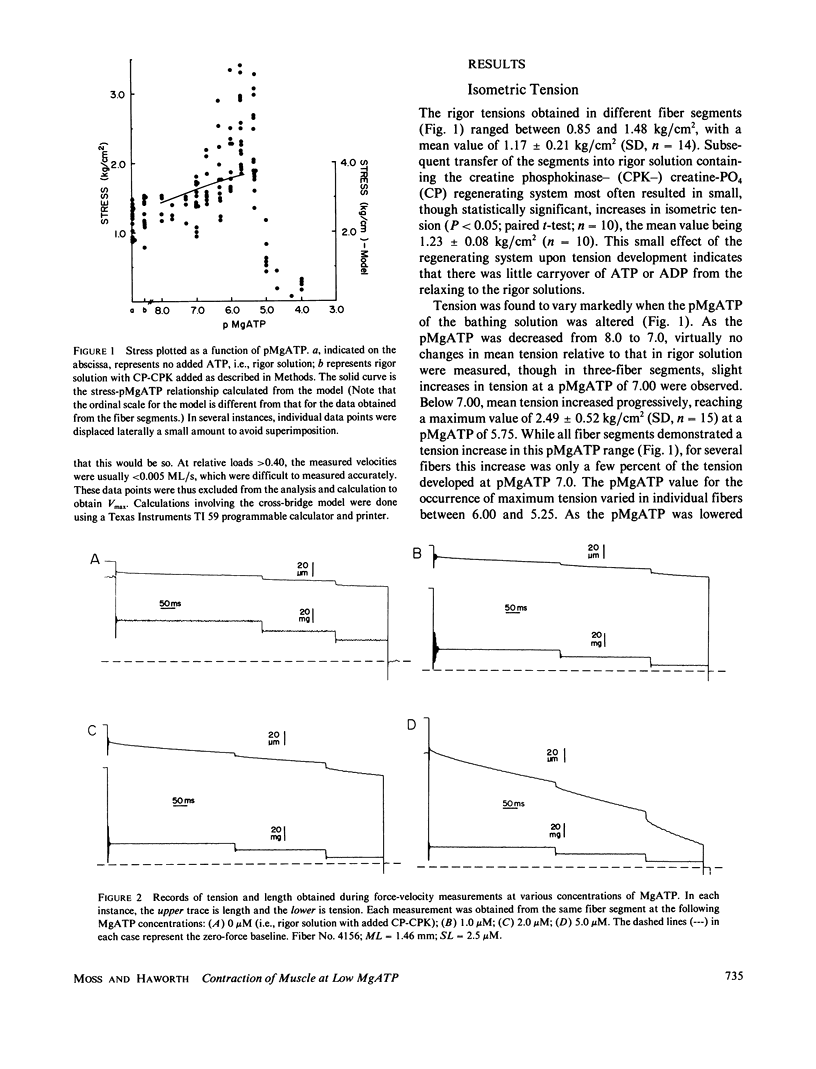
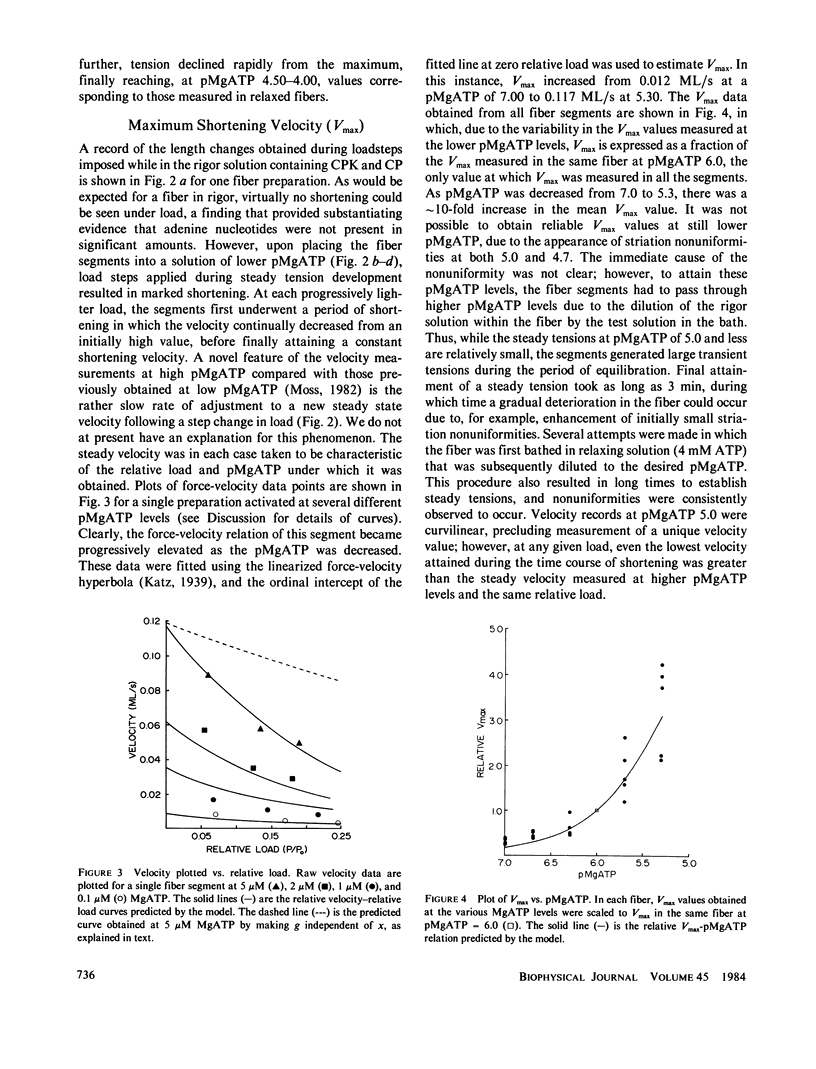
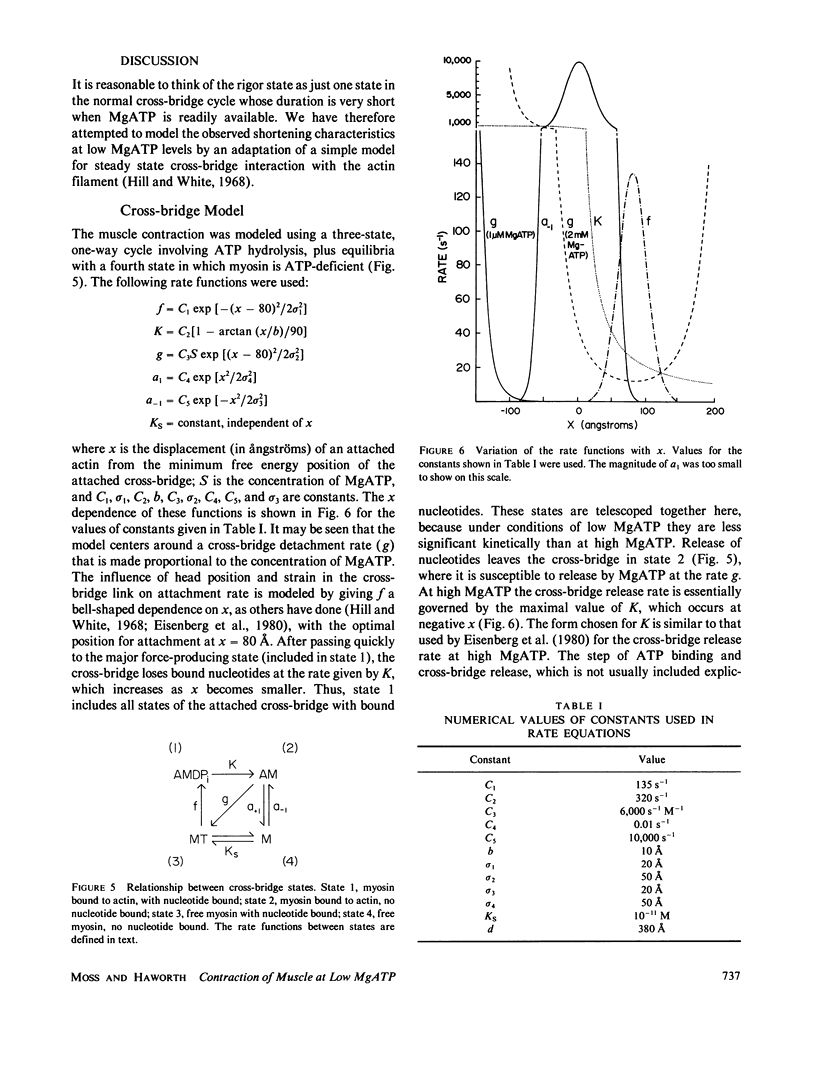
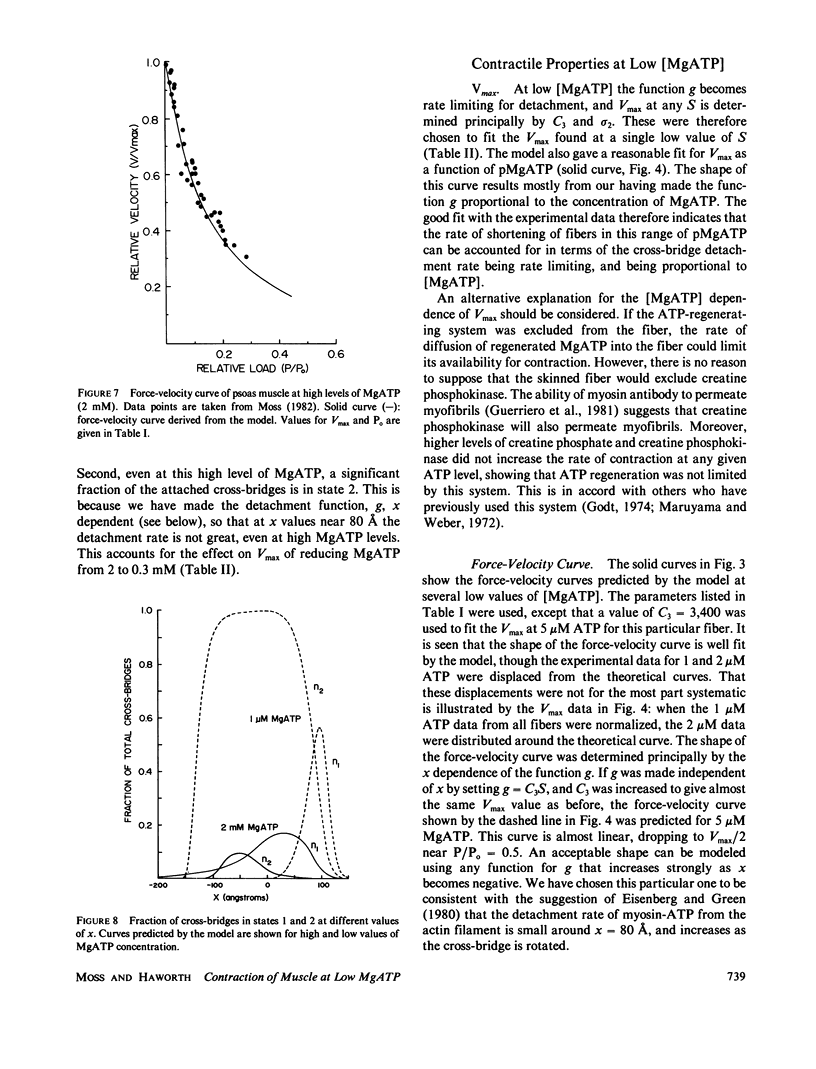
Abstract
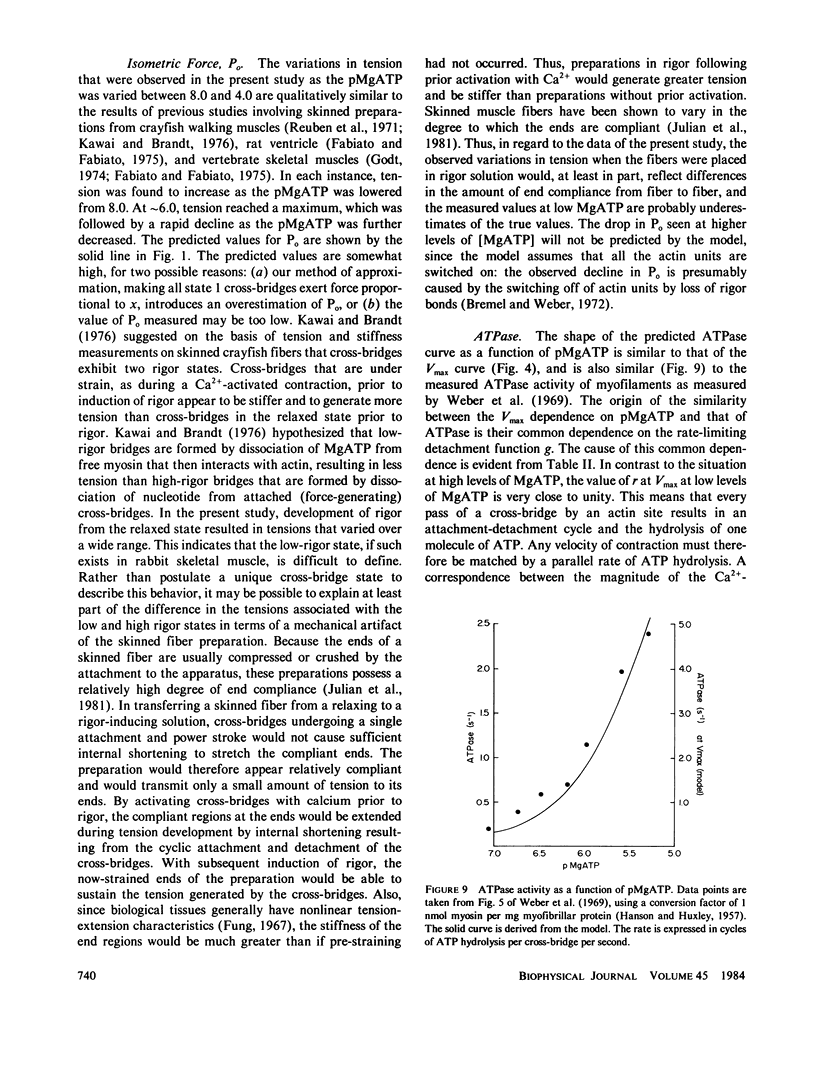
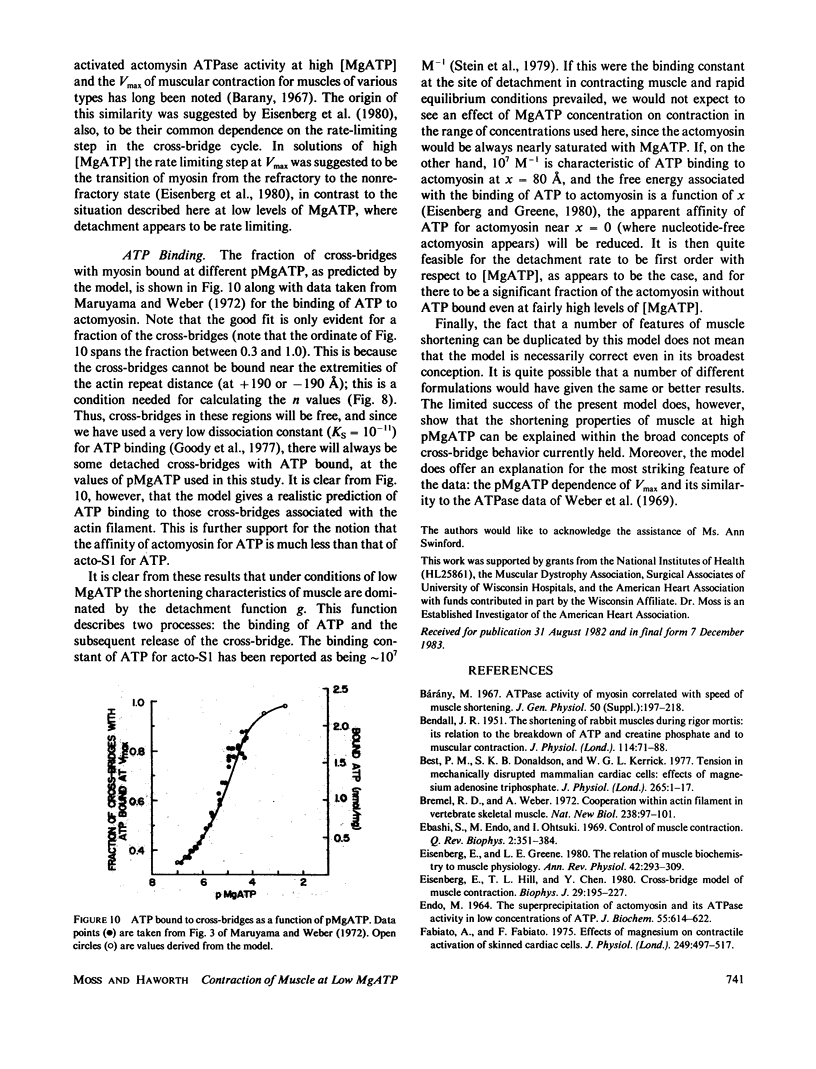
The contractile properties of skinned single fibers from rabbit psoas muscle were investigated under conditions of low MgATP and no Ca2+ (i.e., less than 10(-8) M). At 1 microM MgATP, fibers shortened at a maximum velocity of 660 +/- 420 A/half sarcomere/s (n = 9), compared with 34,000 A/half sarcomere/s measured during maximum Ca2+-activation at 1 mM MgATP (Moss, R. L., 1982. J. Muscle Res. Cell. Motil ., 3:295-311). The observed dependence of Vmax on pMgATP between 7.0 and 5.3 was similar to that of actomyosin ATPase measured previously by Weber, A., R. Herz , and I. Reiss (1969, Biochemistry, 8:2266-2270). Isometric tension was found to vary with pMgATP in a manner much like that reported by Reuben , J. P., P. W. Brandt, M. Berman , and H. Grundfest (J. Gen. Physiol. 1971. 57:385-407). A simple cross-bridge model was developed to simulate contractile behaviour at both high and low levels of MgATP. It was found that the pMgATP dependence of Vmax and ATPase could be successfully modeled if the rate of detachment of the cross-bridge was made proportional to the concentration of MgATP. In the model, the similar dependence of Vmax and ATPase on pMgATP was derived from the fact that in this range of pMgATP every pass of a cross-bridge by an actin site resulted in an attachment-detachment cycle, and every such cycle caused hydrolysis of one molecule of ATP.