–470. doi: 10.1136/jcp.37.4.467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawker P. C., McKay J. S., Turnberg L. A. Electrolyte transport across colonic mucosa from patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 1980 Sep;79(3):508–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob A. I., Goldberg P. K., Bloom N., Degenshein G. A., Kozinn P. J. Endotoxin and bacteria in portal blood. Gastroenterology. 1977 Jun;72(6):1268–1270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juhlin L., Krause U., Shelley W. B. Endotoxin-induced microclots in ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1980;15(3):311–314. doi: 10.3109/00365528009181475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAMPSCHMIDT R. F., UPCHURCH H. F. Effects of bacteria endotoxin on plasma iron. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1962 May;110:191–193. doi: 10.3181/00379727-110-27463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsner J. B., Shorter R. G. Recent developments in nonspecific inflammatory bowel disease (second of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1982 Apr 8;306(14):837–848. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198204083061404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruis W., Schussler P., Weinzierl M., Galanos C., Eisenburg J. Circulating lipid A antibodies despite absence of systemic endotoxemia in patients with Crohn's disease. Dig Dis Sci. 1984 Jun;29(6):502–507. doi: 10.1007/BF01296269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marin M. L., Greenstein A. J., Geller S. A., Gordon R. E., Aufses A. H., Jr A freeze fracture study of Crohn's disease of the terminal ileum: changes in epithelial tight junction organization. Am J Gastroenterol. 1983 Sep;78(9):537–547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews N., Mayberry J. F., Rhodes J., Neale L., Munro J., Wensinck F., Lawson G. H., Rowland A. C., Berkhoff G. A., Barthold S. W. Agglutinins to bacteria in Crohn's disease. Gut. 1980 May;21(5):376–380. doi: 10.1136/gut.21.5.376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolan D. J. Rapid duodenal and jejunal intubation. Clin Radiol. 1979 Mar;30(2):183–185. doi: 10.1016/s0009-9260(79)80147-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolan J. P., Camara D. S. Endotoxin, sinusoidal cells, and liver injury. Prog Liver Dis. 1982;7:361–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer K. R., Duerden B. I., Holdsworth C. D. Bacteriological and endotoxin studies in cases of ulcerative colitis submitted to surgery. Gut. 1980 Oct;21(10):851–854. doi: 10.1136/gut.21.10.851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutgeerts P., Ghoos Y., Vantrappen G., Eyssen H. Ileal dysfunction and bacterial overgrowth in patients with Crohn's disease. Eur J Clin Invest. 1981 Jun;11(3):199–206. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1981.tb01841.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharon P., Stenson W. F. Enhanced synthesis of leukotriene B4 by colonic mucosa in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 1984 Mar;86(3):453–460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stumacher R. J., Kovnat M. J., McCabe W. R. Limitations of the usefulness of the Limulus assay for endotoxin. N Engl J Med. 1973 Jun 14;288(24):1261–1264. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197306142882402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundqvist T., Magnusson K. E., Sjödahl R., Stjernström I., Tagesson C. Passage of molecules through the wall of the gastrointestinal tract. II. Application of low-molecular weight polyethyleneglycol and a deterministic mathematical model for determining intestinal permeability in man. Gut. 1980 Mar;21(3):208–214. doi: 10.1136/gut.21.3.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Snick J. L., Masson P. L., Heremans J. F. The involvement of lactoferrin in the hyposideremia of acute inflammation. J Exp Med. 1974 Oct 1;140(4):1068–1084. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.4.1068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker R. I. Letter: Endotoxin and stress. Lancet. 1974 Aug 31;2(7879):527–528. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)92057-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker W. A., Isselbacher K. J. Uptake and transport of macromolecules by the intestine. Possible role in clinical disorders. Gastroenterology. 1974 Sep;67(3):531–550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellmann W., Fink P. C., Schmidt F. W. Whole-gut irrigation as antiendotoxinaemic therapy in inflammatory bowel disease. Hepatogastroenterology. 1984 Apr;31(2):91–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellmann W., Schmidt F. W. Intestinal lavage in the treatment of Crohn's disease: a pilot study. Klin Wochenschr. 1982 Apr 1;60(7):371–373. doi: 10.1007/BF01721628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willoughby C. P., Piris J., Truelove S. C. The effect of topical N-acetyl-5-aminosalicylic acid in ulcerative colitis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1980;15(6):715–719. doi: 10.3109/00365528009181520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Hees P. A., van Elteren P. H., van Lier H. J., van Tongeren J. H. An index of inflammatory activity in patients with Crohn's disease. Gut. 1980 Apr;21(4):279–286. doi: 10.1136/gut.21.4.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



