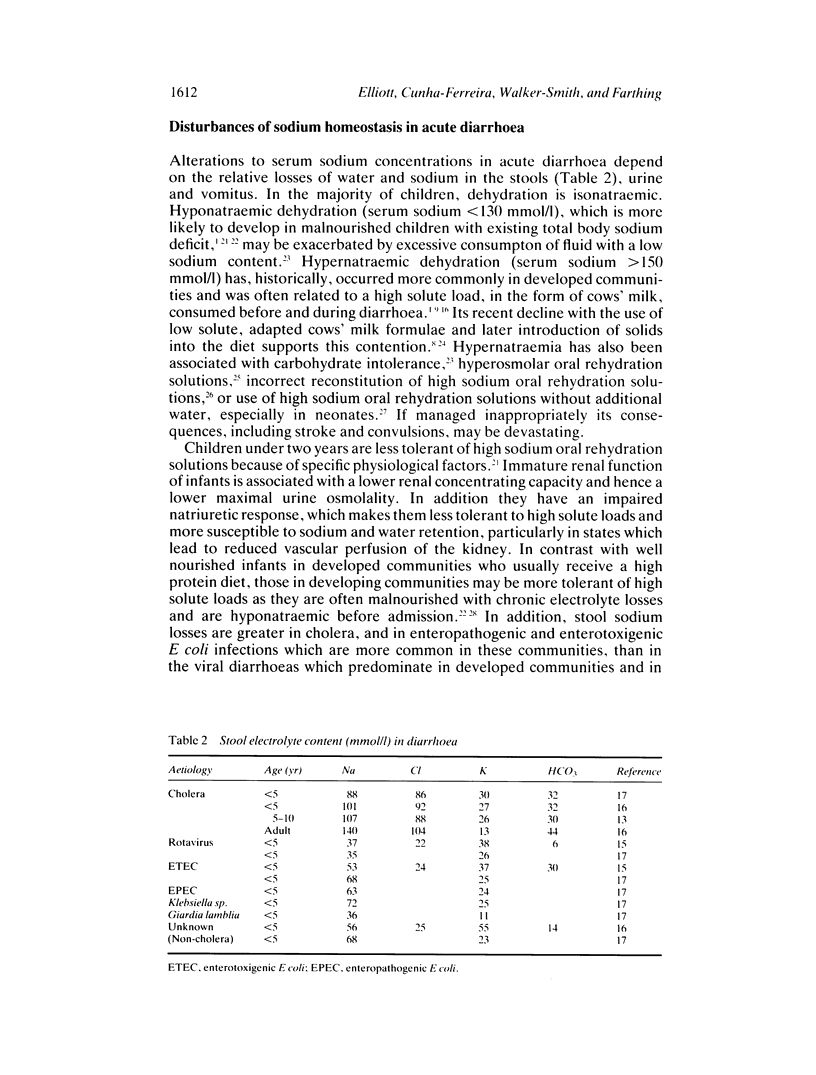
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdalla S., Helmy N., el Essaily M., Nasser S., Hirschhorn Oral rehydration for the low-birthweight baby with diarrhoea. Lancet. 1984 Oct 6;2(8406):818–819. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90749-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aperia A., Marin L., Zetterström R., Günöz H., Neyzi O., Saner G., Sökücü S. Salt and water homeostasis during oral rehydration therapy. J Pediatr. 1983 Sep;103(3):364–369. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(83)80404-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry R. J., Smyth D. H., Wright E. M. Short-circuit current and solute transfer by rat jejunum. J Physiol. 1965 Nov;181(2):410–431. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bart K. J., Finberg L. Single solution for oral therapy of diarrhoea. Lancet. 1976 Sep 18;2(7986):633–635. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)90705-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhargava S. K., Sachdev H. P., Das Gupta B., Daral T. S., Singh H. P., Mohan M. Oral rehydration of neonates and young infants with dehydrating diarrhea: comparison of low and standard sodium content in oral rehydration solutions. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1984 Sep;3(4):500–505. doi: 10.1097/00005176-198409000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum D., Brasseur D., Kahn A., Brachet E. Safe oral rehydration of hypertonic dehydration. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1986 Mar-Apr;5(2):232–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHATTERJEE H. N. Control of vomiting in cholera and oral replacement of fluid. Lancet. 1953 Nov 21;265(6795):1063–1063. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(53)90668-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLLE E., AYOUB E., RAILE R. Hypertonic dehydration (hypernatremia): the role of feedings high in solutes. Pediatrics. 1958 Jul;22(1 Pt 1):5–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CSAKAY T. Z. A possible link between active transport of electrolytes and nonelectrolyes. Fed Proc. 1963 Jan-Feb;22:3–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee A., Mahalanabis D., Jalan K. N., Maitra T. K., Agarwal S. K., Dutta B., Khatua S. P., Bagchi D. K. Oral rehydration in infantile diarrhoea. Controlled trial of a low sodium glucose electrolyte solution. Arch Dis Child. 1978 Apr;53(4):284–289. doi: 10.1136/adc.53.4.284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleary T. G., Cleary K. R., DuPont H. L., El-Malih G. S., Kordy M. I., Mohieldin M. S., Shoukry I., Shukry S., Wyatt R. G., Woodward W. E. The relationship of oral rehydration solution to hypernatremia in infantile diarrhea. J Pediatr. 1981 Nov;99(5):739–741. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(81)80397-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crane R. K. Na+ -dependent transport in the intestine and other animal tissues. Fed Proc. 1965 Sep-Oct;24(5):1000–1006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutting W. A., Belton N. R., Gray J. A., Brettle R. P., Welsby P. D., Todd W. T., Elton R. A., Westwood A., Davidson S. Safety and efficacy of three oral rehydration solutions for children with diarrhoea (Edinburgh 1984-85). Acta Paediatr Scand. 1989 Mar;78(2):253–258. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1989.tb11065.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deorari A. K., Bhan M. K., Arora N. K., Ghai O. P., Kumar R., Mahopatra L. N., Gudmund S. Stool electrolyte composition in relation to etiology in acute gastroenteritis. Indian Pediatr. 1982 Mar;19(3):217–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott E. J., Armitstead J. C., Farthing M. J., Walker-Smith J. A. Oral rehydration therapy without bicarbonate for prevention and treatment of dehydration: a double-blind controlled trial. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1988 Jun;2(3):253–262. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.1988.tb00695.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott E. J., Da Cunha Ferreira R. M., Cameron D., Farthing M. J., Walker-Smith J. A. Evaluation of three oral rehydration solutions designed for use in developed communities. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1989 Jun;3(3):233–243. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.1989.tb00209.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott E. J., Walker-Smith J. A., Farthing M. J. The role of bicarbonate and base precursors in treatment of acute gastroenteritis. Arch Dis Child. 