Abstract
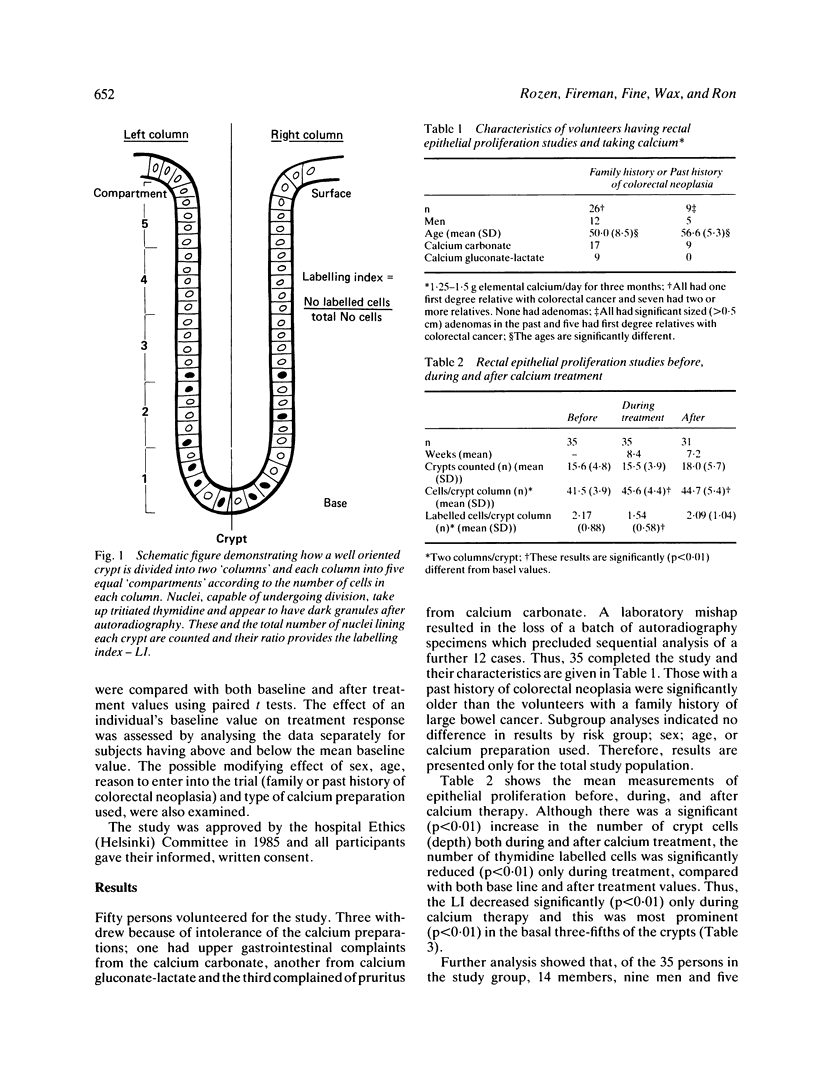
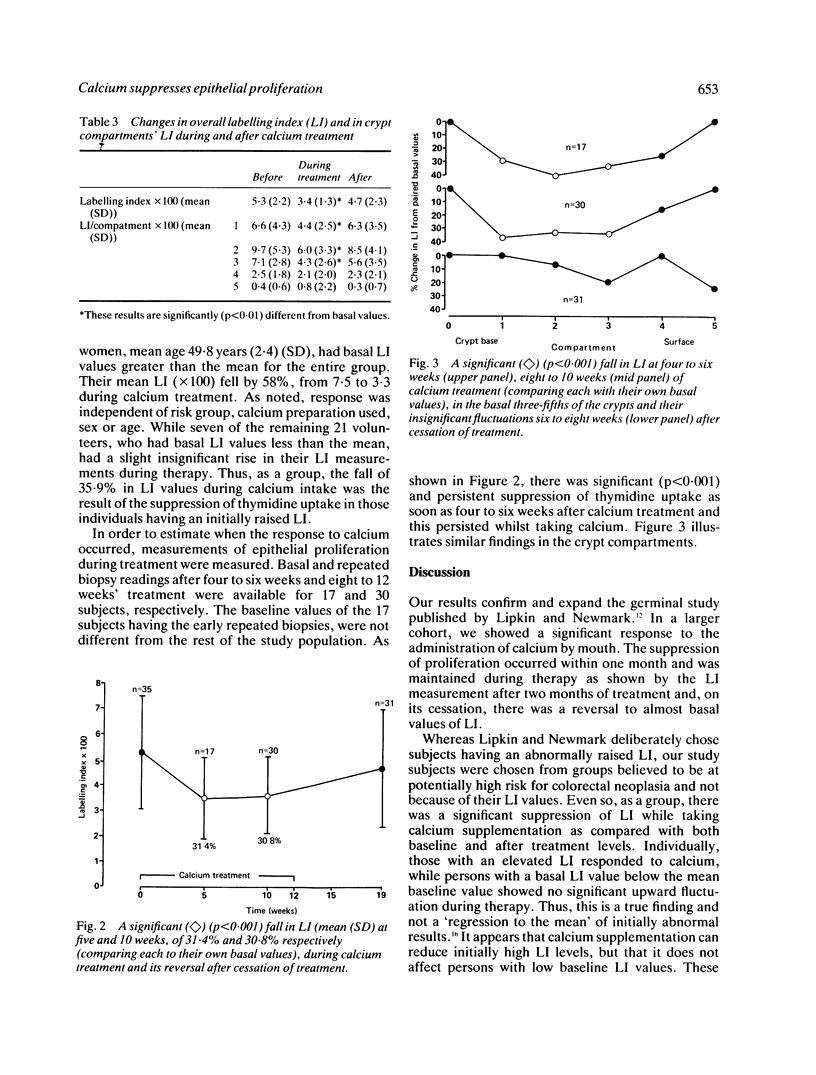
Dietary calcium may inhibit colonic carcinogenesis promoted by high fat, phosphate, and low fibre diets. In persons at risk for colon cancer oral calcium supplements significantly suppress increased rectal epithelial proliferation. This was studied in a cohort of 35 volunteers: 26 first degree relatives of colorectal cancer patients and nine who had had colonic adenomas (mean age 51.6 years, 17 (49%) men, all negative for large bowel neoplasia). 1.25-1.5 g elemental calcium was given in divided daily doses for three months. Rectal pinch biopsies were taken without bowel preparation, before and mean 8.4 weeks during and 7.2 weeks after treatment and incubated with tritiated thymidine. The mean number of labelled cells, as a ratio of the total number of crypt cells (labelling index-LI), and their crypt position, were determined. The mean number of labelled cells decreased during treatment by 29%, especially in the basal three-fifths of crypts. There was also a significant 10% increase in mean number of crypt cells during treatment. [Mean LI decreased by 36% (p less than 0.001) during calcium treatment and almost returned to basal values after cessation.] If a raised LI is a marker of potential malignancy and a randomised clinical trial confirms that calcium suppresses it, dietary intervention studies in high risk persons are indicated.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen L. H. Calcium bioavailability and absorption: a review. Am J Clin Nutr. 1982 Apr;35(4):783–808. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/35.4.783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appleton G. V., Davies P. W., Bristol J. B., Williamson R. C. Inhibition of intestinal carcinogenesis by dietary supplementation with calcium. Br J Surg. 1987 Jun;74(6):523–525. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800740635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry D. A., Eaton M. L., Ekholm B. P., Fox T. L. Assessing differential drug effect. Biometrics. 1984 Dec;40(4):1109–1115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bleiberg H., Buyse M., Galand P. Cell kinetic indicators of premalignant stages of colorectal cancer. Cancer. 