Abstract
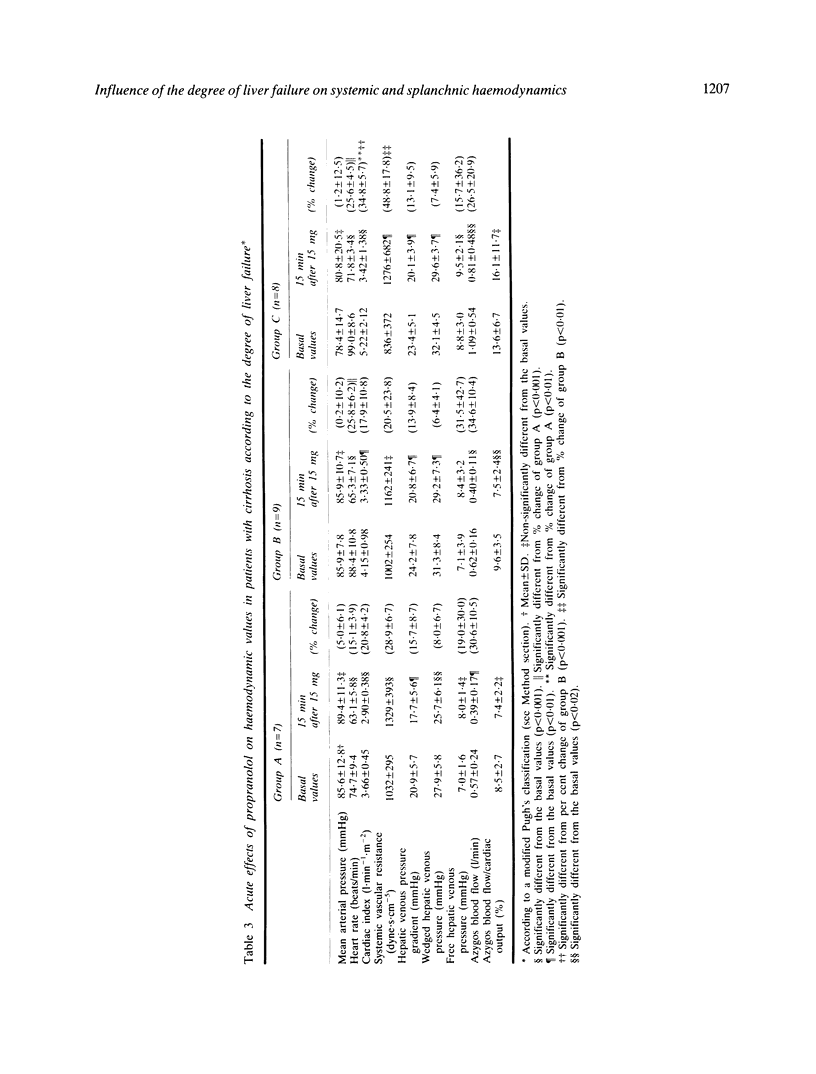
Systemic and splanchnic haemodynamics were studied in patients with cirrhosis who had been classified in three groups (A, B, and C) according to the degree of liver failure (modified Pugh's classification). In patients of group A, cardiac index was significantly lower than that of group C and systemic vascular resistance was higher, but not significantly so, than that of patients with liver failure. Wedged hepatic venous pressure was significantly lower in the former group than in the latter. In patients in group B, corresponding values fell between those of groups A and C. Azygos blood flow averaged 0.477 +/- 0.242 l/min (mean +/- SD) in group A and it was significantly lower than in groups B and C (0.642 +/- 0.224 and 1.061 +/- 0.476 l/min, respectively). In the three groups, acute administration of propranolol induced statistically significant changes in systemic and splanchnic haemodynamics. In patients of group C but not of group B, the mean value of azygos blood flow after propranolol remained significantly higher than in group A. Moreover, the fraction of azygos blood flow to cardiac output decreased in groups A and B while slightly increased in group C. This study shows that in patients with cirrhosis, the degree of liver failure may be a determinant for the haemodynamic responses to drugs acting on portal hypertension.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aoki N., Gerber M. A., Thung S. N., Chen M. L., Christman J. K., Price P. M., Flordellis C. S., Acs G. Ultrastructural studies of fibroblasts transfected with hepatitis B virus DNA. Hepatology. 1984 Jan-Feb;4(1):84–89. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840040115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardi M., Trevisani F., Santini C., Zoli G., Baraldini M., Ligabue A., Gasbarrini G. Plasma norepinephrine, weak neurotransmitters, and renin activity during active tilting in liver cirrhosis: relationship with cardiovascular homeostasis and renal function. Hepatology. 1983 Jan-Feb;3(1):56–64. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840030109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchet L., Lebrec D. Changes in splanchnic blood flow in portal hypertensive rats. Eur J Clin Invest. 1982 Aug;12(4):327–330. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1982.tb02240.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosch J., Mastai R., Kravetz D., Bruix J., Rigau J., Rodés J. Measurement of azygos venous blood flow in the evaluation of portal hypertension in patients with cirrhosis. Clinical and haemodynamic correlations in 100 patients. J Hepatol. 1985;1(2):125–139. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(85)80761-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosch J., Masti R., Kravetz D., Bruix J., Gaya J., Rigau J., Rodes J. Effects of propranolol on azygos venous blood flow and hepatic and systemic hemodynamics in cirrhosis. Hepatology. 1984 Nov-Dec;4(6):1200–1205. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840040617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer T. D., Triger D. R., Horisawa M., Redeker A. G., Reynolds T. B. Direct transhepatic measurement of portal vein pressure using a thin needle. Comparison with wedged hepatic vein pressure. Gastroenterology. 1977 Apr;72(4 Pt 1):584–589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braillon A., Calès P., Jirón M. I., Lebrec D. Estimation du débit sanguin des anastomoses porto-caves supérieures par la mesure du débit sanguin azygos chez les malades atteints de cirrhose alcoolique. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 1984 Jan;8(1):47–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calès P., Braillon A., Jirón M. I., Lebrec D. Superior portosystemic collateral circulation estimated by azygos blood flow in patients with cirrhosis. Lack of correlation with oesophageal varices and gastrointestinal bleeding. Effect of propranolol. J Hepatol. 1985;1(1):37–46. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(85)80066-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman J. C., Jennings G. L., McLean A. J., Mignot P. R., Dudley F. J. Propranolol in decompensated alcoholic cirrhosis. Lancet. 1982 Nov 6;2(8306):1040–1041. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)90067-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henriksen J. H., Christensen N. J., Ring-Larsen H. Noradrenaline and adrenaline concentrations in various vascular beds in patients with cirrhosis. Relation to haemodynamics. Clin Physiol. 1981 Jun;1(3):293–304. doi: 10.1111/j.1475-097x.1981.tb00898.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt S., Vaamonde C. A., Rattassi T., Berian G., Said S. I., Papper S. Circulating levels of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in liver disease. Arch Intern Med. 1979 Sep;139(9):994–996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hörtnagl H., Singer E. A., Lenz K., Kleinberger G., Lochs H. Substance P is markedly increased in plasma of patients with hepatic coma. Lancet. 1984 Mar 3;1(8375):480–483. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92851-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwatsuki S., Reynolds T. B. Effect of increased intraabdominal pressure on hepatic hemodynamics in patients with chronic liver disease and portal hypertension. Gastroenterology. 1973 Aug;65(2):294–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOWALSKI H. J., ABELMANN W. H. The cardiac output at rest in Laennec's cirrhosis. J Clin Invest. 1953 Oct;32(10):1025–1033. doi: 10.1172/JCI102813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEEVY C. M., ZINKE M., BABER J., CHEY W. Y. Observations on the influence of medical therapy on portal hypertension in hepatic cirrhosis. Ann Intern Med. 1958 Oct;49(4):837–851. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-49-4-837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebrec D., Bataille C., Bercoff E., Valla D. Hemodynamic changes in patients with portal venous obstruction. Hepatology. 1983 Jul-Aug;3(4):550–553. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840030412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebrec D., Blanchet L. Effect of two models of portal hypertension on splanchnic organ blood flow in the rat. Clin Sci (Lond) 1985 Jan;68(1):23–28. doi: 10.1042/cs0680023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebrec D., Goldfarb G., Degott C., Rueff B., Benhamou J. P. Transvenous liver biopsy: an experience based on 1000 hepatic tissue samplings with this procedure. Gastroenterology. 1982 Aug;83(2):338–340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebrec D., Hillon P., Muńoz C., Goldfarb G., Nouel O., Benhamou J. P. The effect of propranolol on portal hypertension in patients with cirrhosis: a hemodynamic study. Hepatology. 1982 Sep-Oct;2(5):523–527. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840020502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nespoli A., Bevilacqua G., Staudacher C., Rossi N., Salerno F., Castelli M. R. Pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy and hyperdynamic syndrome in cirrhosis. Role of false neurotransmitters. Arch Surg. 1981 Sep;116(9):1129–1138. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1981.01380210013003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh R. N., Murray-Lyon I. M., Dawson J. L., Pietroni M. C., Williams R. Transection of the oesophagus for bleeding oesophageal varices. Br J Surg. 1973 Aug;60(8):646–649. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800600817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel J. H., Goldwyn R. M., Farrell E. J., Gallin P., Friedman H. P. Hyperdynamic states and the physiologic determinants of survival in patients with cirrhosis and portal hypertension. Arch Surg. 1974 Mar;108(3):282–292. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1974.01350270016004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valla D., Bercoff E., Menu Y., Bataille C., Lebrec D. Discrepancy between wedged hepatic venous pressure and portal venous pressure after acute propranolol administration in patients with alcoholic cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 1984 Jun;86(6):1400–1403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valla D., Poynard T., Bercoff E., Bataille C., Goldfarb G., Lebrec D. Le syndrome d'hypercinésie circulatoire systémique chez les malades atteints de cirrhose. Relations avec l'insuffisance hépatocellulaire et l'hypertension portale. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 1984 Apr;8(4):321–324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


