Abstract
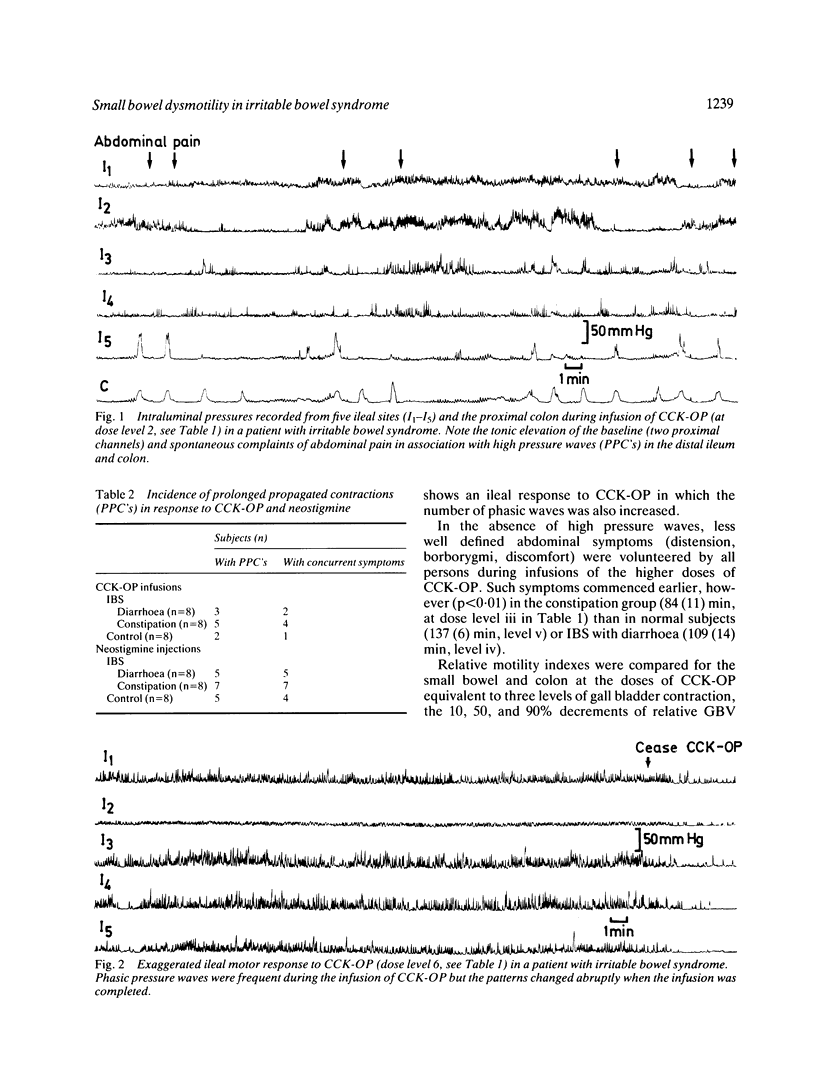
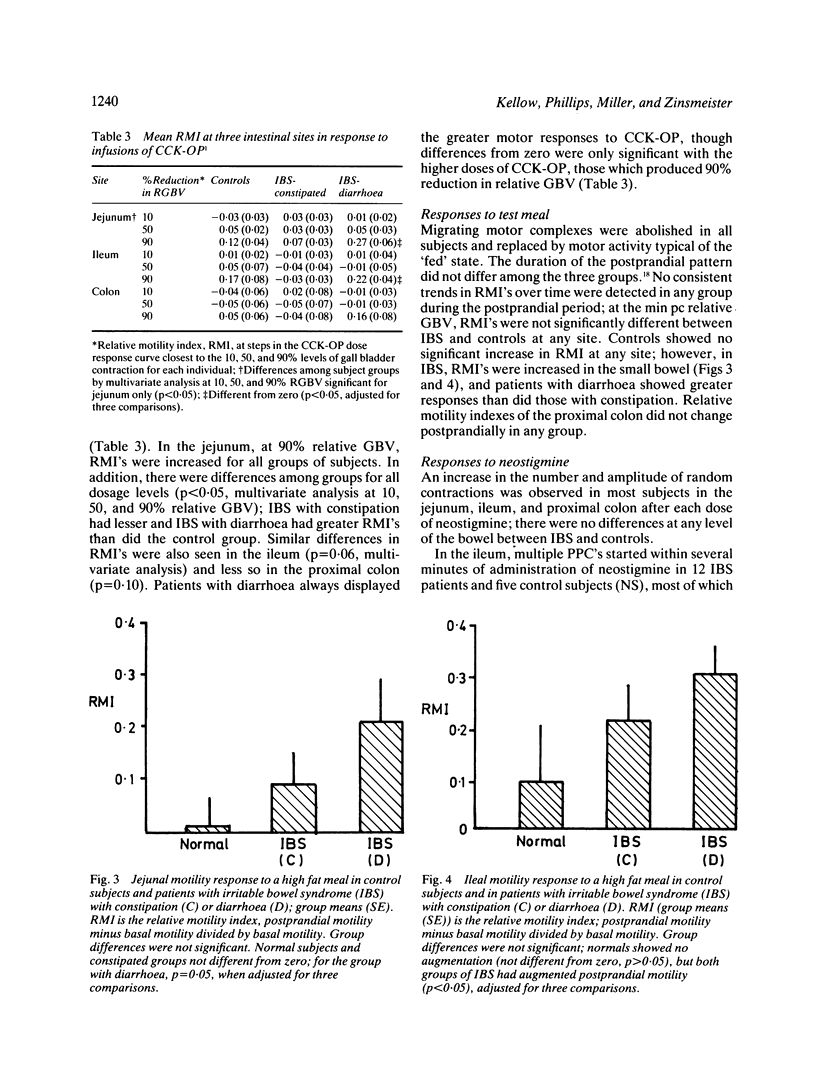
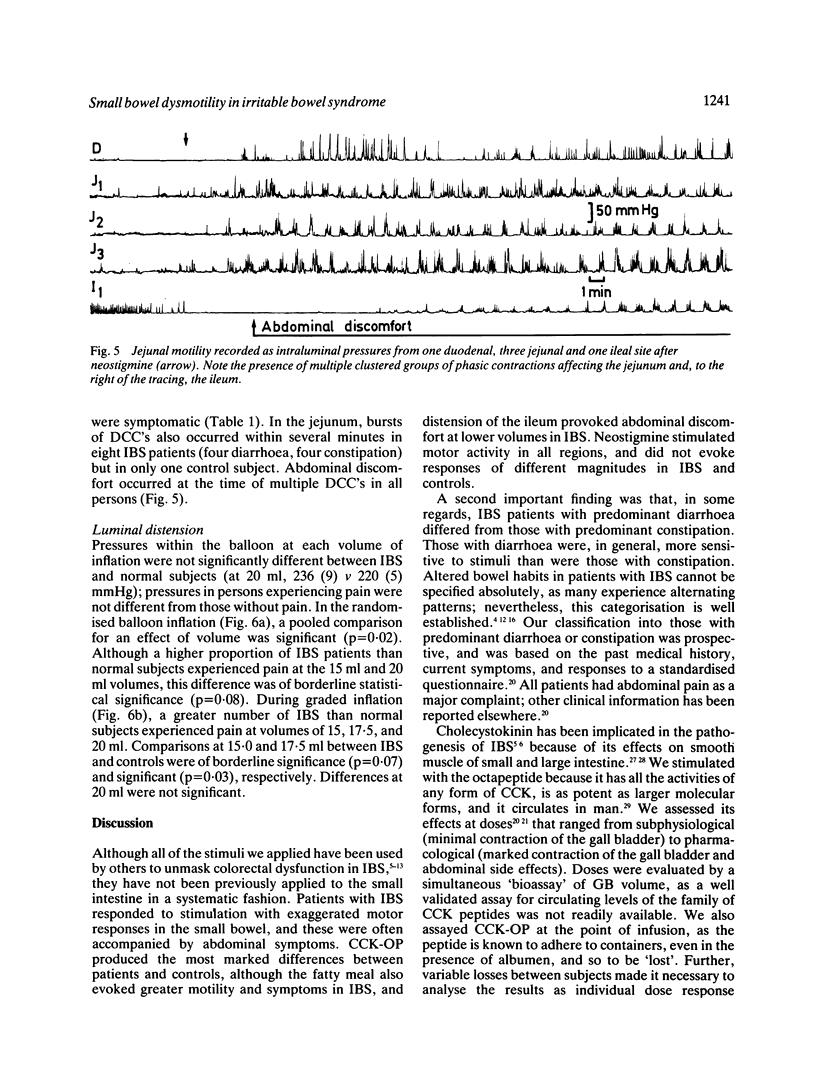
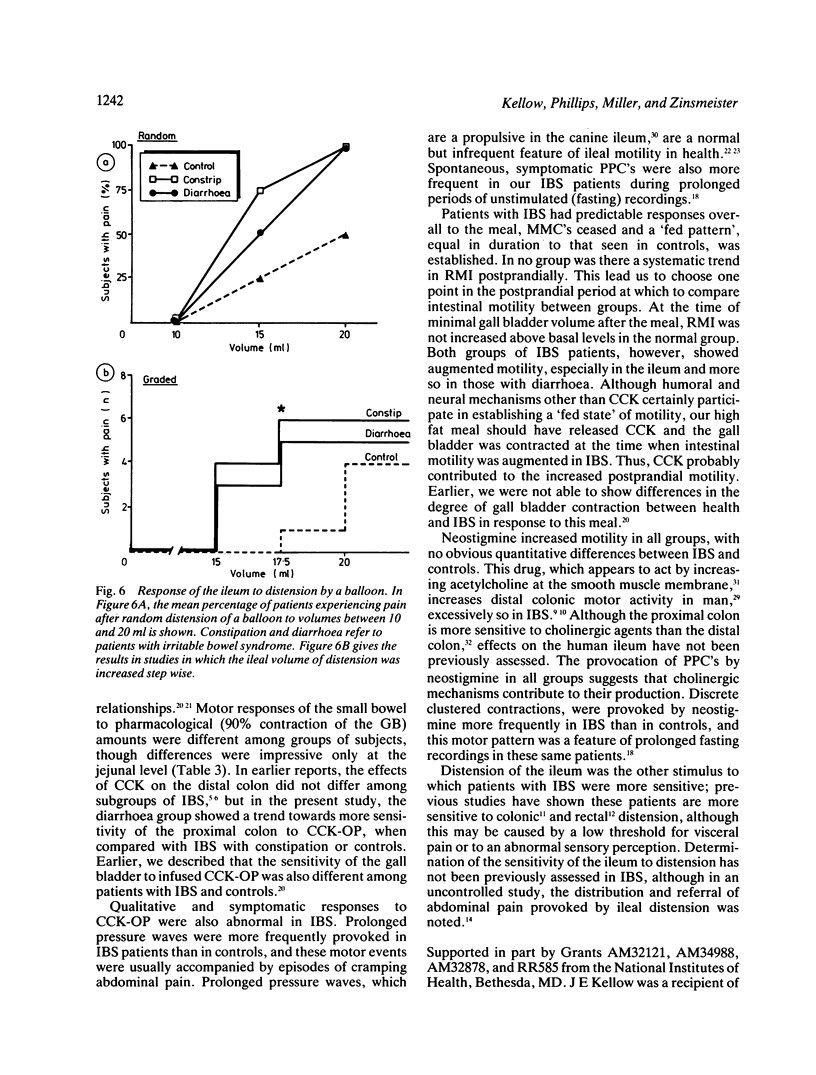
Though the pathophysiology of the irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is commonly attributed to dysfunction of the large intestine, evidence exists to incriminate the small bowel. In order to further explore the role of the small bowel in IBS several stimuli were applied, in an attempt to unmask the dysmotility of the jejunum and ileum. These included infusions of cholecystokinin-octapeptide (CCK-OP), a high fat meal, neostigmine and balloon distension of the ileum. Three groups (n = 8) each of age and sex matched healthy volunteers were studied; patients with IBS complained of predominant constipation (n = 8) or diarrhoea (n = 8). Patients with IBS responded excessively to stimulation by CCK-OP, fatty meal, and ileal distension. In general patients with diarrhoea were more sensitive to stimuli than those with constipation. The ileum responded more to stimulation than the jejunum. As in the large bowel, stimuli appear to unmask intestinal dysmotility in patients with IBS. Motor abnormalities were often accompanied by abdominal symptoms, raising the possibility that dysfunction of the small bowel contributes to the symptoms of IBS.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bueno L., Fioramonti J., Ruckebusch Y., Frexinos J., Coulom P. Evaluation of colonic myoelectrical activity in health and functional disorders. Gut. 1980 Jun;21(6):480–485. doi: 10.1136/gut.21.6.480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHAUDHARY N. A., TRUELOVE S. C. Human colonic motility: a comparative study of normal subjects, patients with ulcerative colitis, and patients with the irritable colon syndrome. II. The effect of prostigmin. Gastroenterology. 