1985 Jul 1;56(1):124–129. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19850701)56:1<124::aid-cncr2820560119>3.0.co;2-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bresalier R. S., Kim Y. S. Diet and colonic cancer: putting the puzzle together. N Engl J Med. 1985 Nov 28;313(22):1413–1414. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198511283132209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buset M., Lipkin M., Winawer S., Swaroop S., Friedman E. Inhibition of human colonic epithelial cell proliferation in vivo and in vitro by calcium. Cancer Res. 1986 Oct;46(10):5426–5430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deschner E. E., Hallak A., Rozen P., Gilat T. Prolonged administration of bile salts for gallstone dissolution and its effect on rectal epithelial cell proliferation. Dig Dis Sci. 1987 Sep;32(9):991–996. doi: 10.1007/BF01297189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garland C. F., Garland F. C. Do sunlight and vitamin D reduce the likelihood of colon cancer? Int J Epidemiol. 1980 Sep;9(3):227–231. doi: 10.1093/ije/9.3.227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garland C., Shekelle R. B., Barrett-Connor E., Criqui M. H., Rossof A. H., Paul O. Dietary vitamin D and calcium and risk of colorectal cancer: a 19-year prospective study in men. Lancet. 1985 Feb 9;1(8424):307–309. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91082-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipkin M., Blattner W. A., Gardner E. J., Burt R. W., Lynch H., Deschner E., Winawer S., Fraumeni J. F., Jr Classification and risk assessment of individuals with familial polyposis, Gardner's syndrome, and familial non-polyposis colon cancer from [3H]thymidine labeling patterns in colonic epithelial cells. Cancer Res. 1984 Sep;44(9):4201–4207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipkin M., Newmark H. Effect of added dietary calcium on colonic epithelial-cell proliferation in subjects at high risk for familial colonic cancer. N Engl J Med. 1985 Nov 28;313(22):1381–1384. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198511283132203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipkin M., Uehara K., Winawer S., Sanchez A., Bauer C., Phillips R., Lynch H. T., Blattner W. A., Fraumeni J. F., Jr Seventh-Day Adventist vegetarians have a quiescent proliferative activity in colonic mucosa. Cancer Lett. 1985 Mar;26(2):139–144. doi: 10.1016/0304-3835(85)90019-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newmark H. L., Wargovich M. J., Bruce W. R. Colon cancer and dietary fat, phosphate, and calcium: a hypothesis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1984 Jun;72(6):1323–1325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rafter J. J., Eng V. W., Furrer R., Medline A., Bruce W. R. Effects of calcium and pH on the mucosal damage produced by deoxycholic acid in the rat colon. Gut. 1986 Nov;27(11):1320–1329. doi: 10.1136/gut.27.11.1320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozen P., Fireman Z., Figer A., Legum C., Ron E., Lynch H. T. Family history of colorectal cancer as a marker of potential malignancy within a screening program. Cancer. 1987 Jul 15;60(2):248–254. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19870715)60:2<248::aid-cncr2820600223>3.0.co;2-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozen P., Horwitz C., Tabenkin C., Ron E., Katz L. Dietary habits and colorectal cancer incidence in a second-defined kibbutz population. Nutr Cancer. 1987;9(2-3):177–184. doi: 10.1080/01635588709513925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheikh M. S., Santa Ana C. A., Nicar M. J., Schiller L. R., Fordtran J. S. Gastrointestinal absorption of calcium from milk and calcium salts. N Engl J Med. 1987 Aug 27;317(9):532–536. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198708273170903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wargovich M. J., Eng V. W., Newmark H. L., Bruce W. R. Calcium ameliorates the toxic effect of deoxycholic acid on colonic epithelium. Carcinogenesis. 1983 Sep;4(9):1205–1207. doi: 10.1093/carcin/4.9.1205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wargovich M. J., Eng V. W., Newmark H. L. Calcium inhibits the damaging and compensatory proliferative effects of fatty acids on mouse colon epithelium. Cancer Lett. 1984 Jul;23(3):253–258. doi: 10.1016/0304-3835(84)90091-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