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BENDALL J. R. The shortening of rabbit muscles during rigor mortis; its relation to the breakdown of adenosine triphosphate and creatine phosphate and to muscular contraction. J Physiol. 1951 Jun;114(1-2):71–88. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Best P. M., Donaldson S. K., Kerrick W. G. Tension in mechanically disrupted mammalian cardiac cells: effects of magnesium adenosine triphosphate. J Physiol. 1977 Feb;265(1):1–17. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bremel R. D., Weber A. Cooperation within actin filament in vertebrate skeletal muscle. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jul 26;238(82):97–101. doi: 10.1038/newbio238097a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bárány M. ATPase activity of myosin correlated with speed of muscle shortening. J Gen Physiol. 1967 Jul;50(6 Suppl):197–218. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.6.197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENDO M. THE SUPERPRECIPITATION OF ACTOMYOSIN AND ITS ATPASE ACTIVITY IN LOW CONCENTRATION OF ATP. J Biochem. 1964 Jun;55:614–622. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a127934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebashi S., Endo M., Otsuki I. Control of muscle contraction. Q Rev Biophys. 1969 Nov;2(4):351–384. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500001190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg E., Greene L. E. The relation of muscle biochemistry to muscle physiology. Annu Rev Physiol. 1980;42:293–309. