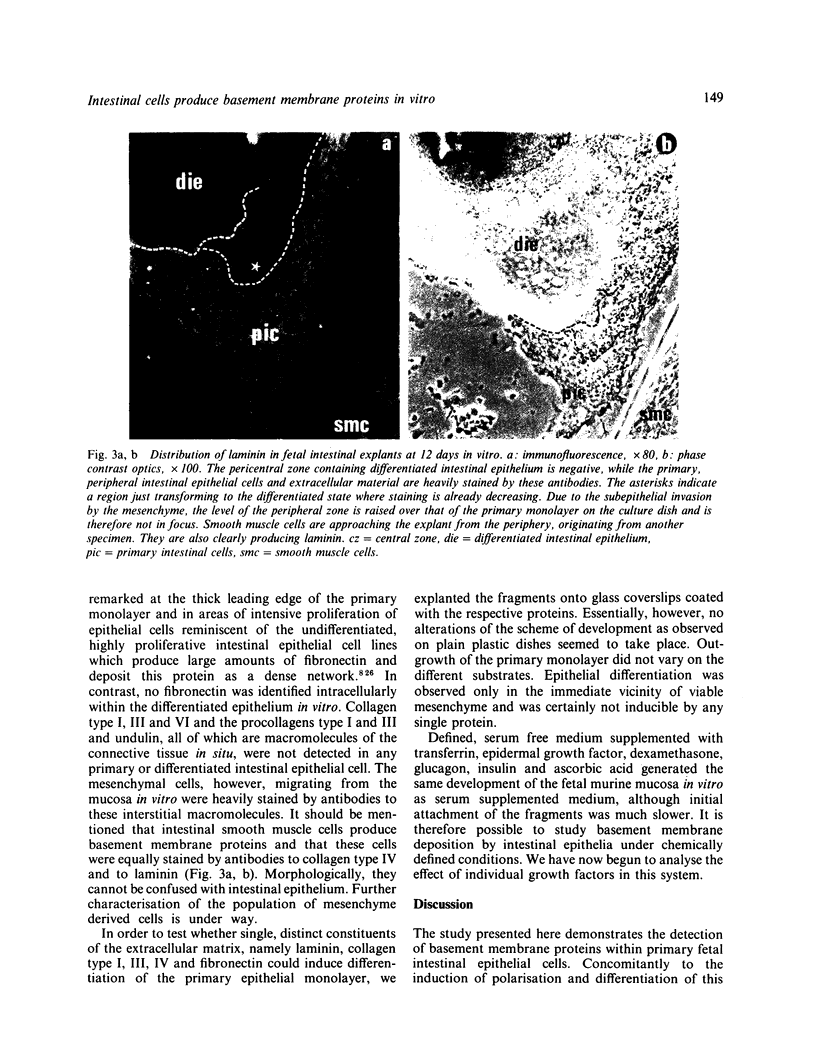
Abstract
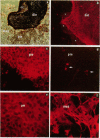
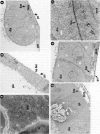
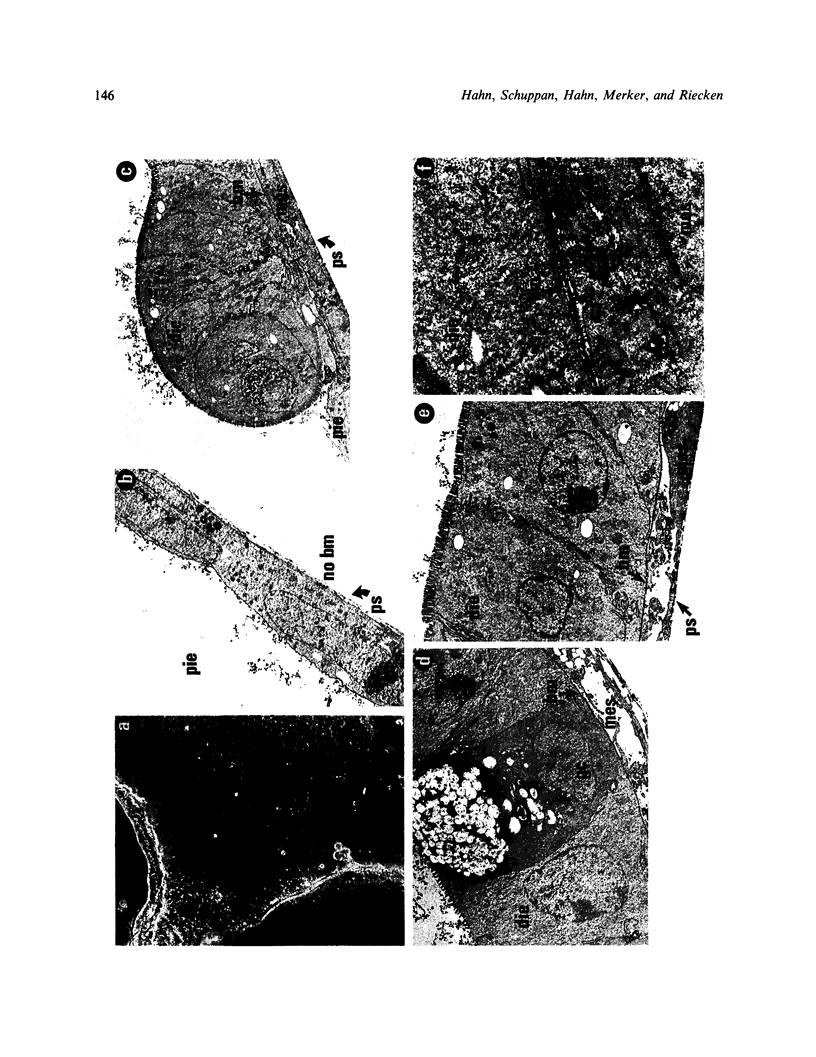
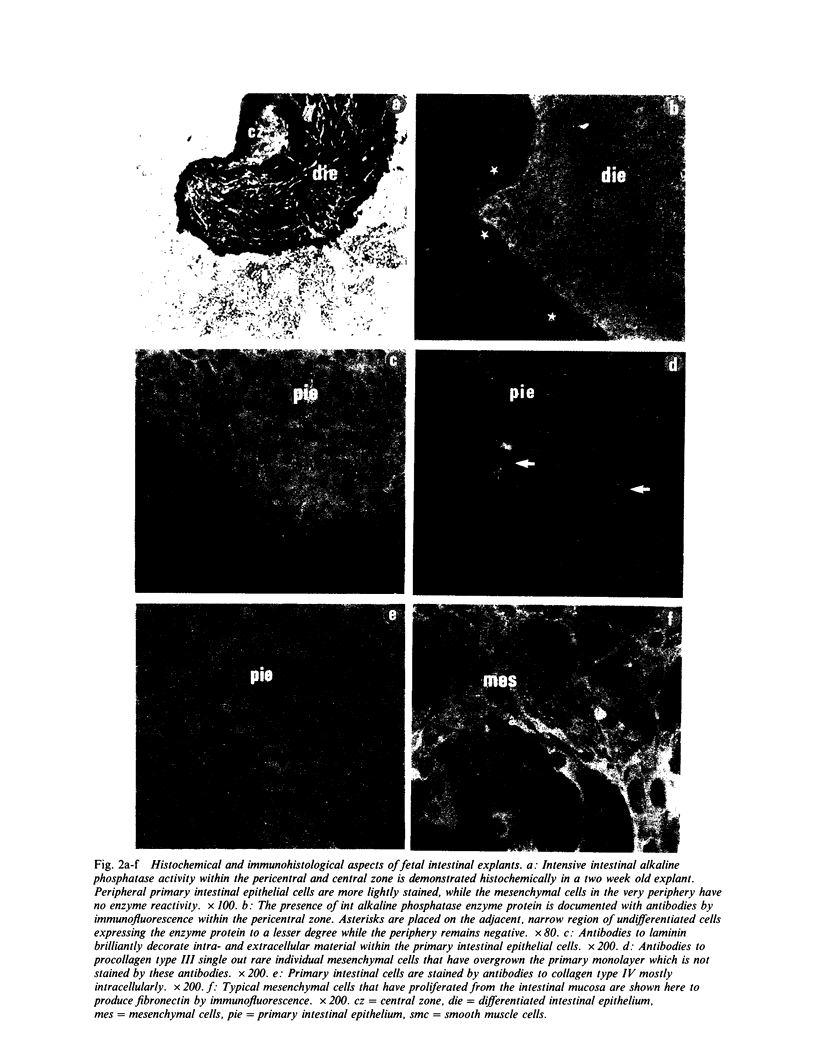
The epithelial-mesenchymal interface of the intestinal mucosa obviously plays an important role in supporting the mucosal architecture. Its significance for the process of migration and differentiation of the epithelial cells remains to be resolved. It consists of a basement membrane, the anchoring zone and the subepithelial connective tissue, the origin of which is unknown. We therefore established an in vitro model to study the development of the endodermal-mesenchymal interface of the fetal human and murine intestinal mucosa. The distribution of the interstitial collagens type I, III, VI and procollagen type III as well as the basement membrane components collagen type IV and laminin was investigated immunohistochemically in these fetal explant cultures. The cultures were also adapted to serum free culture conditions. It was evident that while laminin and collagen type IV could be detected in the primary intestinal epithelium, the formation of an authentic basement membrane required the presence of both the epithelial and the mesenchymal cells. Interstitial collagens and procollagen type III were produced exclusively by the mesenchymal cells. Basement membrane formation in vitro coincided with cytodifferentiation of the endodermal cells as betrayed by electron microscopy and the activity of brush border enzymes. In conclusion, the maturation of the endoderm and the formation of the subepithelial basement membrane require the intimate proximity of viable mesenchyme in vitro.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ekblom P., Alitalo K., Vaheri A., Timpl R., Saxén L. Induction of a basement membrane glycoprotein in embryonic kidney: possible role of laminin in morphogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):485–489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekblom P., Vestweber D., Kemler R. Cell-matrix interactions and cell adhesion during development. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:27–47. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.000331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutschmidt S., Kaul W., Riecken E. O. A quantitative histochemical technique for the characterisation of alpha-glucosidases in the brush-border membrane of rat jejunum. Histochemistry. 