Abstract
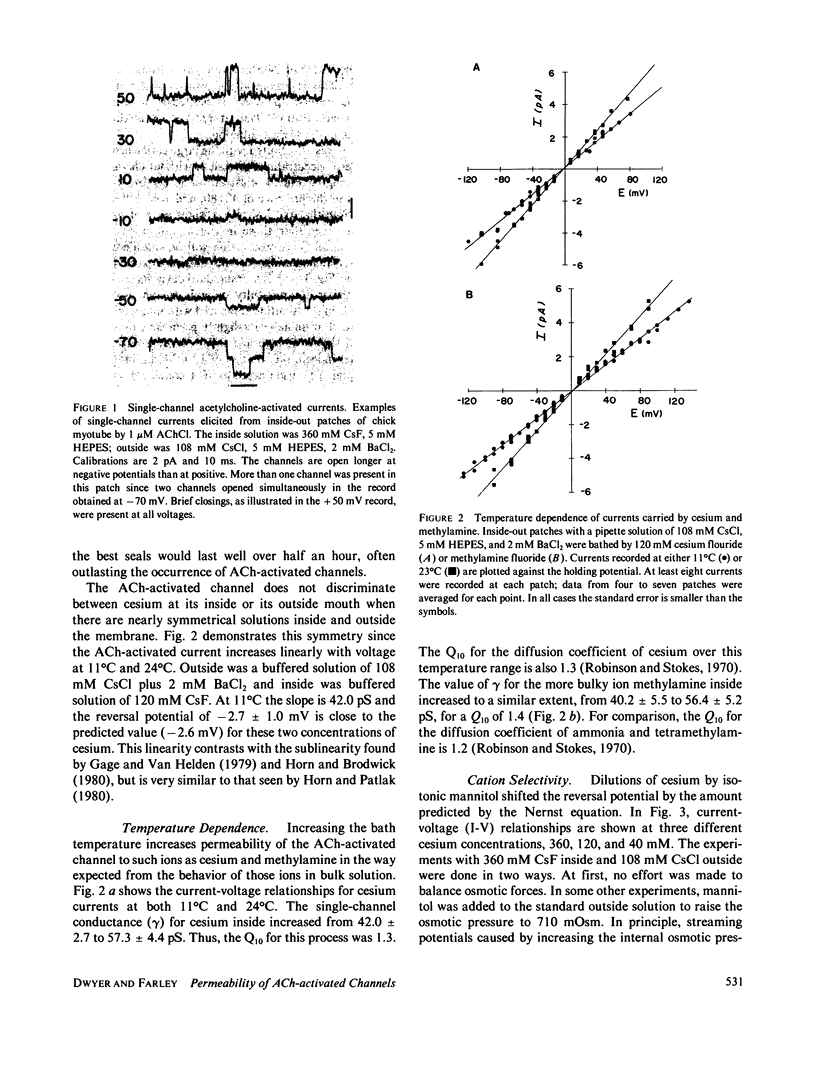
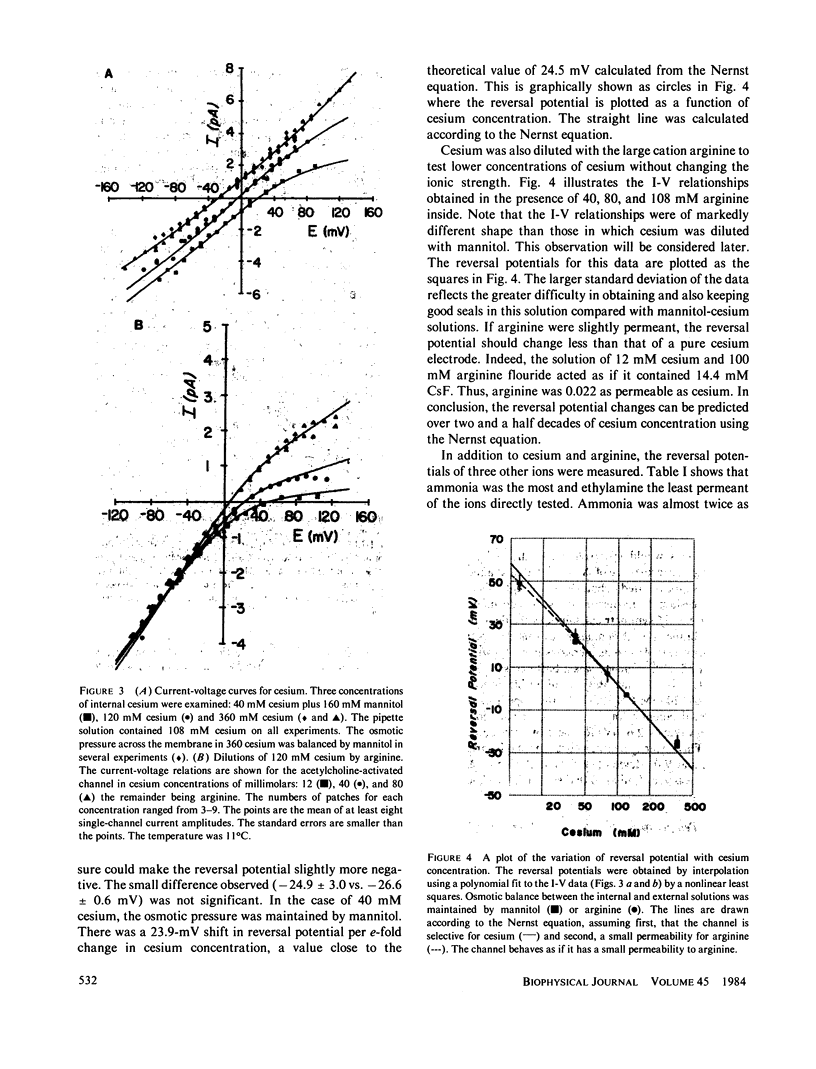
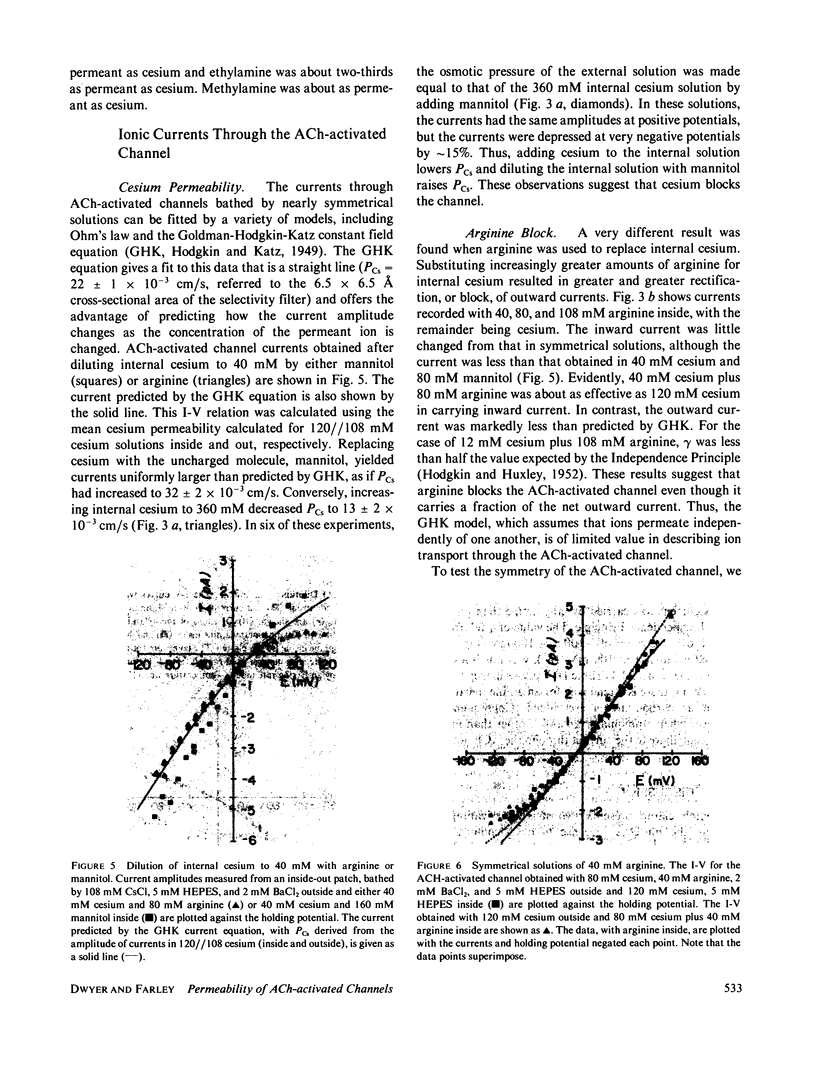
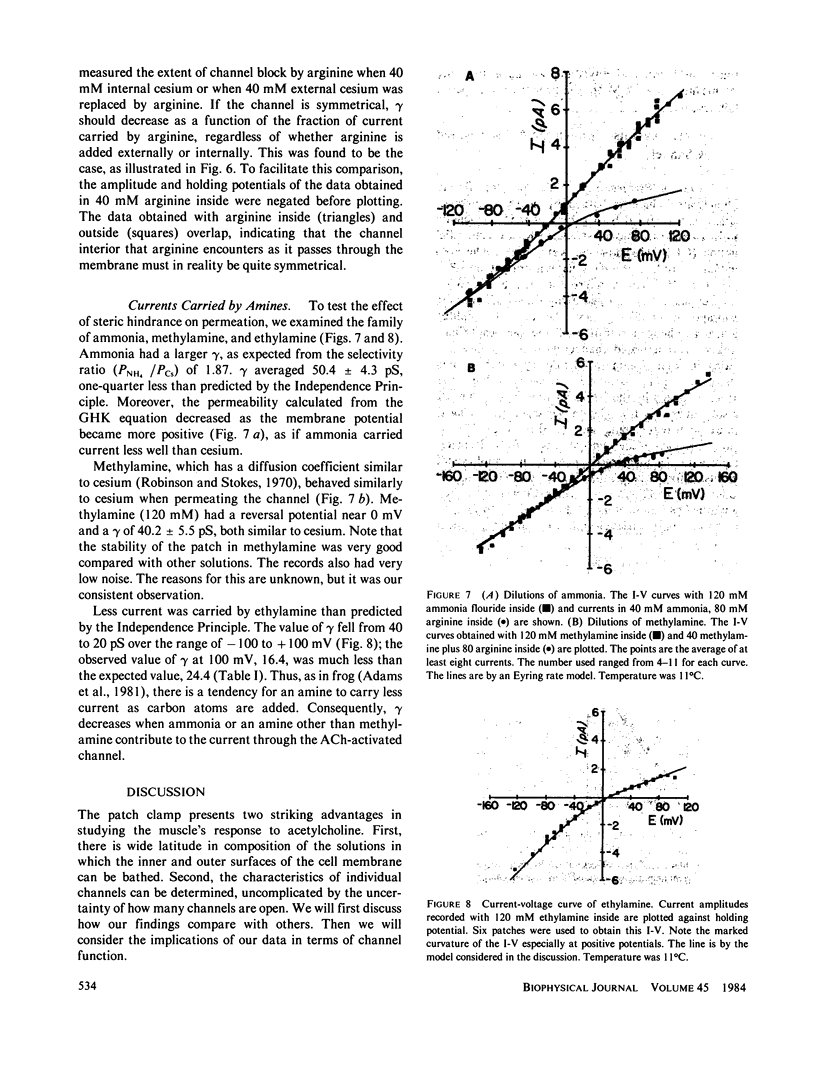
The acetylcholine-(ACh-)activated channels of chick myotubes were studied by the patch-clamp method. Single-channel amplitudes were measured over a wide range of potentials in solutions of cesium, arginine, and three small amines. Symmetrical, isotonic cesium solutions gave a linear I-V relationship with the single-channel conductance, gamma, of 42 pS at 11 degrees C. Dilutions of cesium by mannitol shifted the reversal potential 23.9 mV per e-fold change in internal cesium concentration. Selectivity, as defined by reversal potential criteria, depended on the molecular size of the permeant cation. The Q10 of gamma for the symmetrical isotonic cesium solutions as well as internal isotonic methylamine was 1.3-1.4. These properties are qualitatively similar to those seen at the ACh-activated channel of the frog neuromuscular junction. Partially substituting arginine for internal cesium depressed outward currents. 80 mM arginine acted equally well from the inside or the outside, as if arginine transiently blocks the ACh-activated channel in a current dependent way. Diluting internal cesium almost 10-fold, from 320 to 40 mM, increased the permeability of the channel calculated from Goldman-Hodgkin-Katz equations by almost threefold. Thus, cesium itself appears to block with a dissociation constant of 135 mM. Methylamine blocked the channel approximately as well as did cesium. Ammonia and ethylamine blocked the channel somewhat more than cesium. We conclude that (a) the channel is qualitatively similar to that of frog neuromuscular junction, (b) cations bind within the channel, and (c) arginine decreases channel conductance equally whether applied from the inside or the outside.