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.42.030180.001453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg E., Hill T. L., Chen Y. Cross-bridge model of muscle contraction. Quantitative analysis. Biophys J. 1980 Feb;29(2):195–227. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85126-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A., Fabiato F. Effects of magnesium on contractile activation of skinned cardiac cells. J Physiol. 1975 Aug;249(3):497–517. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung Y. C. Elasticity of soft tissues in simple elongation. Am J Physiol. 1967 Dec;213(6):1532–1544. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1967.213.6.1532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godt R. E. Calcium-activated tension of skinned muscle fibers of the frog. Dependence on magnesium adenosine triphosphate concentration. J Gen Physiol. 1974 Jun;63(6):722–739. doi: 10.1085/jgp.63.6.722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goody R. S., Hofmann W., Mannherz G. H. The binding constant of ATP to myosin S1 fragment. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Sep;78(2):317–324. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11742.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon A. M., Huxley A. F., Julian F. J. The variation in isometric tension with sarcomere length in vertebrate muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1966 May;184(1):170–192. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerriero V., Jr, Rowley D. R., Means A. R. Production and characterization of an antibody to myosin light chain kinase and intracellular localization of the enzyme. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):449–458. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90386-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANSON J., HUXLEY H. E. Quantitative studies on the structure of cross-striated myofibrils. II. Investigations by biochemical techniques. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Feb;23(2):250–260. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90326-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUXLEY A. F. Muscle structure and theories of contraction. Prog Biophys Biophys Chem. 1957;7:255–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haselgrove J. C. X-ray evidence for conformational changes in the myosin filaments of vertebrate striated muscle. J Mol Biol. 1975 Feb 15;92(1):113–143. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90094-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herz R., Weber A., Reiss I. The role of magnesium in the relaxation of myofibrils. Biochemistry. 1969 Jun;8(6):2266–2271. doi: 10.1021/bi00834a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill T. L., White G. M. On the sliding-filament model of muscular contraction, IV. Calculation of force-velocity curves. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Nov;61(3):889–896. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.3.889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julian F. J., Moss R. L. Effects of calcium and ionic strength on shortening velocity and tension development in frog skinned muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1981 Feb;311:179–199. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julian F. J., Moss R. L., Waller G. S. Mechanical properties and myosin light chain composition of skinned muscle fibres from adult and new-born rabbits. J Physiol. 