1979 Sep;63(1):81–101. doi: 10.1007/BF00508014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutschmidt S., Lange U., Riecken E. O. "In situ"--measurements of protein contents in the brush border region along rat jejunal villi and their correlations with four enzyme activities. Histochemistry. 1981;72(3):467–479. doi: 10.1007/BF00501789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haffen K., Lacroix B., Kedinger M., Simon-Assmann P. M. Inductive properties of fibroblastic cell cultures derived from rat intestinal mucosa on epithelial differentiation. Differentiation. 1983;23(3):226–233. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1982.tb01287.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hand P. H., Thor A., Schlom J., Rao C. N., Liotta L. Expression of laminin receptor in normal and carcinomatous human tissues as defined by a monoclonal antibody. Cancer Res. 1985 Jun;45(6):2713–2719. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye G. I., Lane N., Pascal R. R. Colonic pericryptal fibroblast sheath: replication, migration, and cytodifferentiation of a mesenchymal cell system in adult tissue. II. Fine structural aspects of normal rabbit and human colon. Gastroenterology. 1968 May;54(5):852–865. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedinger M., Simon-Assmann P. M., Lacroix B., Marxer A., Hauri H. P., Haffen K. Fetal gut mesenchyme induces differentiation of cultured intestinal endodermal and crypt cells. Dev Biol. 1986 Feb;113(2):474–483. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90183-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinman H. K., Cannon F. B., Laurie G. W., Hassell J. R., Aumailley M., Terranova V. P., Martin G. R., DuBois-Dalcq M. Biological activities of laminin. J Cell Biochem. 1985;27(4):317–325. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240270402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinman H. K., Klebe R. J., Martin G. R. Role of collagenous matrices in the adhesion and growth of cells. J Cell Biol. 1981 Mar;88(3):473–485. doi: 10.1083/jcb.88.3.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacroix B., Kedinger M., Simon-Assmann P. M., Haffen K. Effects of human fetal gastroenteric mesenchymal cells on some developmental aspects of animal gut endoderm. Differentiation. 