Abstract
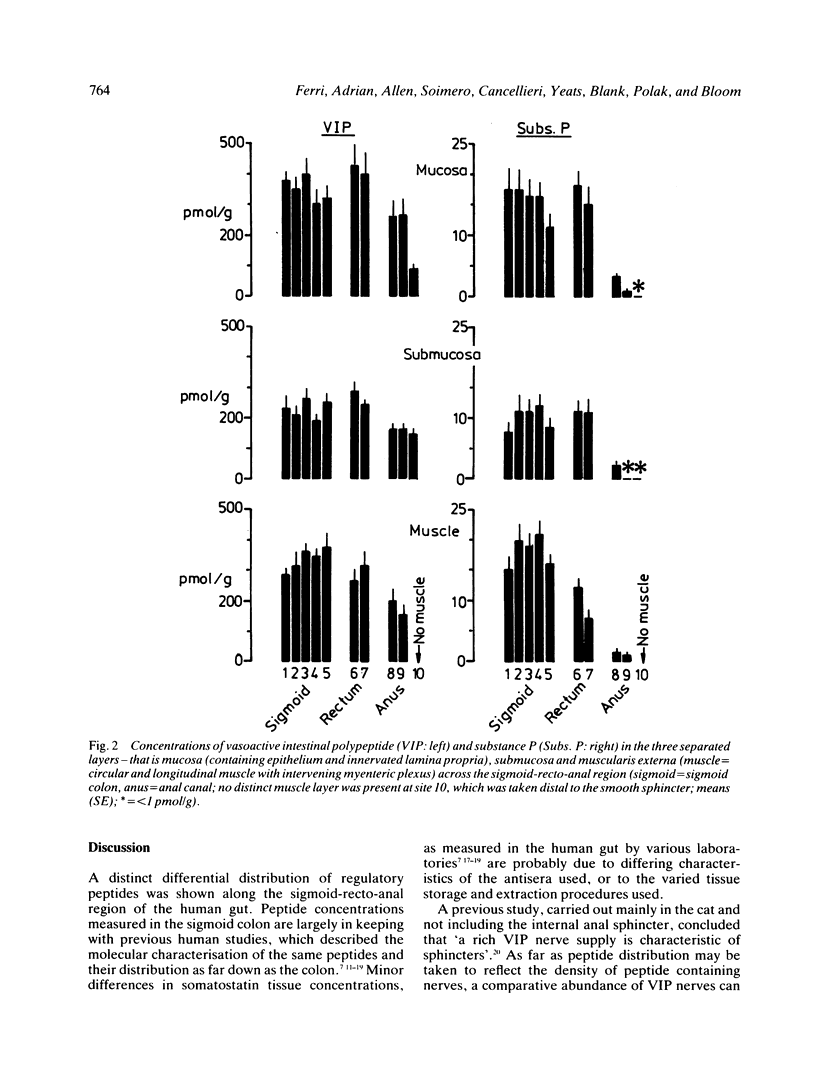
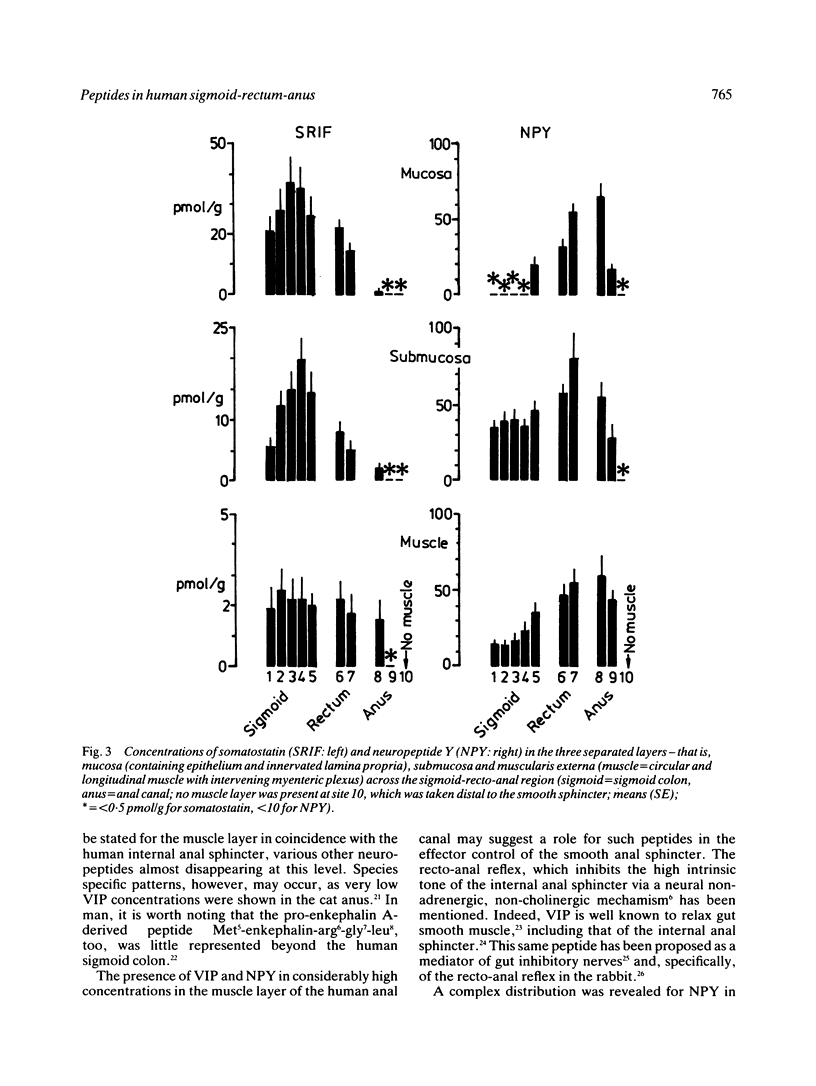
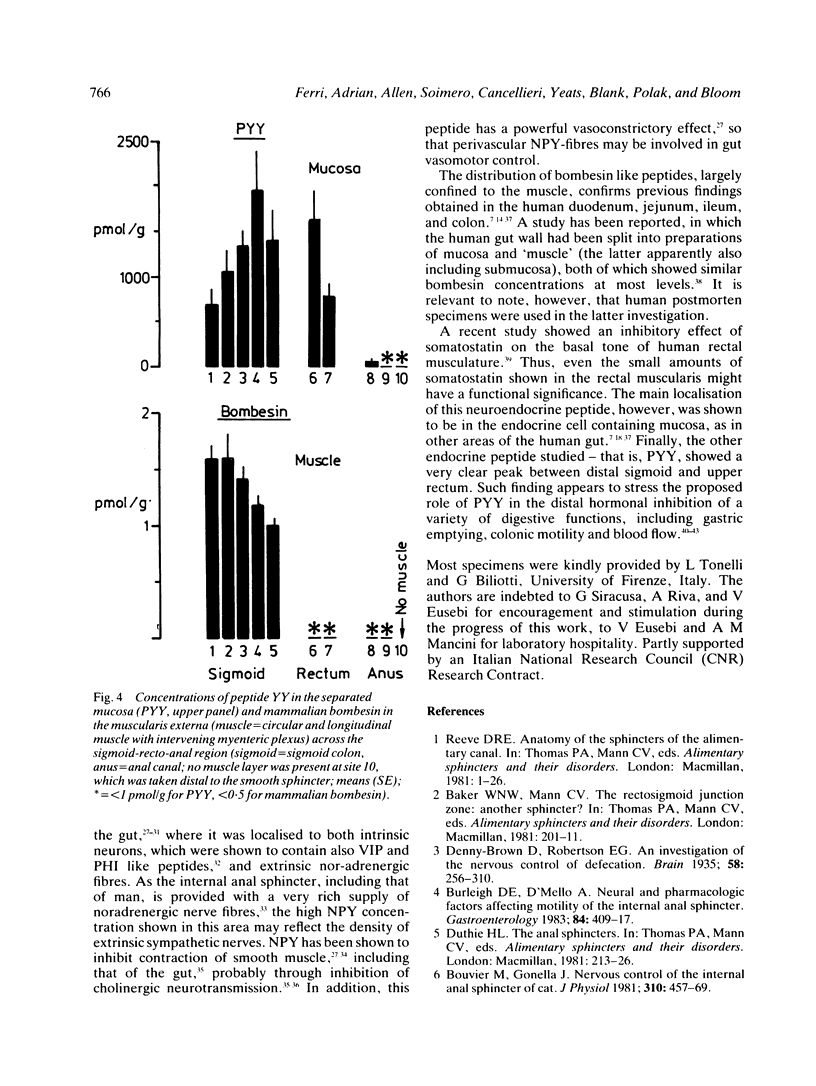
The distribution of regulatory peptides was studied in the separated mucosa, submucosa and muscularis externa taken at 10 sampling sites encompassing the whole human sigmoid colon (five sites), rectum (two sites), and anal canal (three sites). Consistently high concentrations of VIP were measured in the muscle layer at most sites (proximal sigmoid: 286 (16) pmol/g, upper rectum: 269 (17), a moderate decrease being found in the distal smooth sphincter (151 (30) pmol/g). Values are expressed as mean (SE). Conversely, substance P concentrations showed an obvious decline in the recto-anal muscle (mid sigmoid: 19 (2.0) pmol/g, distal rectum: 7.1 (1.3), upper anal canal: 1.6 (0.6)). Somatostatin was mainly present in the sigmoid mucosa and submucosa (37 (9.3) and 15 (3.5) pmol/g, respectively) and showed low, but consistent concentrations in the muscle (mid sigmoid: 2.2 (0.7) pmol/g, upper anal canal: 1.5 (0.8]. Starting in the distal sigmoid colon, a distinct peak of tissue NPY was revealed, which was most striking in the muscle (of mid sigmoid: 16 (3.9) pmol/g, upper rectum: 47 (7.8), anal sphincter: 58 (14)). Peptide YY was confined to the mucosa and showed an earlier peak (upper sigmoid: 709 (186) pmol/g, mid-distal sigmoid: 1965 (484)). A clear differential distribution of regulatory peptides was thus shown in the region studied. A possible role is suggested for NPY and VIP containing nerves in the effector control of the human internal anal sphincter.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian T. E., Ferri G. L., Bacarese-Hamilton A. J., Fuessl H. S., Polak J. M., Bloom S. R. Human distribution and release of a putative new gut hormone, peptide YY. Gastroenterology. 1985 Nov;89(5):1070–1077. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(85)90211-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian T. E., Savage A. P., Sagor G. R., Allen J. M., Bacarese-Hamilton A. J., Tatemoto K., Polak J. M., Bloom S. R. Effect of peptide YY on gastric, pancreatic, and biliary function in humans. Gastroenterology. 1985 Sep;89(3):494–499. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(85)90442-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen J. M., Adrian T. E., Tatemoto K., Polak J. M., Hughes J., Bloom S. R. Two novel related peptides, neuropeptide Y (NPY) and peptide YY (PYY) inhibit the contraction of the electrically stimulated mouse vas deferens. Neuropeptides. 1982 Dec;3(2):71–77. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(82)90001-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen J. M., Hughes J., Bloom S. R. Presence, distribution, and pharmacological effects of neuropeptide Y in mammalian gastrointestinal tract. Dig Dis Sci. 1987 May;32(5):506–512. doi: 10.1007/BF01296034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen J. M., Yeats J. C., Adrian T. E., Bloom S. R. Radioimmunoassay of neuropeptide Y. Regul Pept. 1984 Jan;8(1):61–70. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(84)90029-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alumets J., Schaffalitzky de Muckadell O., Fahrenkrug J., Sundler F., Håkanson R., Uddman R. A rich VIP nerve supply is characteristic of sphincters. Nature. 1979 Jul 12;280(5718):155–156. doi: 10.1038/280155a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldissera F. G., Holst J. J., Jensen S. L., Krarup T. Distribution and molecular forms of peptides containing somatostatin immunodeterminants in extracts from the entire gastrointestinal tract of man and pig. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jan 28;838(1):132–143. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(85)90259-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biancani P., Walsh J., Behar J. Vasoactive intestinal peptide: a neurotransmitter for relaxation of the rabbit internal anal sphincter. Gastroenterology. 1985 Oct;89(4):867–874. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(85)90585-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouvier M., Gonella J. Nervous control of the internal anal sphincter of the cat. J Physiol. 1981 Jan;310:457–469. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodin E., Sjölund K., Håkanson R., Sundler F. Substance P-containing nerve fibers are numerous in human but not in feline intestinal mucosa. Gastroenterology. 1983 Sep;85(3):557–564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burleigh D. E., D'Mello A. Neural and pharmacologic factors affecting motility of the internal anal sphincter. Gastroenterology. 1983 Feb;84(2):409–417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekblad E., Håkanson R., Sundler F. VIP and PHI coexist with an NPY-like peptide in intramural neurones of the small intestine. Regul Pept. 1984 Dec;10(1):47–55. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(84)90052-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahrenkrug J., Haglund U., Jodal M., Lundgren O., Olbe L., de Muckadell O. B. Nervous release of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in the gastrointestinal tract of cats: possible physiological implications. J Physiol. 1978 Nov;284:291–305. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferri G. L., Adrian T. E., Ghatei M. A., O'Shaughnessy D. J., Probert L., Lee Y. C., Buchan A. M., Polak J. M., Bloom S. R. Tissue localization and relative distribution of regulatory peptides in separated layers from the human bowel. Gastroenterology. 1983 Apr;84(4):777–786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferri G. L., Adrian T. E., Soimero L., McGregor G. P., Ghatei M. A., Morreale R. A., Rebecchi L., Tonelli L., Polak J. M., Bloom S. R. Regulatory peptide distribution in separated layers of the human jejunum. Digestion. 