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. J., Dwyer T. M., Hille B. The permeability of endplate channels to monovalent and divalent metal cations. J Gen Physiol. 1980 May;75(5):493–510. doi: 10.1085/jgp.75.5.493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams D. J., Nonner W., Dwyer T. M., Hille B. Block of endplate channels by permeant cations in frog skeletal muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1981 Dec;78(6):593–615. doi: 10.1085/jgp.78.6.593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson C. R., Stevens C. F. Voltage clamp analysis of acetylcholine produced end-plate current fluctuations at frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1973 Dec;235(3):655–691. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Dionne V. E., Steinbach J. H., Stevens C. F. Conductance of channels opened by acetylcholine-like drugs in muscle end-plate. Nature. 1975 Jan 17;253(5488):204–206. doi: 10.1038/253204a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO L., KATZ B. A study of curare action with an electrical micromethod. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1957 May 7;146(924):339–356. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1957.0015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwyer T. M., Adams D. J., Hille B. The permeability of the endplate channel to organic cations in frog muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1980 May;75(5):469–492. doi: 10.1085/jgp.75.5.469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farley J. M., Yeh J. Z., Watanabe S., Narahashi T. Endplate channel block by guanidine derivatives. J Gen Physiol. 1981 Mar;77(3):273–293. doi: 10.1085/jgp.77.3.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick E. M., Marty A., Neher E. A patch-clamp study of bovine chromaffin cells and of their sensitivity to acetylcholine. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:577–597. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischbach G. D., Lass Y. A transition temperature for acetylcholine channel conductance in chick myoballs. J Physiol. 1978 Jul;280:527–536. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischbach G. D. Synapse formation between dissociated nerve and muscle cells in low density cell cultures. Dev Biol. 1972 Jun;28(2):407–429. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(72)90023-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage P. W., Van Helden D. Effects of permeant monovalent cations on end-plate channels. J Physiol. 1979 Mar;288:509–528. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. Currents carried by sodium and potassium ions through the membrane of the giant axon of Loligo. J Physiol. 1952 Apr;116(4):449–472. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KATZ B. The effect of sodium ions on the electrical activity of giant axon of the squid. J Physiol. 1949 Mar 1;108(1):37–77. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann H. M., Dionne V. E. Temperature dependence of ion permeation at the endplate channel. J Gen Physiol. 1983 May;81(5):687–703. doi: 10.1085/jgp.81.5.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn R., Brodwick M. S. Acetylcholine-induced current in perfused rat myoballs. J Gen Physiol. 1980 Mar;75(3):297–321. doi: 10.1085/jgp.75.3.297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn R., Brodwick M. S., Dickey W. D. Asymmetry of the acetylcholine channel revealed by quaternary anesthetics. Science. 1980 Oct 10;210(4466):205–207. doi: 10.1126/science.6251552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn R., Patlak J. Single channel currents from excised patches of muscle membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6930–6934. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang L. Y., Catterall W. A., Ehrenstein G. Selectivity of cations and nonelectrolytes for acetylcholine-activated channels in cultured muscle cells. J Gen Physiol. 