1961 Jan;40:18–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONNELL A. M., JONES F. A., ROWLANDS E. N. MOTILITY OF THE PELVIC COLON. IV. ABDOMINAL PAIN ASSOCIATED WITH COLONIC HYPERMOTILITY AFTER MEALS. Gut. 1965 Apr;6:105–112. doi: 10.1136/gut.6.2.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONNELL A. M. The motility of the pelvic colon. II. Paradoxical motility in diarrhoea and constipation. Gut. 1962 Dec;3:342–348. doi: 10.1136/gut.3.4.342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cann P. A., Read N. W., Brown C., Hobson N., Holdsworth C. D. Irritable bowel syndrome: relationship of disorders in the transit of a single solid meal to symptom patterns. Gut. 1983 May;24(5):405–411. doi: 10.1136/gut.24.5.405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everson G. T., Braverman D. Z., Johnson M. L., Kern F., Jr A critical evaluation of real-time ultrasonography for the study of gallbladder volume and contraction. Gastroenterology. 1980 Jul;79(1):40–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINK S., FRIEDMAN G. The differential effect of drugs on the proximal and distal colon. Am J Med. 1960 Apr;28:534–540. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(60)90147-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutiérrez J. G., Chey W. Y., Dinoso V. P. Actions of cholecystokinin and secretin on the motor activity of the small intestine in man. Gastroenterology. 1974 Jul;67(1):35–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey R. F., Read A. E. Effect of cholecystokinin on colonic motility and symptoms in patients with the irritable-bowel syndrome. Lancet. 1973 Jan 6;1(7793):1–3. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)91219-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellow J. E., Borody T. J., Phillips S. F., Tucker R. L., Haddad A. C. Human interdigestive motility: variations in patterns from esophagus to colon. Gastroenterology. 