Abstract
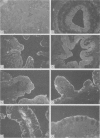
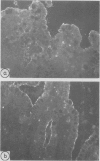
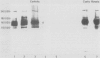
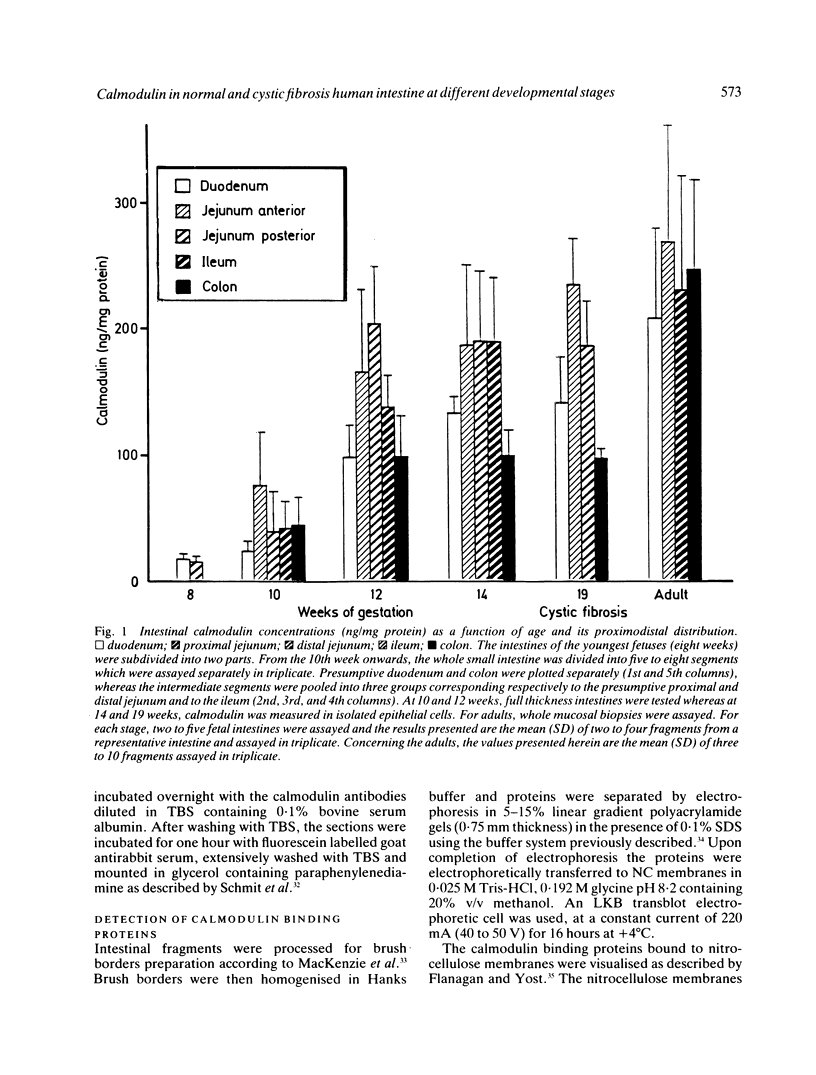
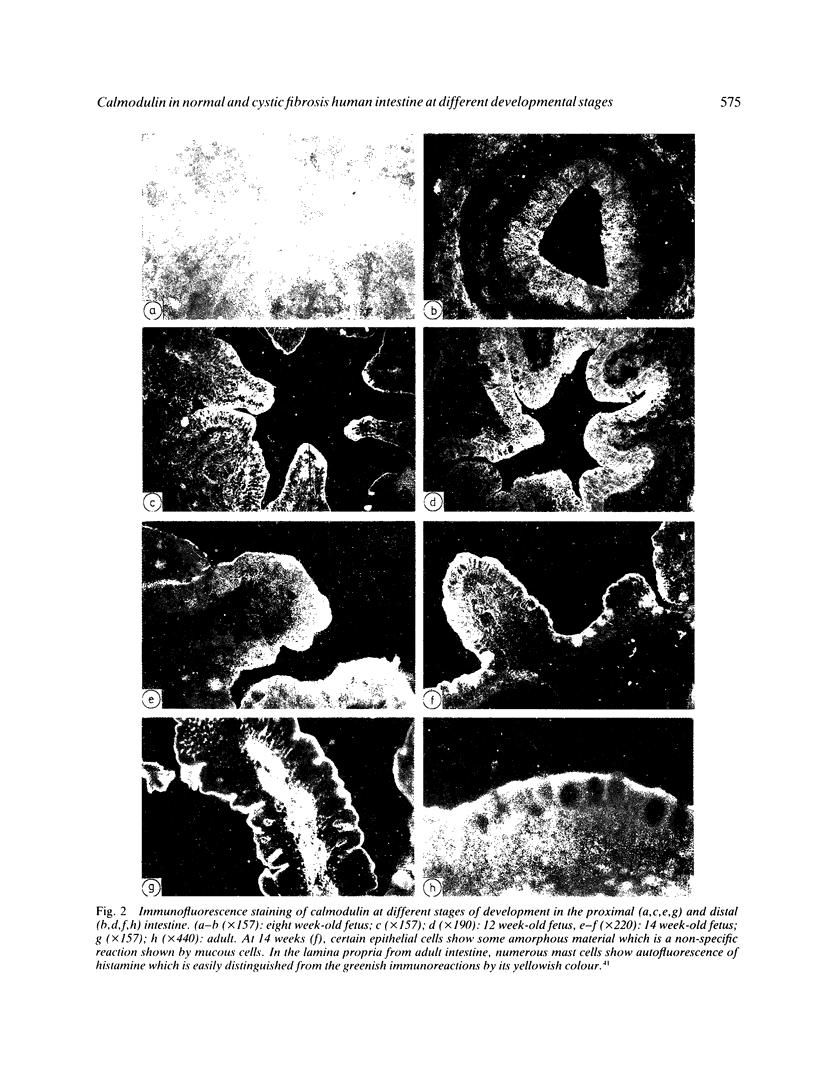
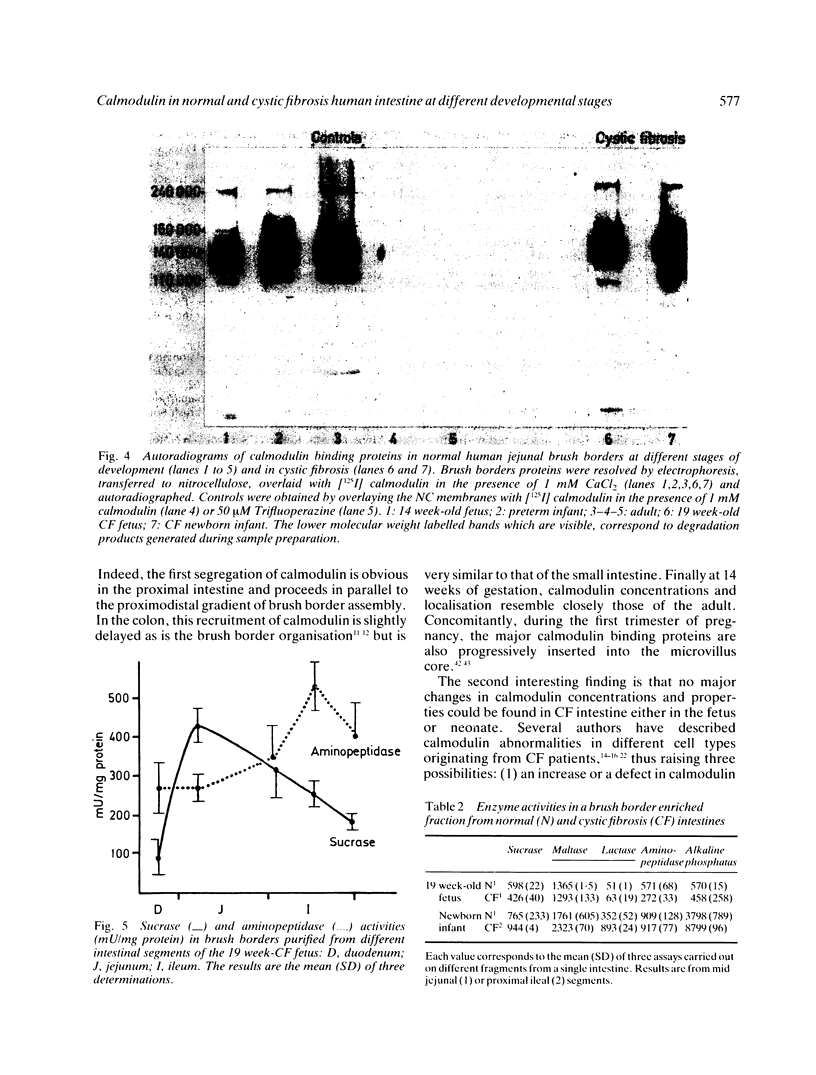
Calmodulin concentrations and localisation have been analysed as a function of development in human intestinal epithelial cells from normal and cystic fibrosis individuals. In normal fetuses up to eight weeks of gestation intestinal epithelial cells which were still undifferentiated were not immunoreactive and their calmodulin content was low. From eight weeks onwards there was a significant overall increase in calmodulin content concomitant with its segregation to the apical side of epithelial cells. At 14 weeks of gestation calmodulin concentrations and localisation closely resembled those of adults. The developmental pattern of calmodulin appeared to parallel the morphological and functional maturation of brush borders which occurs during the first trimester of pregnancy. In the intestinal epithelial cells from a 19 weeks cystic fibrosis fetus and a cystic fibrosis newborn infant neither calmodulin concentration, nor its localisation were affected. Similarly, brush border calmodulin binding proteins and enzymatic activities were similar in normal subjects and the cystic fibrosis intestine.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker S., Dann L. G. Peptidases in amniotic fluid: low values in cystic fibrosis. Lancet. 1983 Mar 26;1(8326 Pt 1):716–717. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)92014-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjerknes M., Cheng H. Methods for the isolation of intact epithelium from the mouse intestine. Anat Rec. 1981 Apr;199(4):565–574. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091990412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbarns N. J., Gosden C., Brock D. J. Microvillar peptidase activity in amniotic fluid: possible use in the prenatal diagnosis of cystic fibrosis. Lancet. 1983 Feb 12;1(8320):329–331. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91630-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Case M. Physiology. Chloride ions and cystic fibrosis. 1986 Jul 31-Aug 6Nature. 322(6078):407–407. doi: 10.1038/322407a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung W. Y. Calmodulin plays a pivotal role in cellular regulation. Science. 1980 Jan 4;207(4426):19–27. doi: 10.1126/science.6243188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotton C. U., Stutts M. J., Knowles M. R., Gatzy J. T., Boucher R. C. Abnormal apical cell membrane in cystic fibrosis respiratory epithelium. An in vitro electrophysiologic analysis. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jan;79(1):80–85. doi: 10.1172/JCI112812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Sant'Agnese P. A., Davis P. B. Research in cystic fibrosis (first of three parts). N Engl J Med. 1976 Aug 26;295(9):481–485. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197608262950905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan S. D., Yost B. Calmodulin-binding proteins: visualization by 125I-calmodulin overlay on blots quenched with Tween 20 or bovine serum albumin and poly(ethylene oxide). Anal Biochem. 