Abstract
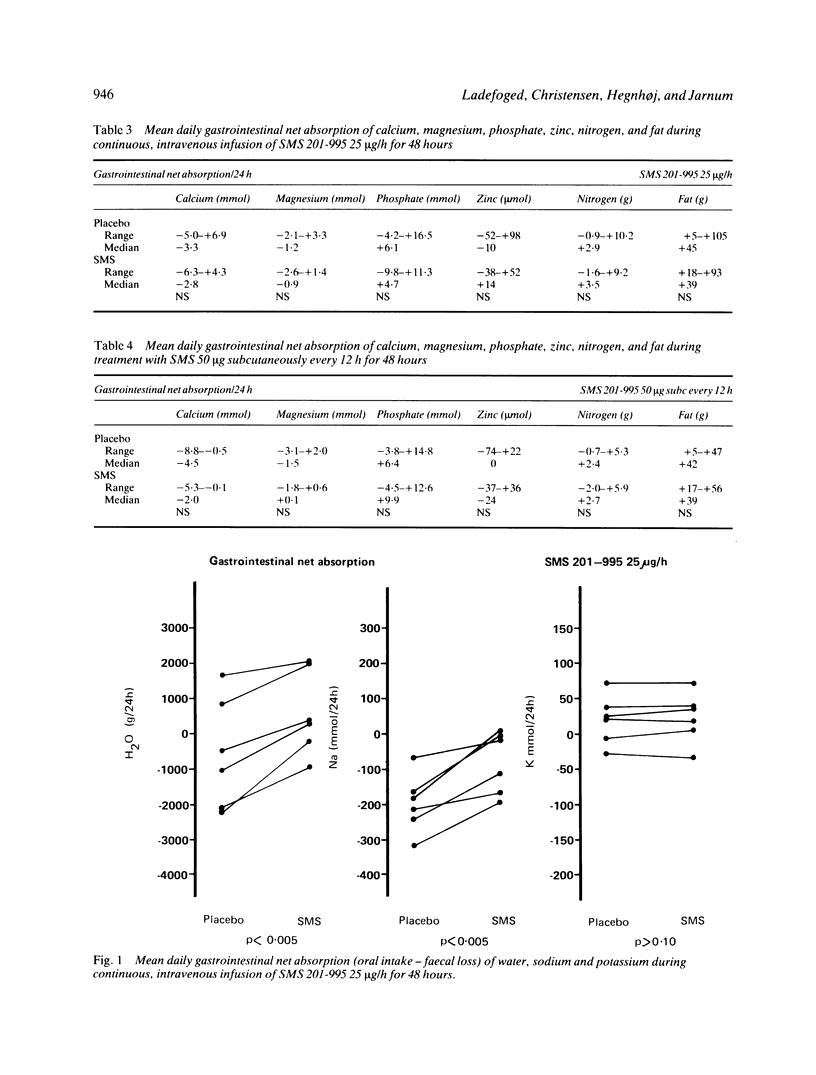
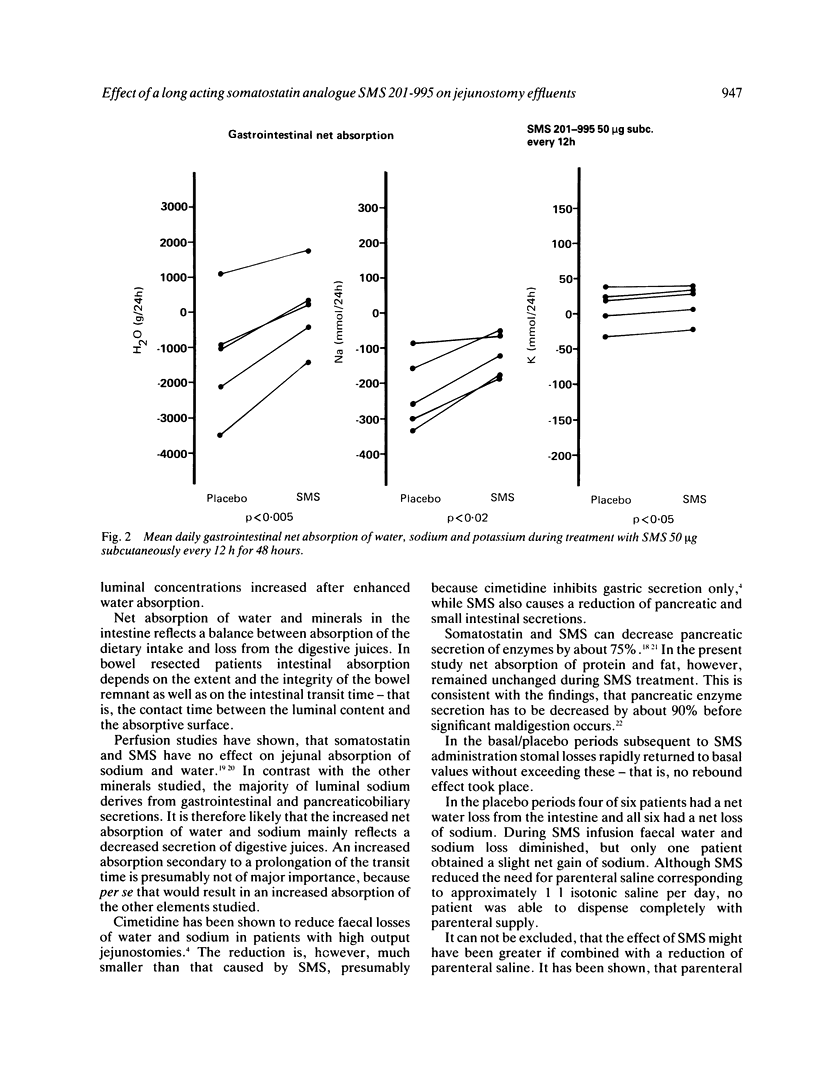
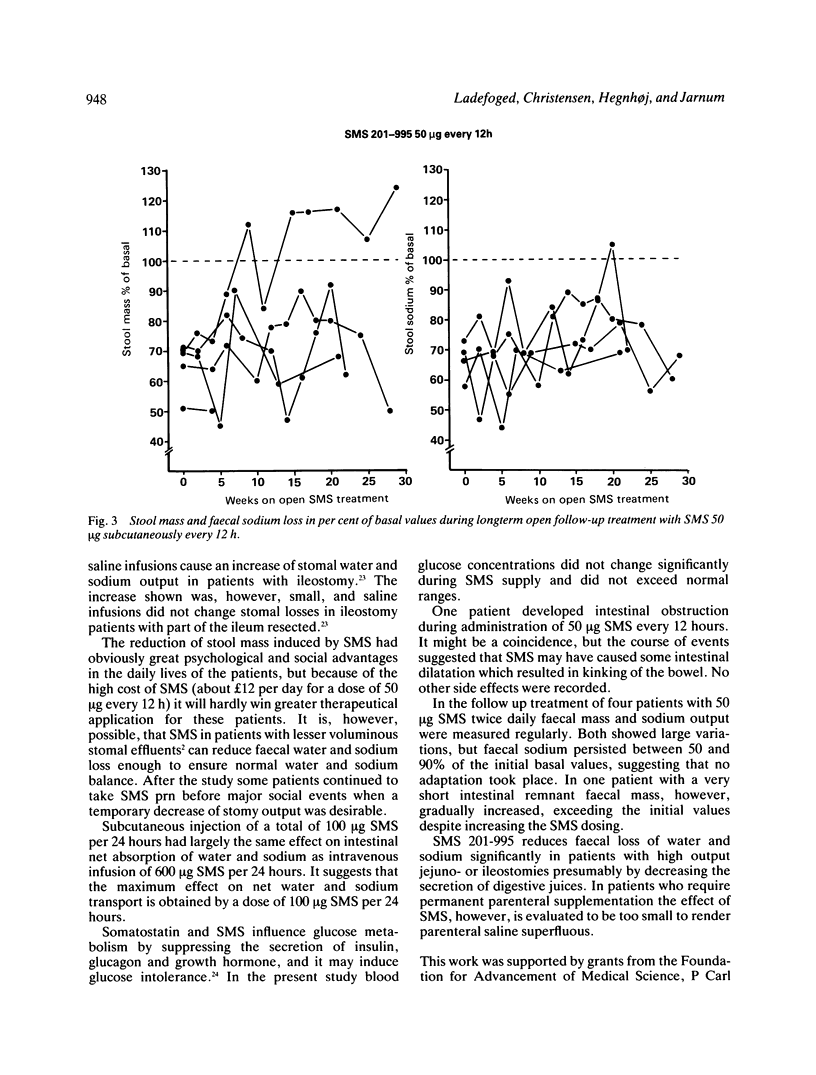
The effect of a long acting somatostatin analogue SMS 201-995 on stomal effluents in patients with severe short bowel syndrome was investigated in a double blind placebo controlled balance study. Six patients, five with Crohn's disease and one with radiation enteropathy were studied. Five patients had a jejunostomy and one an ileostomy. The patients had a normal food intake, but because of severe malabsorption had received home parenteral nutrition for several years. Faecal mass was reduced (p less than 0.005) and intestinal net sodium absorption was increased (p less than 0.005) by intravenous infusion of SMS 25 micrograms/h. Net absorption of potassium, calcium, magnesium phosphate, zinc, nitrogen and fat was not influenced. Subcutaneous injections of 50 micrograms SMS every 12 hours had a similar effect on net intestinal absorption of sodium and water. Four patients continued with a five to six months open follow up study when subcutaneous SMS in the same dose was administered by the patients at home. The effect on faecal sodium loss persisted, but in one patient faecal mass gradually increased and finally exceeded pretreatment values. SMS may decrease net absorption of water and sodium following reduced secretion of digestive juices rather than by increasing absorptive capacity. SMS may be useful as an antidiarrhoeal drug in patients with high output jejuno- or ileostomies, but in patients who need permanent parenteral nutrition the effect is too small to significantly alter management.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bitar K. N., Zfass A. M., Makhlouf G. M. Binding of secretin to plastic surfaces. Gastroenterology. 1978 Dec;75(6):1080–1082. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dharmsathaphorn K., Gorelick F. S., Sherwin R. S., Cataland S., Dobbins J. W. Somatostatin decreases diarrhea in patients with the short-bowel syndrome. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1982 Dec;4(6):521–524. doi: 10.1097/00004836-198212000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dharmsathaphorn K., Sherwin R. S., Cataland S., Jaffe B., Dobbins J. Somatostatin inhibits diarrhea in the carcinoid syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Jan;92(1):68–69. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-92-1-68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMagno E. P., Go V. L., Summerskill W. H. Relations between pancreatic enzyme outputs and malabsorption in severe pancreatic insufficiency. N Engl J Med. 1973 Apr 19;288(16):813–815. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197304192881603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dueno M. I., Bai J. C., Santangelo W. C., Krejs G. J. Effect of somatostatin analog on water and electrolyte transport and transit time in human small bowel. Dig Dis Sci. 1987 Oct;32(10):1092–1096. doi: 10.1007/BF01300194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fielding J. F., Cooke W. T., Williams J. A. Gastric acid secretion in Crohn's disease in relation to disease activity and bowel resection. Lancet. 1971 May 29;1(7709):1106–1107. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91842-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldenberg H., Fernandez A. Simplified method for the estimation of inorganic phosphorus in body fluids. Clin Chem. 1966 Dec;12(12):871–882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gullo L., Priori P., Scarpignato C., Baldoni F., Mattioli G., Barbara L. Effect of somatostatin 14 on pure human pancreatic secretion. Dig Dis Sci. 1987 Oct;32(10):1065–1070. doi: 10.1007/BF01300189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyr K. E., Whitehouse I., Beglinger C., Köhler E., Dettwiler S., Fried M. Human pharmacological effects of SMS 201-995 on gastric secretion. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1986;119:96–102. doi: 10.3109/00365528609087436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill G. L., Mair W. S., Goligher J. C. Impairment of 'ileostomy adaptation' in patients after ileal resection. Gut. 1974 Dec;15(12):982–987. doi: 10.1136/gut.15.12.982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen O., Ladefoged K., Stage J. G., Jarnum S. Effects of cimetidine on jejunostomy effluents in patients with severe short-bowel syndrome. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1986 Sep;21(7):824–828. doi: 10.3109/00365528609011125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston D. G., Davies R. R., Turner S. J. Effects of somatostatin and SMS 201-995 on carbohydrate metabolism in normal man. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1986;119:158–165. doi: 10.3109/00365528609087445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krejs G. J., Browne R., Raskin P. Effect of intravenous somatostatin on jejunal absorption of glucose, amino acids, water, and electrolytes. Gastroenterology. 