Abstract
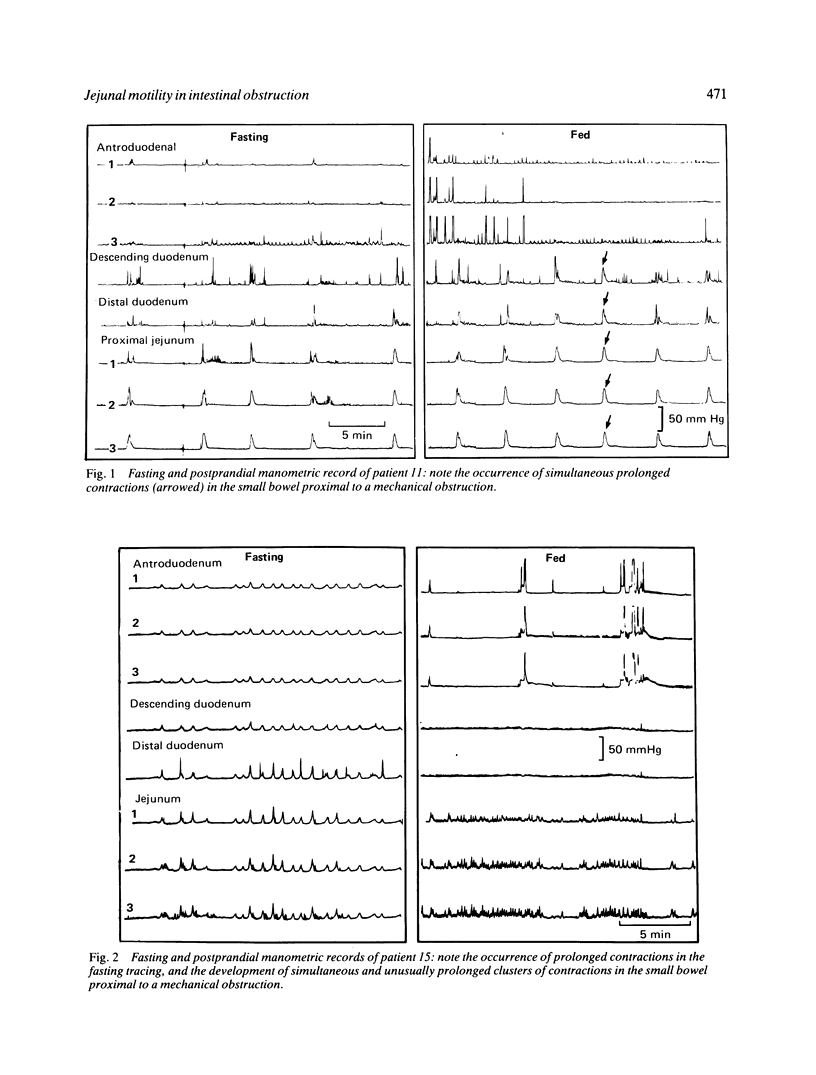
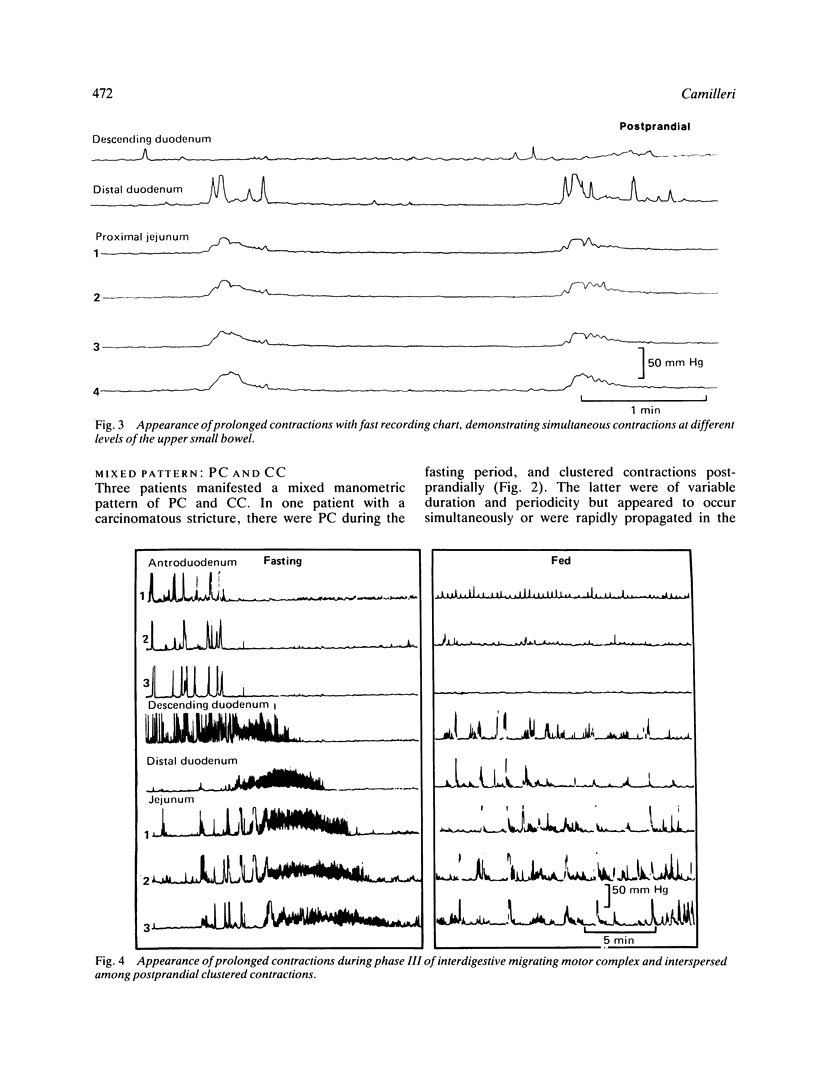
The aim of this study is to assess the value of jejunal manometry in the diagnosis of subacute mechanical obstruction distal to the proximal small bowel. In a retrospective review of 850 manometric tracings carried out in patients with unexplained nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain or altered bowel movements, 16 tracings were identified with features suggestive of mechanical obstruction: prolonged simultaneous contractions (PC) and postprandial clustered contractions (CC). Three patients had CC lasting less than 20 minutes: none proved to have mechanical obstruction. Among seven patients with CC lasting more than 30 minutes, three had proven mechanical obstruction, one probable adhesion obstruction, and in three no obstruction was found. All three patients with PC and three with mixed PC and CC had mechanical obstruction. The obstructed intestine manifests a variety of pressure profiles in the proximal jejunum: PC, CC, or mixed patterns. Prolonged simultaneous contractions are suggestive of distal subacute bowel obstruction; CC lasting over 30 minutes are less specific, whereas CC lasting less than 20 minutes are not associated with obstruction.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antoncic R. F., Lawson H. THE MUSCULAR ACTIVITY OF THE SMALL INTESTINE, IN THE DOG, DURING ACUTE OBSTRUCTION. Ann Surg. 1941 Sep;114(3):415–423. doi: 10.1097/00000658-194109000-00008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camilleri M., Malagelada J. R., Stanghellini V., Fealey R. D., Sheps S. G. Gastrointestinal motility disturbances in patients with orthostatic hypotension. Gastroenterology. 1985 Jun;88(6):1852–1859. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(85)90010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conklin J. L., Anuras S. Radiation-induced recurrent intestinal pseudo-obstruction. Am J Gastroenterol. 1981 Jun;75(6):440–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlgren S., Thorén L. Intestinal motility in low small bowel obstruction. Animal experiments with endoradiosondes. Acta Chir Scand. 1967;133(5):417–421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser I. Motility changes associated with large bowel obstruction and its surgical relief. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 1984 Sep;66(5):321–326. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda S. I., Makishita H., Oguchi K., Yanagisawa N., Nagata T. Gastrointestinal amyloid deposition in familial amyloid polyneuropathy. Neurology. 1982 Dec;32(12):1364–1368. doi: 10.1212/wnl.32.12.1364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellow J. E., Phillips S. F. Altered small bowel motility in irritable bowel syndrome is correlated with symptoms. Gastroenterology. 