1984;28(2):129–135. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1984.tb00276.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurie G. W., Leblond C. P., Martin G. R. Localization of type IV collagen, laminin, heparan sulfate proteoglycan, and fibronectin to the basal lamina of basement membranes. J Cell Biol. 1982 Oct;95(1):340–344. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.1.340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh M. N., Trier J. S. Morphology and cell proliferation of subepithelial fibroblasts in adult mouse jejunum. I. Structural features. Gastroenterology. 1974 Oct;67(4):622–635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. R., Kleinman H. K., Terranova V. P., Ledbetter S., Hassell J. R. The regulation of basement membrane formation and cell-matrix interactions by defined supramolecular complexes. Ciba Found Symp. 1984;108:197–212. doi: 10.1002/9780470720899.ch13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. R., Kleinman H. K. The extracellular matrix in development and in disease. Semin Liver Dis. 1985 May;5(2):147–156. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1063919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Hernandez A., Amenta P. S. The basement membrane in pathology. Lab Invest. 1983 Jun;48(6):656–677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathan M., Hermos J. A., Trier J. S. Structural features of the epithelio-mesenchymal interface of rat duodenal mucosa during development. J Cell Biol. 1972 Mar;52(3):577–588. doi: 10.1083/jcb.52.3.577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merker H. J., Barrach H. J. The morphology of basement membrane formation. Eur J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;26(1):111–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quaroni A. Development of fetal rat intestine in organ and monolayer culture. J Cell Biol. 1985 May;100(5):1611–1622. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.5.1611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quaroni A., Isselbacher K. J., Ruoslahti E. Fibronectin synthesis by epithelial crypt cells of rat small intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5548–5552. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quaroni A., Trelstad R. L. Biochemical characterization of collagens synthesized by intestinal epithelial cell cultures. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 10;255(17):8351–8361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quaroni A., Wands J., Trelstad R. L., Isselbacher K. J. Epithelioid cell cultures from rat small intestine. Characterization by morphologic and immunologic criteria. J Cell Biol. 1979 Feb;80(2):248–265. doi: 10.1083/jcb.80.2.248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risteli J., Bächinger H. P., Engel J., Furthmayr H., Timpl R. 7-S collagen: characterization of an unusual basement membrane structure. Eur J Biochem. 1980;108(1):239–250. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04717.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohde H., Vargas L., Hahn E., Kalbfleisch H., Bruguera M., Timpl R. Radioimmunoassay for type III procollagen peptide and its application to human liver disease. Eur J Clin Invest. 1979 Dec;9(6):451–459. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1979.tb00912.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuppan D., Becker J., Boehm H., Hahn E. G. Immunofluorescent localization of type-V collagen as a fibrillar component of the interstitial connective tissue of human oral mucosa, artery and liver. Cell Tissue Res. 1986;243(3):535–543. doi: 10.1007/BF00218060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuppan D., Besser M., Schwarting R., Hahn E. G. Radioimmunoassay for the carboxy-terminal cross-linking domain of type IV (basement membrane) procollagen in body fluids. Characterization and application to collagen type IV metabolism in fibrotic liver disease. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jul;78(1):241–248. doi: 10.1172/JCI112557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuppan D., Rühlmann T., Hahn E. G. Radioimmunoassay for human type VI collagen and its application to tissue and body fluids. Anal Biochem. 1985 Aug 15;149(1):238–247. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90501-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timpl R., Dziadek M. Structure, development, and molecular pathology of basement membranes. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1986;29:1–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]