1987;37(1):15–21. doi: 10.1159/000199482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferri G. L. Human gut neuroanatomy: methodology for a quantitative analysis of nerve elements and neurotransmitter diversity in the human "enteric nervous system". Basic Appl Histochem. 1988;32(1):117–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferri G. L., Morreale R. A., Soimero L., Biliotti G., Dockray G. J. Intramural distribution of Met5-enkephalin-Arg6-Gly7-Leu8 in sphincter regions of the human gut. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Mar 9;74(3):304–308. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90314-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furness J. B., Costa M., Emson P. C., Håkanson R., Moghimzadeh E., Sundler F., Taylor I. L., Chance R. E. Distribution, pathways and reactions to drug treatment of nerves with neuropeptide Y- and pancreatic polypeptide-like immunoreactivity in the guinea-pig digestive tract. Cell Tissue Res. 1983;234(1):71–92. doi: 10.1007/BF00217403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabella G. Innervation of the gastrointestinal tract. Int Rev Cytol. 1979;59:129–193. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61662-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greeley G. H., Jr, Partin M., Spannagel A., Dinh T., Hill F. L., Trowbridge J., Salter M., Chuo H. F., Thompson J. C. Distribution of bombesin-like peptides in the alimentary canal of several vertebrate species. Regul Pept. 1986 Dec 22;16(2):169–181. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(86)90060-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzer P., Bucsics A., Saria A., Lembeck F. A study of the concentrations of substance P and neurotensin in the gastrointestinal tract of various mammals. Neuroscience. 1982;7(11):2919–2924. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(82)90114-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keast J. R., Furness J. B., Costa M. Somatostatin in human enteric nerves. Distribution and characterization. Cell Tissue Res. 1984;237(2):299–308. doi: 10.1007/BF00217149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y., Shiosaka S., Emson P. C., Powell J. F., Smith A. D., Tohyama M. Neuropeptide Y-like immunoreactive structures in the rat stomach with special reference to the noradrenaline neuron system. Gastroenterology. 1985 Jul;89(1):118–126. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(85)90752-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llewellyn-Smith I. J., Furness J. B., Murphy R., O'Brien P. E., Costa M. Substance P-containing nerves in the human small intestine. Distribution, ultrastructure, and characterization of the immunoreactive peptide. Gastroenterology. 