1978 Apr;71(4):397–410. doi: 10.1085/jgp.71.4.397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson M. B., Lecar H. Single postsynaptic channel currents in tissue cultured muscle. Nature. 1979 Dec 20;282(5741):863–864. doi: 10.1038/282863a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The statistical nature of the acetycholine potential and its molecular components. J Physiol. 1972 Aug;224(3):665–699. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis C. A. Ion-concentration dependence of the reversal potential and the single channel conductance of ion channels at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1979 Jan;286:417–445. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masukawa L. M., Albuquerque E. X. Voltage- and time-dependent action of histrionicotoxin on the endplate current of the frog muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1978 Sep;72(3):351–367. doi: 10.1085/jgp.72.3.351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W. Calcium-dependent potassium activation in nervous tissues. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1978;7:1–18. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.07.060178.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Steinbach J. H. Local anaesthetics transiently block currents through single acetylcholine-receptor channels. J Physiol. 1978 Apr;277:153–176. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. J., Sachs F. Single ionic channels observed in tissue-cultured muscle. Nature. 1979 Dec 20;282(5741):861–863. doi: 10.1038/282861a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peper K., Bradley R. J., Dreyer F. The acetylcholine receptor at the neuromuscular junction. Physiol Rev. 1982 Oct;62(4 Pt 1):1271–1340. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1982.62.4.1271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


