Abstract
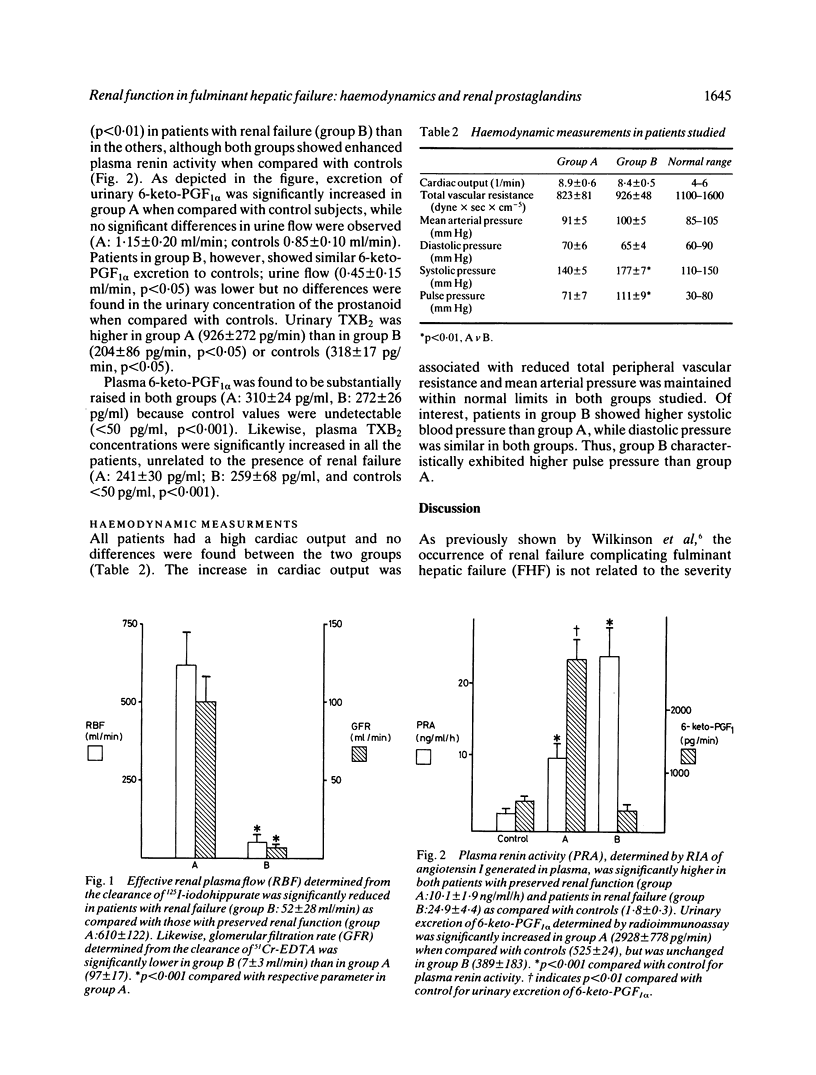
Eighteen patients with fulminant liver failure were studied, 10 with normal renal function (group A) and eight with renal failure (group B, plasma creatinine greater than 200 mumol/l). Renal function was assessed by standard clearance techniques and patients in group B had a marked reduction compared with group A in both renal plasma flow and glomerular filtration rate. Raised plasma renin activity was observed in both groups, but levels in group B were significantly higher than in group A. Renal prostacyclin production was estimated by radioimmunoassay (RIA) of 6-keto-prostaglandin F1 alpha in urine, and the excretion rate was markedly increased in group A as compared with nine healthy controls, but was low in group B. The plasma concentrations of 6-keto-prostaglandin F1 alpha and thromboxane B2 were similar in groups A and B and were both significantly higher than in controls. Haemodynamic measurements showed a high cardiac output with low vascular resistance and mean arterial pressure within normal limits in both groups. The pulse pressure, however, was significantly higher in group B than in group A. In conclusion, patients in FHF with renal failure have marked renal vasoconstriction with increased plasma renin activity and reduced renal prostaglandin excretion indicative of an imbalance between vasoactive forces.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arroyo V., Planas R., Gaya J., Deulofeu R., Rimola A., Pérez-Ayuso R. M., Rivera F., Rodés J. Sympathetic nervous activity, renin-angiotensin system and renal excretion of prostaglandin E2 in cirrhosis. Relationship to functional renal failure and sodium and water excretion. Eur J Clin Invest. 1983 Jun;13(3):271–278. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1983.tb00100.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardi M., Wilkinson S. P., Wernze H., Spech H. J., Müller G., Poston L., Williams R. The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in fulminant hepatic failure. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1983 May;18(3):369–375. doi: 10.3109/00365528309181609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer T. D., Zia P., Reynolds T. B. Effect of indomethacin and prostaglandin A1 on renal function and plasma renin activity in alcoholic liver disease. Gastroenterology. 1979 Aug;77(2):215–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn M. J. Role of eicosanoids in the control of renal function in severe hepatic disease. Gastroenterology. 1984 Dec;87(6):1392–1395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dusting G. J., Moncada S., Vane J. R. Prostacyclin: its biosynthesis, actions, and clinical potential. Adv Prostaglandin Thromboxane Leukot Res. 1982;10:59–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FitzGerald G. A., Pedersen A. K., Patrono C. Analysis of prostacyclin and thromboxane biosynthesis in cardiovascular disease. Circulation. 