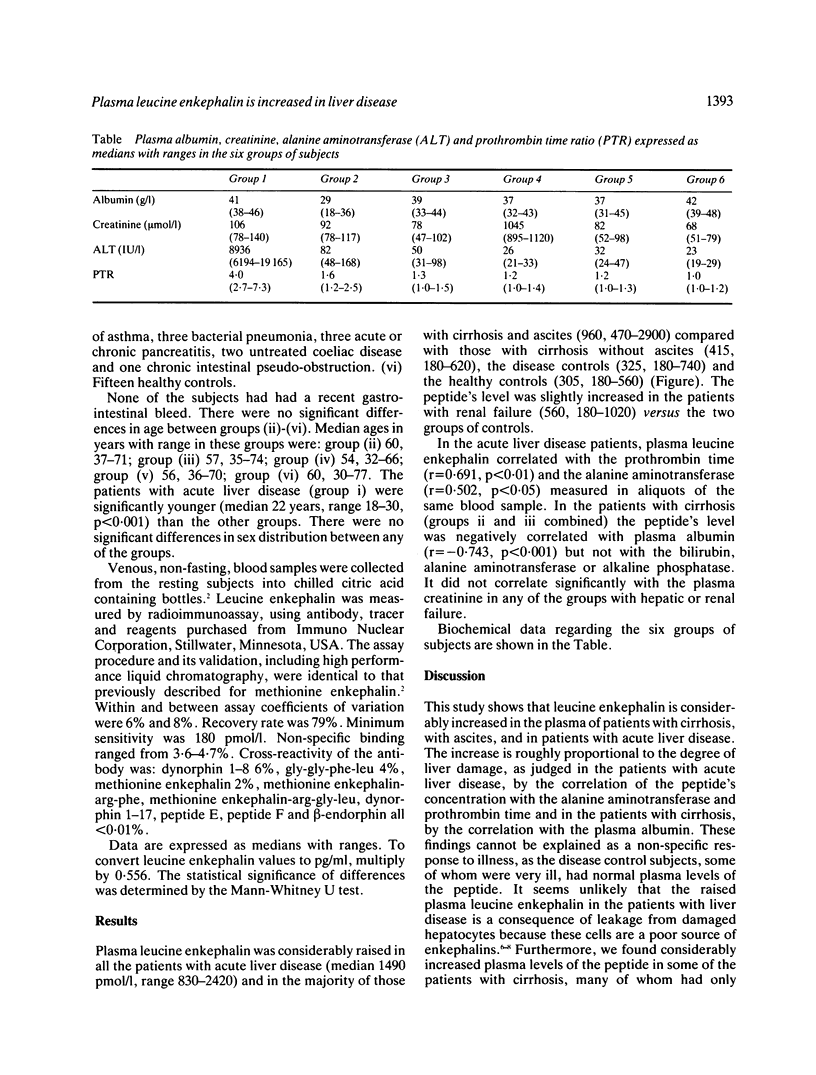
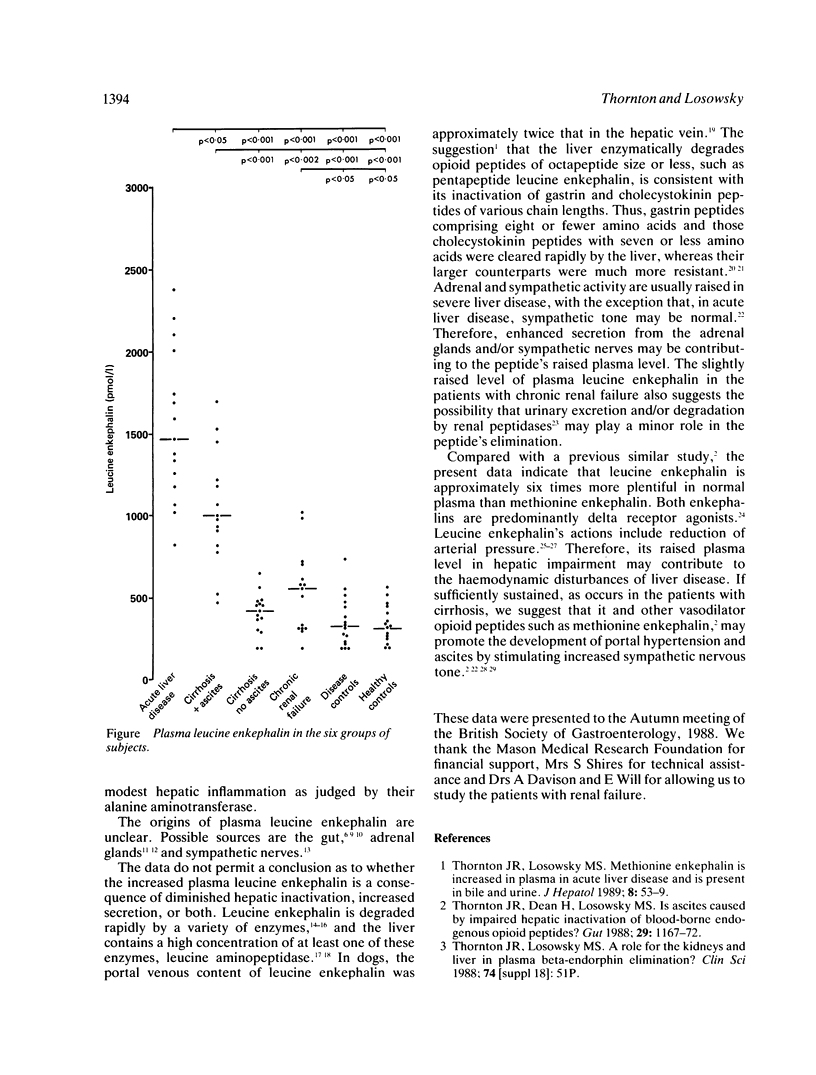
Abstract
Plasma methionine enkephalin is increased in liver disease and may contribute to some of the clinical manifestations of hepatic failure. To determine if another 'small' opioid peptide is increased in the plasma of patients with liver disease, leucine enkephalin was measured by radioimmunoassay. Its plasma concentration was raised approximately five-fold in patients with acute liver disease (median 1490 pmol/l, range 830-2420) and three-fold in patients with cirrhosis with ascites (960 pmol/l, 470-2900), compared with disease controls (325 pmol/l, 180-740) and healthy controls (305 pmol/l, 180-560). The increase in plasma leucine enkephalin was proportional to the degree of liver damage, as judged in the patients with acute liver disease by its correlation with the prothrombin time (r = 0.691, p less than 0.01) and alanine aminotransferase (r = 0.502, p less than 0.05), and in the patients with cirrhosis by its negative correlation with the plasma albumin (r = -0.743, p less than 0.001). It is unclear whether the raised plasma leucine enkephalin in liver disease is a consequence of diminished hepatic inactivation, increased secretion from sympathetic nerves and adrenal glands, or both.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Doyle J. W., Wolfe M. M., McGuigan J. E. Hepatic clearance of gastrin and cholecystokinin peptides. Gastroenterology. 1984 Jul;87(1):60–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell L. D., Harrison T. S., Demers L. M. Immunoreactive met-enkephalin in the canine adrenal; response to acute hypovolemic stress. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1983 Sep;173(4):515–518. doi: 10.3181/00379727-173-41680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feurle G. E., Helmstaedter V., Weber U. Met- and leu-enkephalin immuno- and bio-reactivity in human stomach and pancreas. Life Sci. 1982 Dec 27;31(26):2961–2969. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90062-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman A., Clement-Jones V. Opiate receptors: enkephalins and endorphins. Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 Mar;12(1):31–56. doi: 10.1016/s0300-595x(83)80028-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanbauer I., Kelly G. D., Saiani L., Yang H. Y. [Met5]-enkephalin-like peptides of the adrenal medulla: release by nerve stimulation and functional implications. Peptides. 1982 May-Jun;3(3):469–473. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(82)90109-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hersh L. B. Reaction of opioid peptides with neutral endopeptidase ("enkephalinase"). J Neurochem. 1984 Aug;43(2):487–493. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb00925.