1986 Aug;91(2):386–395. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90573-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellow J. E., Miller L. J., Phillips S. F., Haddad A. C., Zinsmeister A. R., Charboneau J. W. Sensitivities of human jejunum, ileum, proximal colon, and gallbladder to cholecystokinin octapeptide. Am J Physiol. 1987 Mar;252(3 Pt 1):G345–G356. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1987.252.3.G345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellow J. E., Miller L. J., Phillips S. F., Zinsmeister A. R., Charboneau J. W. Altered sensitivity of the gallbladder to cholecystokinin octapeptide in irritable bowel syndrome. Am J Physiol. 1987 Nov;253(5 Pt 1):G650–G655. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1987.253.5.G650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellow J. E., Phillips S. F. Altered small bowel motility in irritable bowel syndrome is correlated with symptoms. Gastroenterology. 1987 Jun;92(6):1885–1893. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)90620-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruis W., Azpiroz F., Phillips S. F. Contractile patterns and transit of fluid in canine terminal ileum. Am J Physiol. 1985 Aug;249(2 Pt 1):G264–G270. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1985.249.2.G264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar D., Wingate D. L. The irritable bowel syndrome: a paroxysmal motor disorder. Lancet. 1985 Nov 2;2(8462):973–977. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)90525-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasser R. B., Bond J. H., Levitt M. D. The role of intestinal gas in functional abdominal pain. N Engl J Med. 1975 Sep 11;293(11):524–526. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197509112931103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latimer P., Sarna S., Campbell D., Latimer M., Waterfall W., Daniel E. E. Colonic motor and myoelectrical activity: a comparative study of normal subjects, psychoneurotic patients, and patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology. 1981 May;80(5 Pt 1):893–901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. J., Jardine I., Weissman E., Go V. L., Speicher D. Characterization of cholecystokinin from the human brain. J Neurochem. 1984 Sep;43(3):835–840. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb12806.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriarty K. J., Dawson A. M. Functional abdominal pain: further evidence that whole gut is affected. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1982 Jun 5;284(6330):1670–1672. doi: 10.1136/bmj.284.6330.1670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quigley E. M., Borody T. J., Phillips S. F., Wienbeck M., Tucker R. L., Haddad A. Motility of the terminal ileum and ileocecal sphincter in healthy humans. Gastroenterology. 1984 Oct;87(4):857–866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snape W. J., Jr, Carlson G. M., Cohen S. Colonic myoelectric activity in the irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology. 1976 Mar;70(3):326–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snape W. J., Jr, Carlson G. M., Cohen S. Human colonic myoelectric activity in response to prostigmin and the gastrointestinal hormones. Am J Dig Dis. 1977 Oct;22(10):881–887. doi: 10.1007/BF01076164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snape W. J., Jr, Carlson G. M., Matarazzo S. A., Cohen S. Evidence that abnormal myoelectrical activity produces colonic motor dysfunction in the irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology. 