Abstract
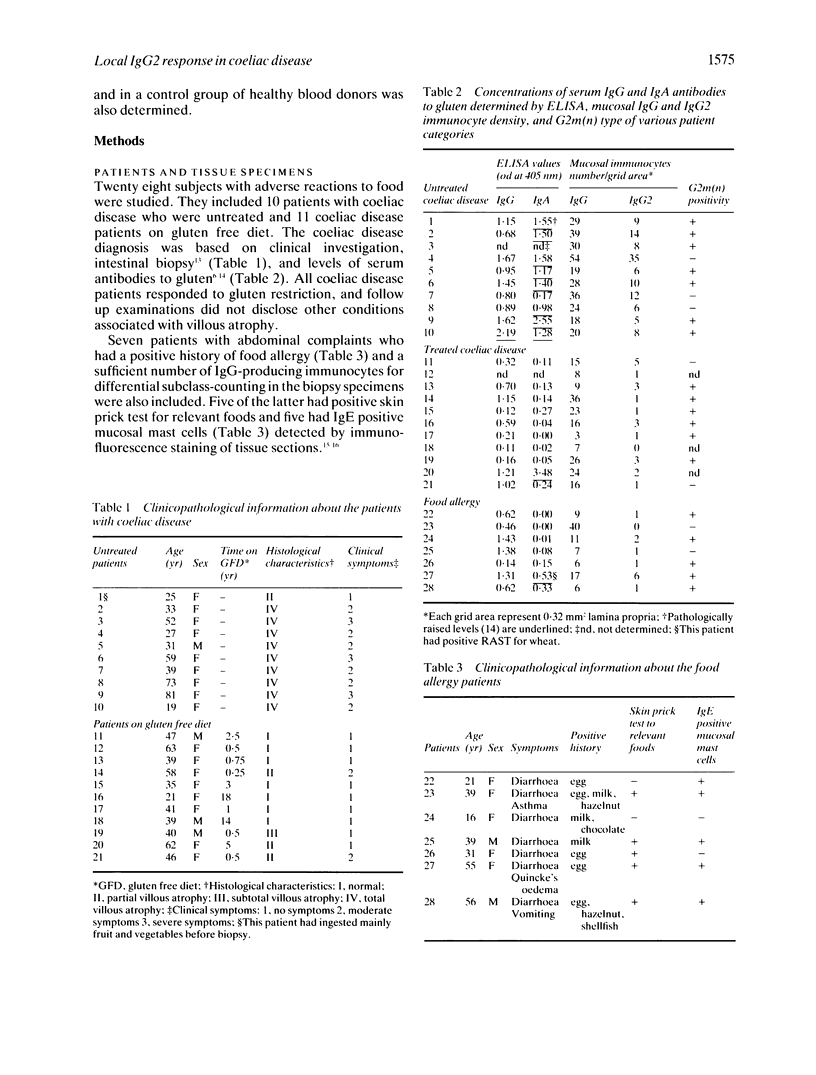
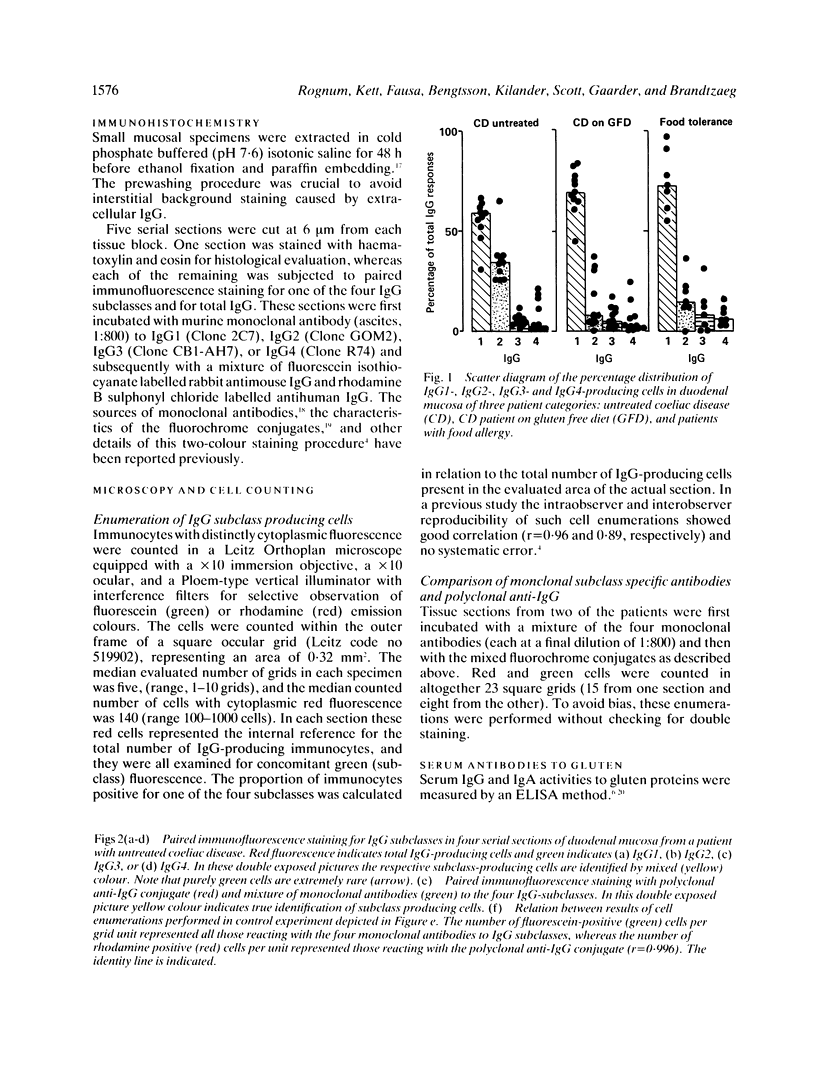
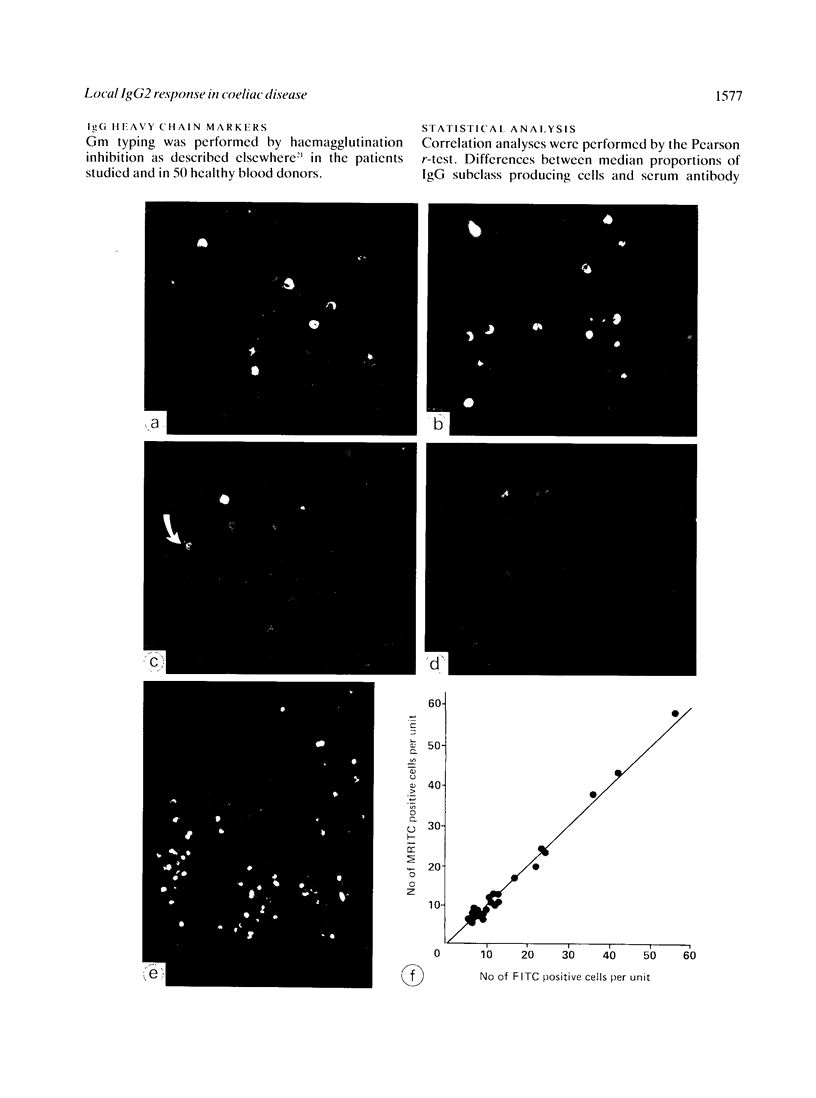
The subclass distribution of IgG-producing immunocytes was studied by two colour immunohistochemistry with monoclonal antibodies in jejunal biopsy specimens from 10 adults with untreated coeliac disease, 11 coeliac disease patients on a gluten free diet, and seven patients with established food allergy. Paired immunofluorescence staining was performed with subclass specific murine monoclonal antibodies in combination with polyclonal rabbit antibody reagent to total IgG; the proportion of cells belonging to each subclass could thereby be determined. The ratio of IgG2 immunocytes was significantly higher (p less than 0.05) in untreated coeliac disease patients (median, 35.2%; range, 26.7-65.2%) than in those on a gluten free diet (median, 7.3%; range, 0-31.9%) or those having food allergy (median, 12.5%; range, 0-36.5%). The disparity in the local IgG2 response between patients with untreated coeliac disease and those with food allergy might be due to differences in the nature of the antigenic stimuli, dissimilar genetic 'make-up' of the subjects, or both.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brandtzaeg P., Karlsson G., Hansson G., Petruson B., Björkander J., Hanson L. A. The clinical condition of IgA-deficient patients is related to the proportion of IgD- and IgM-producing cells in their nasal mucosa. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 Mar;67(3):626–636. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P., Kett K., Rognum T. O., Söderström R., Björkander J., Söderström T., Petrusson B., Hanson L. A. Distribution of mucosal IgA and IgG subclass-producing immunocytes and alterations in various disorders. Monogr Allergy. 1986;20:179–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P. Mucosal and glandular distribution of immunoglobulin components. Immunohistochemistry with a cold ethanol-fixation technique. Immunology. 1974 Jun;26(6):1101–1114. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P., Valnes K., Scott H., Rognum T. O., Bjerke K., Baklien K. The human gastrointestinal secretory immune system in health and disease. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1985;114:17–38. doi: 10.3109/00365528509093765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciclitira P. J., Ellis H. J., Richards D., Kemeny D. M. Gliadin IgG subclass antibodies in patients with coeliac disease. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1986;80(3):258–261. doi: 10.1159/000234062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DONIACH I., SHINER M. Duodenal and jejunal biopsies. II. Histology. Gastroenterology. 