1984 Mar;86(3):421–435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Tatemoto K., Terenius L., Hellström P. M., Mutt V., Hökfelt T., Hamberger B. Localization of peptide YY (PYY) in gastrointestinal endocrine cells and effects on intestinal blood flow and motility. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(14):4471–4475. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.14.4471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Terenius L., Hökfelt T., Martling C. R., Tatemoto K., Mutt V., Polak J., Bloom S., Goldstein M. Neuropeptide Y (NPY)-like immunoreactivity in peripheral noradrenergic neurons and effects of NPY on sympathetic function. Acta Physiol Scand. 1982 Dec;116(4):477–480. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1982.tb07171.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGregor G. P., Bishop A. E., Blank M. A., Christofides N. D., Yiangou Y., Polak J. M., Bloom S. R. Comparative distribution of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP), substance P and PHI in the enteric sphincters of the cat. Experientia. 1984 May 15;40(5):469–471. doi: 10.1007/BF01952390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappas T. N., Debas H. T., Chang A. M., Taylor I. L. Peptide YY release by fatty acids is sufficient to inhibit gastric emptying in dogs. Gastroenterology. 1986 Dec;91(6):1386–1389. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90191-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penman E., Wass J. A., Butler M. G., Penny E. S., Price J., Wu P., Rees L. H. Distribution and characterisation of immunoreactive somatostatin in human gastrointestinal tract. Regul Pept. 1983 Sep;7(1):53–65. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(83)90281-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price J., Penman E., Wass J. A., Rees L. H. Bombesin-like immunoreactivity in human gastrointestinal tract. Regul Pept. 1984 Sep;9(1-2):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(84)90002-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundler F., Moghimzadeh E., Håkanson R., Ekelund M., Emson P. Nerve fibers in the gut and pancreas of the rat displaying neuropeptide-Y immunoreactivity. Intrinsic and extrinsic origin. Cell Tissue Res. 1983;230(3):487–493. doi: 10.1007/BF00216194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki T., Nakaya M., Itoh Z., Tatemoto K., Mutt V. Inhibition of interdigestive contractile activity in the stomach by peptide YY in Heidenhain pouch dogs. Gastroenterology. 1983 Jul;85(1):114–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley J., Owyang C. Neuropeptide Y inhibits cholinergic transmission in the isolated guinea pig colon: mediation through alpha-adrenergic receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):2047–2051. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.2047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