1977 Mar;72(3):383–387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan M. A., Cohen S., Snape W. J., Jr Colonic myoelectrical activity in irritable-bowel syndrome. Effect of eating and anticholinergics. N Engl J Med. 1978 Apr 20;298(16):878–883. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197804202981604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swarbrick E. T., Hegarty J. E., Bat L., Williams C. B., Dawson A. M. Site of pain from the irritable bowel. Lancet. 1980 Aug 30;2(8192):443–446. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)91885-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WANGEL A. G., DELLER D. J. INTESTINAL MOTILITY IN MAN. 3. MECHANISMS OF CONSTIPATION AND DIARRHEA WITH PARTICULAR REFERENCE TO THE IRRITABLE COLON SYNDROME. Gastroenterology. 1965 Jan;48:69–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh J. H., Lamers C. B., Valenzuela J. E. Cholecystokinin-octapeptidelike immunoreactivity in human plasma. Gastroenterology. 1982 Mar;82(3):438–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead W. E., Engel B. T., Schuster M. M. Irritable bowel syndrome: physiological and psychological differences between diarrhea-predominant and constipation-predominant patients. Dig Dis Sci. 1980 Jun;25(6):404–413. doi: 10.1007/BF01395503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whorwell P. J., Lupton E. W., Erduran D., Wilson K. Bladder smooth muscle dysfunction in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Gut. 1986 Sep;27(9):1014–1017. doi: 10.1136/gut.27.9.1014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wienbeck M., Christensen J. Effects of some drugs on electrical activity of the isolated colon of the cat. Gastroenterology. 1971 Oct;61(4):470–478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