1957 Jul;33(1):71–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedrick J. A., Pandey J. P., Verkasalo M., Teppo A. M., Fudenberg H. H. Immunoglobulin allotypes and the immune response to wheat gliadin in a Finnish population with celiac disease. Exp Clin Immunogenet. 1985;2(4):185–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaarder P. I., Natvig J. B. Distribution of isotypic and allotypic human IgG antigens in non-human primates. J Immunol. 1974 Aug;113(2):635–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferis R., Reimer C. B., Skvaril F., de Lange G., Ling N. R., Lowe J., Walker M. R., Phillips D. J., Aloisio C. H., Wells T. W. Evaluation of monoclonal antibodies having specificity for human IgG sub-classes: results of an IUIS/WHO collaborative study. Immunol Lett. 1985;10(3-4):223–252. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(85)90082-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kett K., Brandtzaeg P. Local IgA subclass alterations in ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease of the colon. Gut. 1987 Aug;28(8):1013–1021. doi: 10.1136/gut.28.8.1013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kett K., Rognum T. O., Brandtzaeg P. Mucosal subclass distribution of immunoglobulin G-producing cells is different in ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease of the colon. Gastroenterology. 1987 Nov;93(5):919–924. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)90552-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDermott R. P., Nash G. S., Bertovich M. J., Mohrman R. F., Kodner I. J., Delacroix D. L., Vaerman J. P. Altered patterns of secretion of monomeric IgA and IgA subclass 1 by intestinal mononuclear cells in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 1986 Aug;91(2):379–385. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90572-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rautonen N., Pelkonen J., Sipinen S., Käyhty H., Mäkelä O. Isotype concentrations of human antibodies to group A meningococcal polysaccharide. J Immunol. 1986 Oct 15;137(8):2670–2675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawcliffe P. M., Jewell D. P., Faux J. A. Specific IgG subclass antibodies, IgE and IgG S-TS antibodies to wheat gluten fraction B in patients with coeliac disease. Clin Allergy. 1985 Mar;15(2):155–162. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1985.tb02268.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rognum T. O., Brandtzaeg P., Baklien K., Hognestad J. Immunoglobulin-producing cells in the "transitional" mucosa adjacent to adenocarcinomas of the human large bowel. Int J Cancer. 