1981 Feb;311:201–218. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julian F. J. The effect of calcium on the force-velocity relation of briefly glycerinated frog muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1971 Oct;218(1):117–145. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B. The relation between force and speed in muscular contraction. J Physiol. 1939 Jun 14;96(1):45–64. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1939.sp003756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai M., Brandt P. W. Two rigor states in skinned crayfish single muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Sep;68(3):267–280. doi: 10.1085/jgp.68.3.267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marston S., Weber A. The dissociation constant of the actin-heavy meromyosin subfragment-1 complex. Biochemistry. 1975 Aug 26;14(17):3868–3873. doi: 10.1021/bi00688a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama K., Weber A. Binding of adenosine triphosphate to myofibrils during contraction and relaxation. Biochemistry. 1972 Aug 1;11(16):2990–2998. doi: 10.1021/bi00766a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss R. L. Sarcomere length-tension relations of frog skinned muscle fibres during calcium activation at short lengths. J Physiol. 1979 Jul;292:177–192. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss R. L. The effect of calcium on the maximum velocity of shortening in skinned skeletal muscle fibres of the rabbit. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1982 Sep;3(3):295–311. doi: 10.1007/BF00713039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulvany M. J. Mechanical properties of frog skeletal muscles in iodoacetic acid rigor. J Physiol. 1975 Nov;252(2):319–334. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuben J. P., Brandt P. W., Berman M., Grundfest H. Regulation of tension in the skinned crayfish muscle fiber. I. Contraction and relaxation in the absence of Ca (pCa is greater than 9). J Gen Physiol. 1971 Apr;57(4):385–407. doi: 10.1085/jgp.57.4.385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. A., Huxley H. E., Finch J. T. Regulation of skeletal muscle contraction. II. Structural studies of the interaction of the tropomyosin-troponin complex with actin. J Mol Biol. 1972 Dec 30;72(3):619–632. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90180-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein L. A., Schwarz R. P., Jr, Chock P. B., Eisenberg E. Mechanism of actomyosin adenosine triphosphatase. Evidence that adenosine 5'-triphosphate hydrolysis can occur without dissociation of the actomyosin complex. Biochemistry. 1979 Sep 4;18(18):3895–3909. doi: 10.1021/bi00585a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White D. C. Rigor contraction and the effect of various phosphate compounds on glycerinated insect flight and vertebrate muscle. J Physiol. 1970 Jul;208(3):583–605. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood D. S., Zollman J., Reuben J. P., Brandt P. W. Human skeletal muscle: properties of the "chemically skinned%" fiber. Science. 1975 Mar 21;187(4181):1075–1076. doi: 10.1126/science.187.4181.1075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