1983 Jun;67(6):1174–1177. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.67.6.1174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarner C., Colina I., Guarner F., Corzo J., Prieto J., Vilardell F. Renal prostaglandins in cirrhosis of the liver. Clin Sci (Lond) 1986 May;70(5):477–484. doi: 10.1042/cs0700477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarner F., Guarner C., Prieto J., Colina I., Quiroga J., Casas J., Freixa R., Rosello J., Gelpi E., Balanzo J. Increased synthesis of systemic prostacyclin in cirrhotic patients. Gastroenterology. 1986 Mar;90(3):687–694. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)91124-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langley P. G., Hughes R. D., Williams R. Platelet adhesiveness to glass beads in liver disease. Acta Haematol. 1982;67(2):124–127. doi: 10.1159/000207038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenz K., Kleinberger G., Hörtnagl H., Base W., Druml W., Laggner A. Kreislaufverhalten von Patienten mit Leberinsuffizienz. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 1985 May 10;97(10):469–474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patrono C., Pugliese F., Ciabattoni G., Patrignani P., Maseri A., Chierchia S., Peskar B. A., Cinotti G. A., Simonetti B. M., Pierucci A. Evidence for a direct stimulatory effect of prostacyclin on renin release in man. J Clin Invest. 1982 Jan;69(1):231–239. doi: 10.1172/JCI110435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin M. H., Weston M. J., Bullock G., Roberts J., Langley P. G., White Y. S., Williams R. Abnormal platelet function and ultrastructure in fulminant hepatic failure. Q J Med. 1977 Jul;46(183):339–352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trewby P. N., Williams R. Pathophysiology of hypotension in patients with fulminant hepatic failure. Gut. 1977 Dec;18(12):1021–1026. doi: 10.1136/gut.18.12.1021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson S. P., Portmann B., Hurst D., Williams R. Pathogenesis of renal failure in cirrhosis and fulminant hepatic failure. Postgrad Med J. 1975 Aug;51(598):503–505. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.51.598.503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson S. P., Williams R. Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in cirrhosis. Gut. 1980 Jun;21(6):545–554. doi: 10.1136/gut.21.6.545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zipser R. D., Hoefs J. C., Speckart P. F., Zia P. K., Horton R. Prostaglandins: modulators of renal function and pressor resistance in chronic liver disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1979 Jun;48(6):895–900. doi: 10.1210/jcem-48-6-895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zipser R. D., Kronborg I., Rector W., Reynolds T., Daskalopoulos G. Therapeutic trial of thromboxane synthesis inhibition in the hepatorenal syndrome. Gastroenterology. 1984 Dec;87(6):1228–1232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