1979 Feb;23(2):165–173. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910230205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rognum T. O., Brandtzaeg P. IgE-positive cells in human intestinal mucosa are mainly mast cells. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1989;89(2-3):256–260. doi: 10.1159/000234956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott H., Ek J., Baklien K., Brandtzaeg P. Immunoglobulin-producing cells in jejunal mucosa of children with coeliac disease on a gluten-free diet and after gluten challenge. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1980;15(1):81–88. doi: 10.3109/00365528009181436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott H., Fausa O., Ek J., Brandtzaeg P. Immune response patterns in coeliac disease. Serum antibodies to dietary antigens measured by an enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Jul;57(1):25–32. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott H., Rognum T. O., Brandtzaeg P. Performance testing of antigen-coated polystyrene microplates for ELISA measurements of serum antibodies to bacterial and dietary antigens. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand C. 1985 Jun;93(3):117–123. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1985.tb02932.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott H., Rognum T. O., Midtvedt T., Brandtzaeg P. Age-related changes of human serum antibodies to dietary and colonic bacterial antigens measured by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand C. 1985 Apr;93(2):65–70. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1985.tb02924.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelberg H. L. Biological activities of immunoglobulins of different classes and subclasses. Adv Immunol. 1974;19(0):259–294. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60254-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unkeless J. C., Fleit H., Mellman I. S. Structural Aspects and Heterogeneity of Immunoglobulin Fc Receptors. Adv Immunol. 1981;31:247–270. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60922-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker L., Johnson G. D., MacLennan I. C. The IgG subclass responses of human lymphocytes to B-cell activators. Immunology. 1983 Oct;50(2):269–272. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J. B., Austin R. K., Schanfield M. S., Kagnoff M. F. Gluten-sensitive enteropathy. Immunoglobulin G heavy-chain (Gm) allotypes and the immune response to wheat gliadin. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):96–101. doi: 10.1172/JCI110988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]