1984 Aug 1;140(2):510–519. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90202-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr, Bretscher A., Weber K. Calcium control of the intestinal microvillus cytoskeleton: its implications for the regulation of microfilament organizations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6458–6462. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr, Glenney P. Comparison of Ca++-regulated events in the intestinal brush border. J Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;100(3):754–763. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.3.754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gnegy M. E., Erickson R. P., Markovac J. Increased calmodulin in cultured skin fibroblasts from patients with cystic fibrosis. Biochem Med. 1981 Dec;26(3):294–298. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(81)90004-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grand R. J., Watkins J. B., Torti F. M. Development of the human gastrointestinal tract. A review. Gastroenterology. 1976 May;70(5 PT1):790–810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirokawa N., Cheney R. E., Willard M. Location of a protein of the fodrin-spectrin-TW260/240 family in the mouse intestinal brush border. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):953–965. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90080-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe C. L., Mooseker M. S., Graves T. A. Brush-border calmodulin. A major component of the isolated microvillus core. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jun;85(3):916–923. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.3.916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishimura K., Fujita H., Ban T., Matsuda H., Sobue K., Kakiuchi S. Immunocytochemical demonstration of caldesmon (a calmodulin-binding, F-actin-interacting protein) in smooth muscle fibers and absorptive epithelial cells in the small intestine of the rat. Cell Tissue Res. 1984;235(1):207–209. doi: 10.1007/BF00213742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowlton R. G., Cohen-Haguenauer O., Van Cong N., Frézal J., Brown V. A., Barker D., Braman J. C., Schumm J. W., Tsui L. C., Buchwald M. A polymorphic DNA marker linked to cystic fibrosis is located on chromosome 7. 1985 Nov 28-Dec 4Nature. 318(6044):380–382. doi: 10.1038/318380a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacroix B., Kedinger M., Simon-Assmann P., Haffen K. Early organogenesis of human small intestine: scanning electron microscopy and brush border enzymology. Gut. 1984 Sep;25(9):925–930. doi: 10.1136/gut.25.9.925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacroix B., Kedinger M., Simon-Assmann P., Rousset M., Zweibaum A., Haffen K. Developmental pattern of brush border enzymes in the human fetal colon. Correlation with some morphogenetic events. Early Hum Dev. 1984 Feb;9(2):95–103. doi: 10.1016/0378-3782(84)90089-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacroix B., Wolff-Quenot M. J., Haffen K. Early human hand morphology: an estimation of fetal age. Early Hum Dev. 1984 Feb;9(2):127–136. doi: 10.1016/0378-3782(84)90093-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackenzie N. M., Morris B., Morris R. Protein binding to brush borders of enterocytes from the jejunum of the neonatal rat. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jan 25;755(2):204–209. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(83)90204-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangos J. A., Donnelly W. H. Isolated parotid acinar cells from patients with cystic fibrosis. Morphology and composition. J Dent Res. 1981 Jan;60(1):19–25. doi: 10.1177/00220345810600010301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maroux S., Louvard D., Baratti J. The aminopeptidase from hog intestinal brush border. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Sep 15;321(1):282–295. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(73)90083-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Means A. R., Dedman J. R. Calmodulin--an intracellular calcium receptor. Nature. 1980 May 8;285(5760):73–77. doi: 10.1038/285073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messer M., Dahlqvist A. A one-step ultramicro method for the assay of intestinal disaccharidases. Anal Biochem. 1966 Mar;14(3):376–392. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90280-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mooseker M. S., Keller T. C., 3rd, Hirokawa N. Regulation of cytoskeletal structure and contractility in the brush border. Ciba Found Symp. 1983;95:195–215. doi: 10.1002/9780470720769.ch12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mooseker M. S. Organization, chemistry, and assembly of the cytoskeletal apparatus of the intestinal brush border. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:209–241. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.001233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park R. W., Grand R. J. Gastrointestinal manifestations of cystic fibrosis: a review. Gastroenterology. 1981 Dec;81(6):1143–1161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson D. S., Brush P. J., Foulkes J. A., Sweasey D. Copper metabolism and the composition of wool in Border disease. Vet Rec. 1974 Sep 7;95(10):214–215. doi: 10.1136/vr.95.10.214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rochette-Egly C., Boschetti E., Basset P., Egly J. M. Interactions between calmodulin and immobilized phenothiazines. J Chromatogr. 1982 Jun 4;241(2):333–344. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)81758-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rochette-Egly C., Garaud J. C., Kedinger M., Haffen K. Calmodulin in epithelial intestinal cells during rat development. Experientia. 1986 Sep 15;42(9):1043–1046. doi: 10.1007/BF01940724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rochette-Egly C., Haffen K. Developmental pattern of calmodulin-binding proteins in rat jejunal epithelial cells. Differentiation. 1987;35(3):219–227. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1987.tb00172.