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J. Isolation of an endogenous compound from the brain with pharmacological properties similar to morphine. Brain Res. 1975 May 2;88(2):295–308. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90391-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J., Kosterlitz H. W., Smith T. W. The distribution of methionine-enkephalin and leucine-enkephalin in the brain and peripheral tissues. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Dec;61(4):639–647. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1977.tb07557.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laasberg L. H., Johnson E. E., Hedley-Whyte J. Effect of morphine and naloxone on leu-enkephalin-like immunoreactivity in dogs. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1980 Mar;212(3):496–502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livett B. G., Dean D. M., Whelan L. G., Udenfriend S., Rossier J. Co-release of enkephalin and catecholamines from cultured adrenal chromaffin cells. Nature. 1981 Jan 22;289(5795):317–319. doi: 10.1038/289317a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malfroy B., Schwartz J. C. Purification and substrate specificity of rat kidney "enkephalinase". Life Sci. 1982 Oct 18;31(16-17):1745–1748. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90200-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreau R., Lee S. S., Hadengue A., Braillon A., Lebrec D. Hemodynamic effects of a clonidine-induced decrease in sympathetic tone in patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology. 1987 Jan-Feb;7(1):149–154. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840070129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NACHLAS M. M., CRAWFORD D. T., SELIGMAN A. M. The histochemical demonstration of leucine aminopeptidase. J Histochem Cytochem. 1957 May;5(3):264–278. doi: 10.1177/5.3.264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh R. N., Murray-Lyon I. M., Dawson J. L., Pietroni M. C., Williams R. Transection of the oesophagus for bleeding oesophageal varices. Br J Surg. 1973 Aug;60(8):646–649. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800600817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUTENBURG A. M., GOLDBARG J. A., PINEDA E. P. Leucine aminopeptidase activity; observations in patients with cancer of the pancreas and other diseases. N Engl J Med. 1958 Sep 4;259(10):469–472. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195809042591003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roscetti G., Possenti R., Bassano E., Roda L. G. Mechanisms of leu-enkephalin hydrolysis in human plasma. Neurochem Res. 1985 Oct;10(10):1393–1404. doi: 10.1007/BF00964980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto M., Nakao K., Yoshimasa T., Ikeda Y., Suda M., Takasu K., Shimbo S., Yanaihara N., Imura H. Occurrence of methionine-enkephalin-Arg6-Gly7-Leu8 with methionine-enkephalin, leucine-enkephalin and methionine-enkephalin-Arg6-Phe7 in human gastric antrum. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 Jan;56(1):202–204. doi: 10.1210/jcem-56-1-202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaz K., Stock G., Simon W., Schlör K. H., Unger T., Rockhold R., Ganten D. Enkephalin effects on blood pressure, heart rate, and baroreceptor reflex. Hypertension. 1980 Jul-Aug;2(4):395–407. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.2.4.395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultzberg M., Hökfelt T., Lundberg J. M., Terenius L., Elfvin L. G., Elde R. Enkephalin-like immunoreactivity in nerve terminals in sympathetic ganglia and adrenal medulla and in adrenal medullary gland cells. Acta Physiol Scand. 1978 Aug;103(4):475–477. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1978.tb06243.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strunz U. T., Thompson M. R., Elashoff J., Grossman M. I. Hepatic inactivation of gastrins of various chain lengths in dogs. Gastroenterology. 1978 Mar;74(3):550–553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang J., Yang H. Y., Costa E. Distribution of met5-enkephalin-Arg6-Phe7 (MEAP) in various tissues of rats and guinea pigs. Life Sci. 1982 Nov 15;31(20-21):2303–2306. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90143-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornton J. R., Dean H. G., Losowsky M. S. Do increased catecholamines and plasma methionine enkephalin in cirrhosis promote bleeding oesophageal varices? Q J Med. 1988 Jul;68(255):541–551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornton J. R., Dean H., Losowsky M. S. Is ascites caused by impaired hepatic inactivation of blood borne endogenous opioid peptides? Gut. 1988 Sep;29(9):1167–1172. doi: 10.1136/gut.29.9.1167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornton J. R., Losowsky M. S. Methionine enkephalin is increased in plasma in acute liver disease and is present in bile and urine. J Hepatol. 1989 Jan;8(1):53–59. doi: 10.1016/0168-8278(89)90161-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornton J. R., Losowsky M. S. Opioid peptides and primary biliary cirrhosis. BMJ. 1988 Dec 10;297(6662):1501–1504. doi: 10.1136/bmj.297.6662.1501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viveros O. H., Diliberto E. J., Jr, Hazum E., Chang K. J. Opiate-like materials in the adrenal medulla: evidence for storage and secretion with catecholamines. Mol Pharmacol. 1979 Nov;16(3):1101–1108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willett I. R., Esler M., Jennings G., Dudley F. J. Sympathetic tone modulates portal venous pressure in alcoholic cirrhosis. Lancet. 1986 Oct 25;2(8513):939–943. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90599-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