1987 Jun;92(6):1885–1893. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)90620-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerlin P., Phillips S. Variability of motility of the ileum and jejunum in healthy humans. Gastroenterology. 1982 Apr;82(4):694–700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerlin P., Zinsmeister A., Phillips S. Motor responses to food of the ileum, proximal colon, and distal colon of healthy humans. Gastroenterology. 1983 Apr;84(4):762–770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malagelada J. R., Camilleri M. Unexplained vomiting: a diagnostic challenge. Ann Intern Med. 1984 Aug;101(2):211–218. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-101-2-211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malagelada J. R., Stanghellini V. Manometric evaluation of functional upper gut symptoms. Gastroenterology. 1985 May;88(5 Pt 1):1223–1231. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(85)80083-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novak J. M., Collins J. T., Donowitz M., Farman J., Sheahan D. G., Spiro H. M. Effects of radiation on the human gastrointestinal tract. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1979 Mar;1(1):9–39. doi: 10.1097/00004836-197903000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohman U. Studies on small intestinal obstruction. I. Intraluminal pressure in experimental low small bowel obstruction in the cat. Acta Chir Scand. 1975;141(5):413–416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quigley E. M., Borody T. J., Phillips S. F., Wienbeck M., Tucker R. L., Haddad A. Motility of the terminal ileum and ileocecal sphincter in healthy humans. Gastroenterology. 1984 Oct;87(4):857–866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanghellini V., Camilleri M., Malagelada J. R. Chronic idiopathic intestinal pseudo-obstruction: clinical and intestinal manometric findings. Gut. 1987 Jan;28(1):5–12. doi: 10.1136/gut.28.1.5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryker S. J., Borody T. J., Phillips S. F., Kelly K. A., Dozois R. R., Beart R. W., Jr Motility of the small intestine after proctocolectomy and ileal pouch-anal anastomosis. Ann Surg. 1985 Mar;201(3):351–356. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198503000-00017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers R. W., Anuras S., Green J. Jejunal manometry patterns in health, partial intestinal obstruction, and pseudoobstruction. Gastroenterology. 1983 Dec;85(6):1290–1300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers R. W., Yanda R., Prihoda M., Flatt A. Acute intestinal obstruction: an electromyographic study in dogs. Gastroenterology. 1983 Dec;85(6):1301–1306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


