Abstract
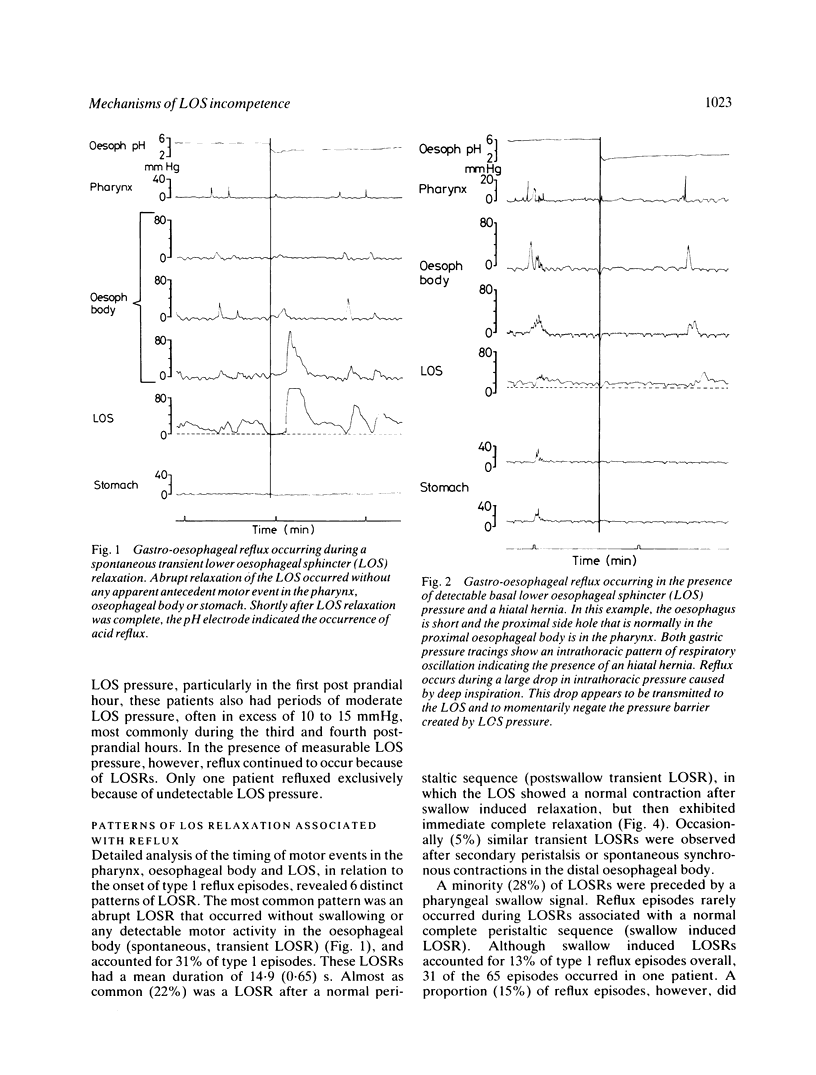
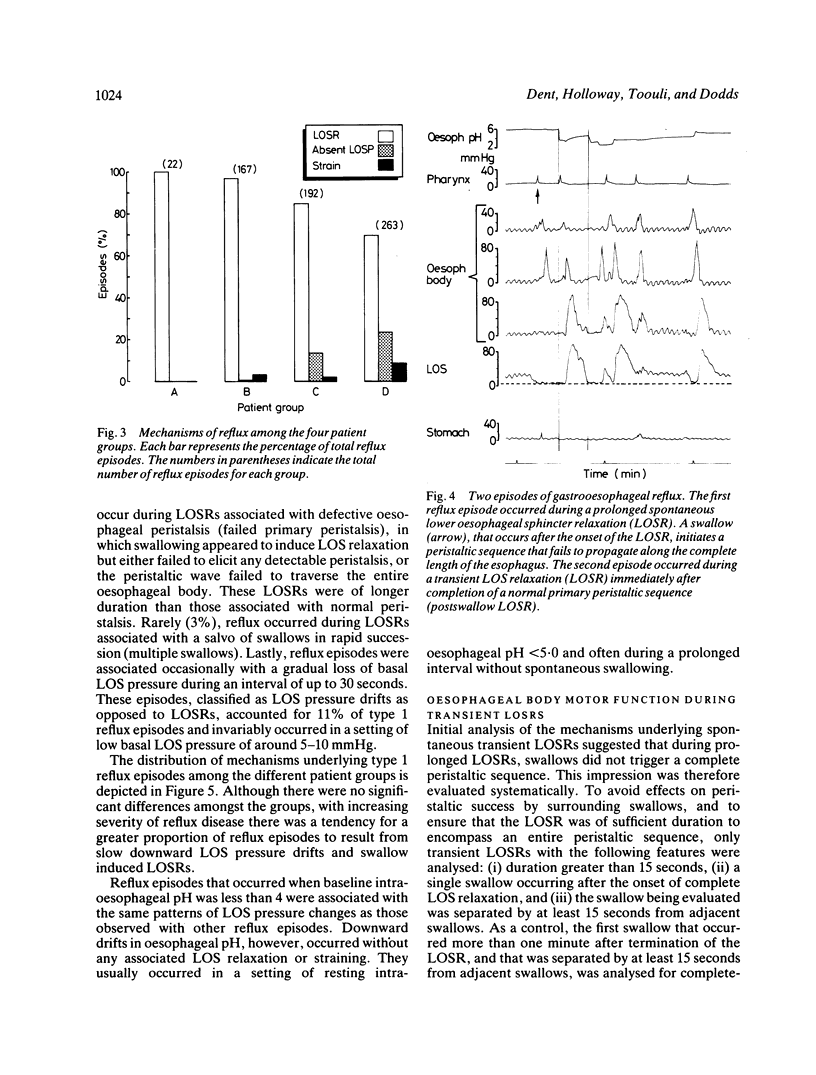
Patterns of lower oesophageal sphincter (LOS) function associated with the onset of 644 reflux episodes were recorded and analysed in 67 patients referred for evaluation of gastro-oesophageal reflux (GOR). Patients were studied recumbent, for one hour before and four hours after a standard meal. Transient LOS relaxation was the most prevalent mechanism and overall accounted for 82% of reflux episodes. With increasing severity of oesophagitis, absent basal LOS pressure became a progressively more common mechanism, accounting for 23% of episodes in the patients with severe oesophagitis. Patients commonly exhibited more than one mechanism. The timing of most (69%) LOS relaxations associated with reflux was not compatible with triggering by swallowing. Prolonged transient LOS relaxations were associated with inhibition of oesophageal peristalsis suggesting that this response is produced by neural inhibition. This study suggests the primary importance of transient LOS relaxations as the cause of GOR across the spectrum of severity of reflux disease.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldi F., Ferrarini F., Balestra R., Borioni D., Longanesi A., Miglioli M., Barbara L. Oesophageal motor events at the occurrence of acid reflux and during endogenous acid exposure in healthy subjects and in patients with oesophagitis. Gut. 1985 Apr;26(4):336–341. doi: 10.1136/gut.26.4.336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behar J., Biancani P., Sheahan D. G. Evaluation of esophageal tests in the diagnosis of reflux esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 1976 Jul;71(1):9–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Harris L. D. Does hiatus hernia affect competence of the gastroesophageal sphincter? N Engl J Med. 1971 May 13;284(19):1053–1056. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197105132841902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corazziari E., Bontempo I., Anzini F., Torsoli A. Motor activity of the distal oesophagus and gastrooesophageal reflux. Gut. 1984 Jan;25(1):7–13. doi: 10.1136/gut.25.1.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dent J. A new technique for continuous sphincter pressure measurement. Gastroenterology. 1976 Aug;71(2):263–267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dent J., Dodds W. J., Friedman R. H., Sekiguchi T., Hogan W. J., Arndorfer R. C., Petrie D. J. Mechanism of gastroesophageal reflux in recumbent asymptomatic human subjects. J Clin Invest. 1980 Feb;65(2):256–267. doi: 10.1172/JCI109667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dent J., Dodds W. J., Sekiguchi T., Hogan W. J., Arndorfer R. C. Interdigestive phasic contractions of the human lower esophageal sphincter. Gastroenterology. 1983 Mar;84(3):453–460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodds W. J., Dent J., Hogan W. J., Helm J. F., Hauser R., Patel G. K., Egide M. S. Mechanisms of gastroesophageal reflux in patients with reflux esophagitis. N Engl J Med. 1982 Dec 16;307(25):1547–1552. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198212163072503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodds W. J., Stewart E. T., Hodges D., Zboralske F. F. Movement of the feline esophagus associated with respiration and peristalsis. An evaluation using tantalum markers. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jan;52(1):1–13. doi: 10.1172/JCI107152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. S., Malmud L. S., Roberts G. S., Lobis I. F. The lower esophageal sphincter as a barrier to gastroesophageal reflux. Gastroenterology. 1977 Jan;72(1):19–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman M. I. Letter: Do refluxers have sick sphincters? N Engl J Med. 1974 Jan 17;290(3):167–167. doi: 10.1056/nejm197401172900324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway R. H., Hongo M., Berger K., McCallum R. W. Gastric distention: a mechanism for postprandial gastroesophageal reflux. Gastroenterology. 1985 Oct;89(4):779–784. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(85)90572-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyams J. S., Leichtner A. M., Zamett L. O., Walters J. K. Effect of metoclopramide on prolonged intraesophageal pH testing in infants with gastroesophageal reflux. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1986 Sep-Oct;5(5):716–720. doi: 10.1097/00005176-198609000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krejs G. J., Seefeld U., Brändli H. H., Bron B. A., Caro G., Schmid P., Blum A. L. Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease: correlation of subjective symptoms with 7 objective oesophageal function tests. Acta Hepatogastroenterol (Stuttg) 1976 Apr;23(2):130–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin C. J., Patrikios J., Dent J. Abolition of gas reflux and transient lower esophageal sphincter relaxation by vagal blockade in the dog. Gastroenterology. 1986 Oct;91(4):890–896. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90691-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittal R. K., McCallum R. W. Characteristics of transient lower esophageal sphincter relaxation in humans. Am J Physiol. 1987 May;252(5 Pt 1):G636–G641. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1987.252.5.G636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr W. C., Robinson M. G., Johnson L. F. Acid clearance during sleep in the pathogenesis of reflux esophagitis. Dig Dis Sci. 1981 May;26(5):423–427. doi: 10.1007/BF01313584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson W. G., Rattan S., Goyal R. K. Experimental induction of isolated lower esophageal sphincter relaxation in anesthetized opossums. J Clin Invest. 1986 Apr;77(4):1187–1193. doi: 10.1172/JCI112420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pope C. E., 2nd A dynamic test of sphincter strength: its application to the lower esophageal sphincter. Gastroenterology. 1967 May;52(5):779–786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanciu C., Hoare R. C., Bennett J. R. Correlation between manometric and pH tests for gastro-oesophageal reflux. Gut. 1977 Jul;18(7):536–540. doi: 10.1136/gut.18.7.536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WANKLING W. J., WARRIAN W. G., LIND J. F. THE GASTROESOPHAGEAL SPHINCTER IN HIATUS HERNIA. Can J Surg. 1965 Jan;8:61–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