1980 Jan;78(1):26–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krejs G. J. Physiological role of somatostatin in the digestive tract: gastric acid secretion, intestinal absorption, and motility. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1986;119:47–53. doi: 10.3109/00365528609087431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVITAN R., INGELFINGER F. J. EFFECT OF D-ALDOSTERONE ON SALT AND WATER ABSORPTION FROM THE INTACT HUMAN COLON. J Clin Invest. 1965 May;44:801–808. doi: 10.1172/JCI105192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladefoged K., Nicolaidou P., Jarnum S. Calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, zinc, and nitrogen balance in patients with severe short bowel syndrome. Am J Clin Nutr. 1980 Oct;33(10):2137–2144. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/33.10.2137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladefoged K., Olgaard K. Fluid and electrolyte absorption and renin-angiotensin-aldosterone axis in patients with severe short-bowel syndrome. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1979;14(6):729–735. doi: 10.3109/00365527909181945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladefoged K., Olgaard K. Sodium homeostasis after small-bowel resection. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1985 Apr;20(3):361–369. doi: 10.3109/00365528509091665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen J. A., Loud F. B., Christiansen J. Inhibition of meal stimulated gastric acid secretion by an octapeptide somatostatin analogue SMS 201-995. Gut. 1987 Apr;28(4):464–467. doi: 10.1136/gut.28.4.464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichlin S. Somatostatin. N Engl J Med. 1983 Dec 15;309(24):1495–1501. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198312153092406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahren J. Influence of somatostatin on carbohydrate disposal and absorption in diabetes mellitus. Lancet. 1976 Dec 4;2(7997):1213–1216. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91142-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams N. S., Cooper J. C., Axon A. T., King R. F., Barker M. Use of a long acting somatostatin analogue in controlling life threatening ileostomy diarrhoea. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1984 Oct 20;289(6451):1027–1028. doi: 10.1136/bmj.289.6451.1027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


