Abstract
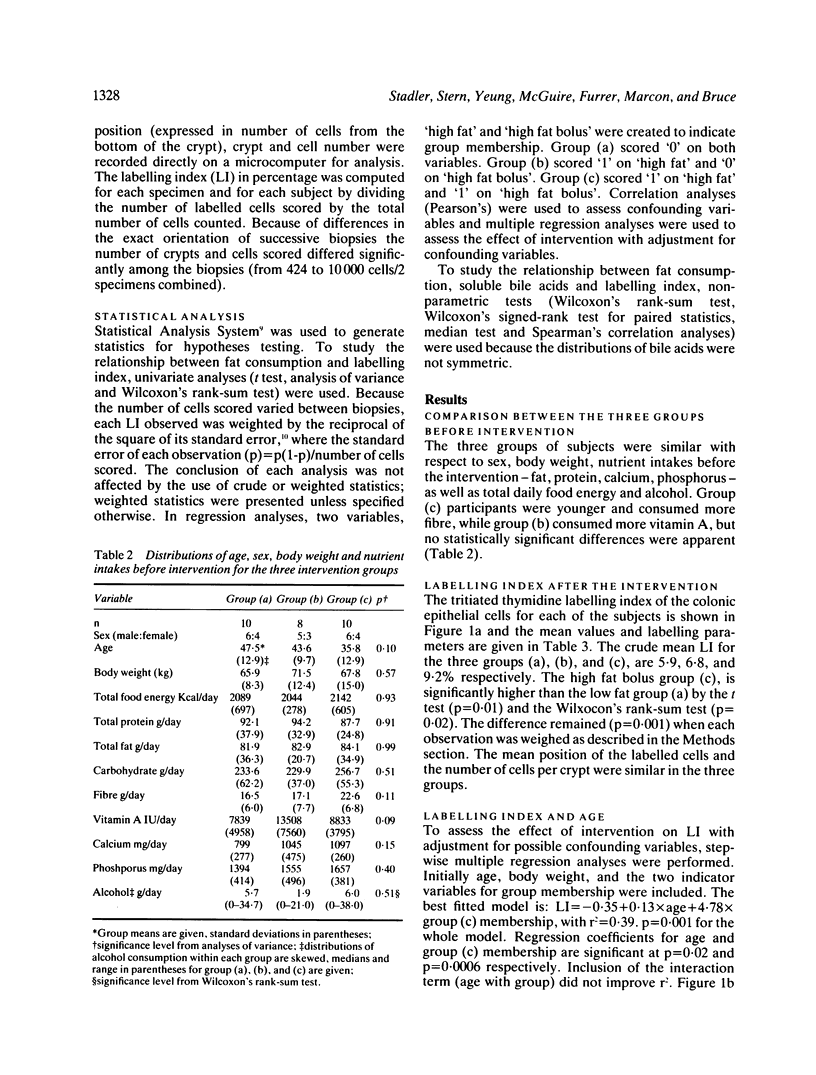
To assess the effect of fat consumption on the proliferation of the rectal mucosa, 30 normal volunteers (22 to 71 years) were randomly allocated to three groups: (a) basal low fat diet containing 30 g of fat per day; (b) the basal diet with doses of 30 g corn oil taken with each of the three meals: 120 g fat/day; (c) the basal diet with one dose of 90 g corn oil after the last meal: 120 g fat/day. Rectal biopsies were taken 15 cm from the anal verge after five days on the diets and mucosal cell proliferation was measured by labelling index (LI). The LI was significantly (p less than 0.01) higher in group (c) (9.2) than in group (a) (5.9), with group (b) intermediate (6.8). In multiple stepwise regression analysis, the data were best fitted with age and the variable indicating fat consumed as a bolus as predictors of LI (r2 = 0.39, p less than 0.001). In separate analyses the regression coefficient with age in the fat bolus group was 0.23, p less than 0.001. There was some tendency towards lower bile acids in the faecal water in group (a) than in groups (b) and (c) following the diets and between the bile acids and LI (for lithocholic acid r = 0.48, p = 0.01). These data show that dietary fat given as a bolus can lead to an increase in the proliferation of human colonic cells, possibly as a consequence of raised levels of cytotoxic acidic lipids in the faecal stream.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bird R. P., Medline A., Furrer R., Bruce W. R. Toxicity of orally administered fat to the colonic epithelium of mice. Carcinogenesis. 1985 Jul;6(7):1063–1066. doi: 10.1093/carcin/6.7.1063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird R. P., Stamp D. Effect of a high fat diet on the proliferative indices of murine colonic epithelium. Cancer Lett. 1986 Apr;31(1):61–67. doi: 10.1016/0304-3835(86)90167-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Child P., Aloe M., Mee D. Separation and quantitation of fatty acids, sterols and bile acids in feces by gas chromatography as the butyl ester-acetate derivatives. J Chromatogr. 1987 Mar 20;415(1):13–26. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)83187-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goerg K. J., Specht W., Nell G., Rummel W., Schulz L. Effect of deoxycholate on the perfused rat colon. Scanning and transmission electron microscopic study of the morphological alterations occurring during the secretagogue action of deoxycholate. Digestion. 1982;25(3):145–154. doi: 10.1159/000198823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipkin M., Newmark H. Effect of added dietary calcium on colonic epithelial-cell proliferation in subjects at high risk for familial colonic cancer. N Engl J Med. 1985 Nov 28;313(22):1381–1384. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198511283132203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipkin M., Uehara K., Winawer S., Sanchez A., Bauer C., Phillips R., Lynch H. T., Blattner W. A., Fraumeni J. F., Jr Seventh-Day Adventist vegetarians have a quiescent proliferative activity in colonic mucosa. Cancer Lett. 1985 Mar;26(2):139–144. doi: 10.1016/0304-3835(85)90019-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeown-Eyssen G. E., Yeung K. S., Bright-See E. Assessment of past diet in epidemiologic studies. Am J Epidemiol. 1986 Jul;124(1):94–103. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer J. S., Bauer W. C. In vitro determination of tritiated thymidine labeling index (LI). Evaluation of a method utilizing hyperbaric oxygen and observations on the LI of human mammary carcinoma. Cancer. 1975 Oct;36(4):1374–1380. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197510)36:4<1374::aid-cncr2820360428>3.0.co;2-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rafter J. J., Child P., Anderson A. M., Alder R., Eng V., Bruce W. R. Cellular toxicity of fecal water depends on diet. Am J Clin Nutr. 1987 Mar;45(3):559–563. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/45.3.559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rafter J. J., Eng V. W., Furrer R., Medline A., Bruce W. R. Effects of calcium and pH on the mucosal damage produced by deoxycholic acid in the rat colon. Gut. 1986 Nov;27(11):1320–1329. doi: 10.1136/gut.27.11.1320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terpstra O. T., van Blankenstein M., Dees J., Eilers G. A. Abnormal pattern of cell proliferation in the entire colonic mucosa of patients with colon adenoma or cancer. Gastroenterology. 1987 Mar;92(3):704–708. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)90021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usugane M., Fujita M., Lipkin M., Palmer R., Friedman E., Augenlicht L. Cell proliferation in explant cultures of human colon. Digestion. 1982;24(4):225–233. doi: 10.1159/000198801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wargovich M. J., Medline A., Bruce W. R. Early histopathologic events to evolution of colon cancer in C57BL/6 and CF1 mice treated with 1,2-dimethylhydrazine. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1983 Jul;71(1):125–131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