1987 Jan;62(1):91–95. doi: 10.1136/adc.62.1.91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott E. J., Watson A. J., Walker-Smith J. A., Farthing M. J. Effect of bicarbonate on efficacy of oral rehydration therapy: studies in an experimental model of secretory diarrhoea. Gut. 1988 Aug;29(8):1052–1057. doi: 10.1136/gut.29.8.1052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finberg L. The role of oral electrolyte-glucose solutions in hydration for children--international and domestic aspects. J Pediatr. 1980 Jan;96(1):51–54. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80323-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fordtran J. S., Rector F. C., Jr, Carter N. W. The mechanisms of sodium absorption in the human small intestine. J Clin Invest. 1968 Apr;47(4):884–900. doi: 10.1172/JCI105781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fordtran J. S. Stimulation of active and passive sodium absorption by sugars in the human jejunum. J Clin Invest. 1975 Apr;55(4):728–737. doi: 10.1172/JCI107983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fordtran J. S. Stimulation of active and passive sodium absorption by sugars in the human jejunum. J Clin Invest. 1975 Apr;55(4):728–737. doi: 10.1172/JCI107983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRISON H. E. The treatment of diarrhea in infancy. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1954 May;:335–348. doi: 10.1016/s0031-3955(16)30071-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschhorn N., Cash R. A., Woodward W. E., Spivey G. H. Oral fluid therapy of Apache children with acute infectious diarrhoea. Lancet. 1972 Jul 1;2(7766):15–18. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)91277-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschhorn N., McCarthy B. J., Ranney B., Hirschhorn M. A., Woodward S. T., Lacapa A., Cash R. A., Woodward W. E. Ad libitum oral glucose-electrolyte therapy for acute diarrhea in Apache children. J Pediatr. 1973 Oct;83(4):562–571. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80215-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschhorn N. The treatment of acute diarrhea in children. An historical and physiological perspective. Am J Clin Nutr. 1980 Mar;33(3):637–663. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/33.3.637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isolauri E. Evaluation of an oral rehydration solution with Na+ 60 mmol/l in infants hospitalized for acute diarrhoea or treated as outpatients. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1985 Sep;74(5):643–649. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1985.tb10005.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins H. R., Milla P. J. The development of colonic transport mechanisms in early life: evidence for reduced anion exchange. Early Hum Dev. 1988 Mar;16(2-3):213–218. doi: 10.1016/0378-3782(88)90101-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson R. A., Schedl H. P. Absorption of sodium, chloride, water, and simple sugars in rat small intestine. Am J Physiol. 1966 Oct;211(4):939–942. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.211.4.939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Listernick R., Zieserl E., Davis A. T. Oral glucose-electrolyte solutions as maintenance therapy of acute diarrhea. Am J Dis Child. 1985 Jun;139(6):571–574. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1985.02140080041029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahalanabis D., Wallace C. K., Kallen R. J., Mondal A., Pierce N. F. Water and electrolyte losses due to cholera in infants and small children: a recovery balance study. Pediatrics. 1970 Mar;45(3):374–385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuel P. D., Walker-Smith J. A. Decline of hypernatraemia as a problem in gastroenteritis. Arch Dis Child. 1980 Feb;55(2):124–127. doi: 10.1136/adc.55.2.124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marin L., Sanér G., Sökücü S., Günoz H., Neyzi O., Zetterström R. Oral rehydration therapy in neonates and young infants with infectious diarrhoea. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1987 May;76(3):431–437. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1987.tb10494.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molla A. M., Rahman M., Sarker S. A., Sack D. A., Molla A. Stool electrolyte content and purging rates in diarrhea caused by rotavirus, enterotoxigenic E. coli, and V. cholerae in children. J Pediatr. 1981 May;98(5):835–838. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(81)80863-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murtaza A., Zulfiqar I., Khan S. R., Lindblad B. S., Aperia A. Regulation of serum sodium in dehydrated and orally rehydrated infants. Influence of age and of purging rates. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1987 May;76(3):424–430. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1987.tb10493.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PHILLIPS R. A. WATER AND ELECTROLYTE LOSSES IN CHOLERA. Fed Proc. 1964 May-Jun;23:705–712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patra F. C., Mahalanabis D., Jalan K. N., Sen A., Banerjee P. Is oral rice electrolyte solution superior to glucose electrolyte solution in infantile diarrhoea? Arch Dis Child. 1982 Dec;57(12):910–912. doi: 10.1136/adc.57.12.910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Banwell J. G., Rupak D. M., Mitra R. C., Caranasos G. J., Keimowitz R. I., Mondal A., Manji P. M. Effect of intragastric glucose-electrolyte infusion upon water and electrolyte balance in Asiatic cholera. Gastroenterology. 1968 Sep;55(3):333–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Hirschhorn N. Oral fluid--a simple weapon against dehydration in diarrhoea: how it works and how to use it. WHO Chron. 1977 Mar;31(3):87–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizarro D., Posada G., Mata L., Nalin D., Mohs E. Oral rehydration of neonates with dehydrating diarrhoeas. Lancet. 1979 Dec 8;2(8154):1209–1210. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)92332-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizarro D., Posada G., Mata L. Treatment of 242 neonates with dehydrating diarrhea with an oral glucose-electrolyte solution. J Pediatr. 1983 Jan;102(1):153–156. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(83)80318-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RIKLIS E., QUASTEL J. H. Effects of cations on sugar absorption by isolated surviving guinea pig intestine. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1958 Mar;36(3):347–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid E. W. Intestinal absorption of solutions. J Physiol. 1902 May 28;28(3):241–256. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1902.sp000913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolston D. D., Borodo M. M., Kelly M. J., Dawson A. M., Farthing M. J. Efficacy of oral rehydration solutions in a rat model of secretory diarrhea. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1987 Jul-Aug;6(4):624–630. doi: 10.1097/00005176-198707000-00023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHULTZ S. G., ZALUSKY R. ION TRANSPORT IN ISOLATED RABBIT ILEUM. II. THE INTERACTION BETWEEN ACTIVE SODIUM AND ACTIVE SUGAR TRANSPORT. J Gen Physiol. 1964 Jul;47:1043–1059. doi: 10.1085/jgp.47.6.1043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saberi M. S., Assaee M. Oral hydration of diarrhoeal dehydration. Comparison of high and low sodium concentration in rehydration solutions. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1983 Mar;72(2):167–170. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1983.tb09690.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandhu B. K., Jones B. J., Brook C. G., Silk D. B. Oral rehydration in acute infantile diarrhoea with a glucose-polymer electrolyte solution. Arch Dis Child. 1982 Feb;57(2):152–154. doi: 10.1136/adc.57.2.152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santosham M., Carrera E., Sack R. B. Oral rehydration therapy in well-nourished ambulatory children. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1983 Jul;32(4):804–808. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1983.32.804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santosham M., Daum R. S., Dillman L., Rodriguez J. L., Luque S., Russell R., Kourany M., Ryder R. W., Bartlett A. V., Rosenberg A. Oral rehydration therapy of infantile diarrhea: a controlled study of well-nourished children hospitalized in the United States and Panama. N Engl J Med. 1982 May 6;306(18):1070–1076. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198205063061802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speelman P., Butler T., Kabir I., Ali A., Banwell J. Colonic dysfunction during cholera infection. Gastroenterology. 1986 Nov;91(5):1164–1170. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(86)80012-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiller R. C., Jones B. J., Silk D. B. Jejunal water and electrolyte absorption from two proprietary enteral feeds in man: importance of sodium content. Gut. 1987 Jun;28(6):681–687. doi: 10.1136/gut.28.6.681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wapnir R. A., Lifshitz F. Osmolality and solute concentration--their relationship with oral hydration solution effectiveness: an experimental assessment. Pediatr Res. 1985 Sep;19(9):894–898. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198509000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