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rupp G. M. The pathogenesis of cystic fibrosis: a proposal for calmodulin as the basic biochemical defect. Med Hypotheses. 1986 Jul;20(3):245–253. doi: 10.1016/0306-9877(86)90040-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scambler P. J., McPherson M. A., Bates G., Bradbury N. A., Dormer R. L., Williamson R. Biochemical and genetic exclusion of calmodulin as the site of the basic defect in cystic fibrosis. Hum Genet. 1987 Jul;76(3):278–282. doi: 10.1007/BF00283623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz J., Preiser H., Maestracci D., Ghosh B. K., Cerda J. J., Crane R. K. Purification of the human intestinal brush border membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Sep 27;323(1):98–112. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90434-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto-Ohshima A., Kitajima S., Sano M., Kato K., Mizutani A. Immunohistochemical appearance of calmodulin in the developing brain: a comparison with neuron specific enolase. Cell Struct Funct. 1984 Dec;9(4):337–344. doi: 10.1247/csf.9.337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro B. L., Feigal R. J., Laible N. J., Biros M. H., Warwick W. J. Doubling time alpha-aminoisobutyrate transport and calcium exchange in cultured fibroblasts from cystic fibrosis and control subjects. Clin Chim Acta. 1978 Jan 2;82(1-2):125–131. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(78)90035-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sips H. J., Claass A. H., van Dongen J. M., Willemsen R., Hoogeveen A. T., Galjaard H., Sinaasappel M., Hauri H. P., Sterchi E. E. Sucrase-isomaltase and cystic fibrosis. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1985;8(4):163–168. doi: 10.1007/BF01805427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stutts M. J., Cotton C. U., Yankaskas J. R., Cheng E., Knowles M. R., Gatzy J. T., Boucher R. C. Chloride uptake into cultured airway epithelial cells from cystic fibrosis patients and normal individuals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6677–6681. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh M. J., Liedtke C. M. Chloride and potassium channels in cystic fibrosis airway epithelia. 1986 Jul 31-Aug 6Nature. 322(6078):467–470. doi: 10.1038/322467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R., Woodward S., Leppert M., O'Connell P., Hoff M., Herbst J., Lalouel J. M., Dean M., Vande Woude G. A closely linked genetic marker for cystic fibrosis. 1985 Nov 28-Dec 4Nature. 318(6044):382–384. doi: 10.1038/318382a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf P., Hall C., Kilbourn J. P. Demonstration of calcitonin and calmodulin by immunoperoxidase in the cystic fibrosis lung. Chest. 1986 Mar;89(3):327–330. doi: 10.1378/chest.89.3.327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweibaum A., Triadou N., Kedinger M., Augeron C., Robine-Léon S., Pinto M., Rousset M., Haffen K. Sucrase-isomaltase: a marker of foetal and malignant epithelial cells of the human colon. Int J Cancer. 1983 Oct 15;32(4):407–412. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910320403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]