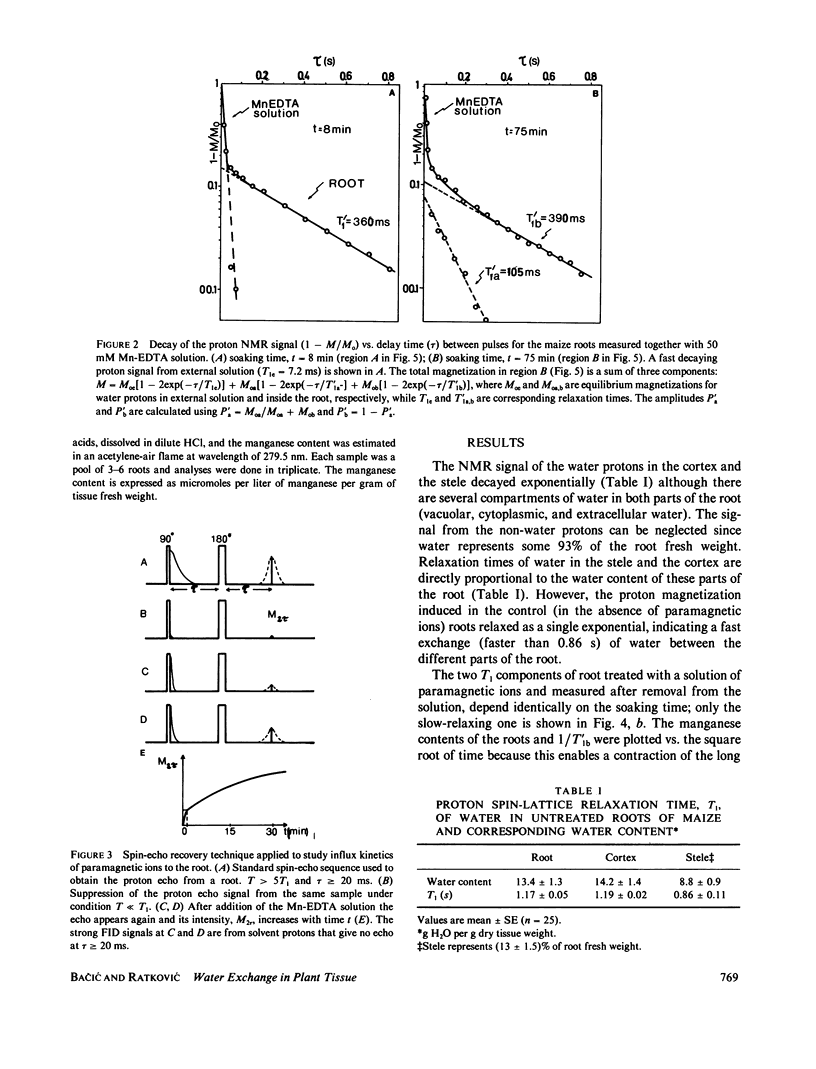
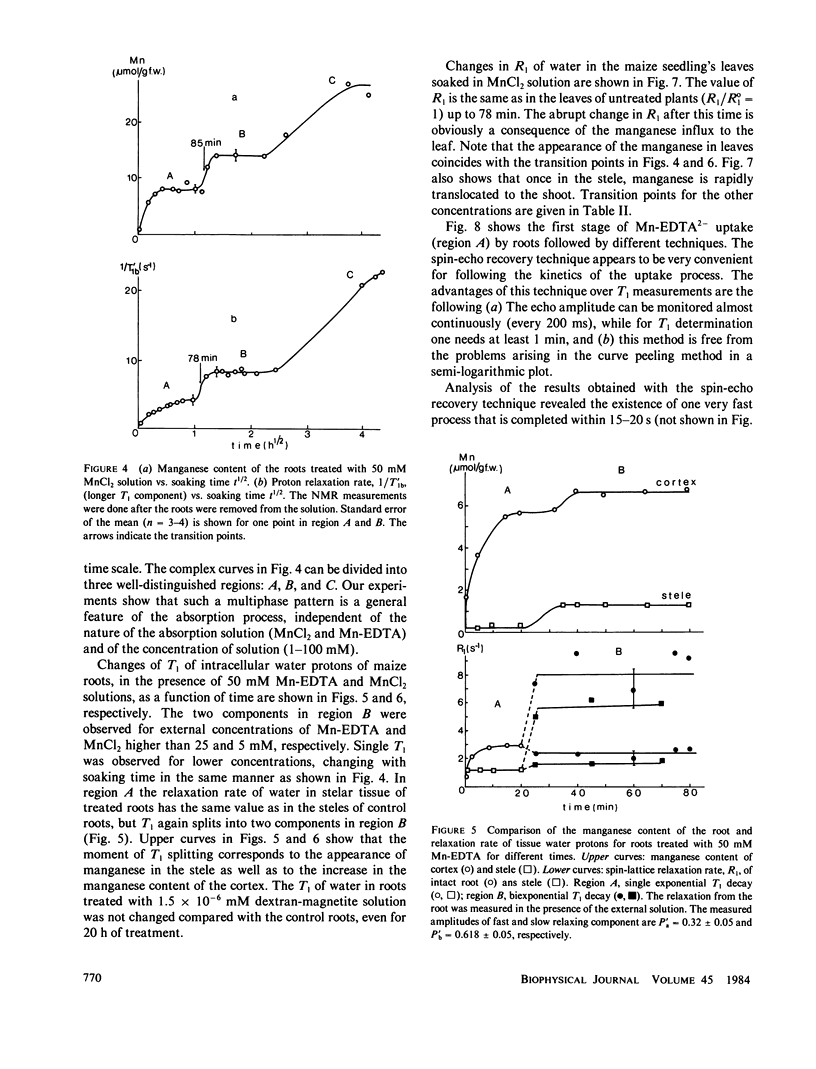
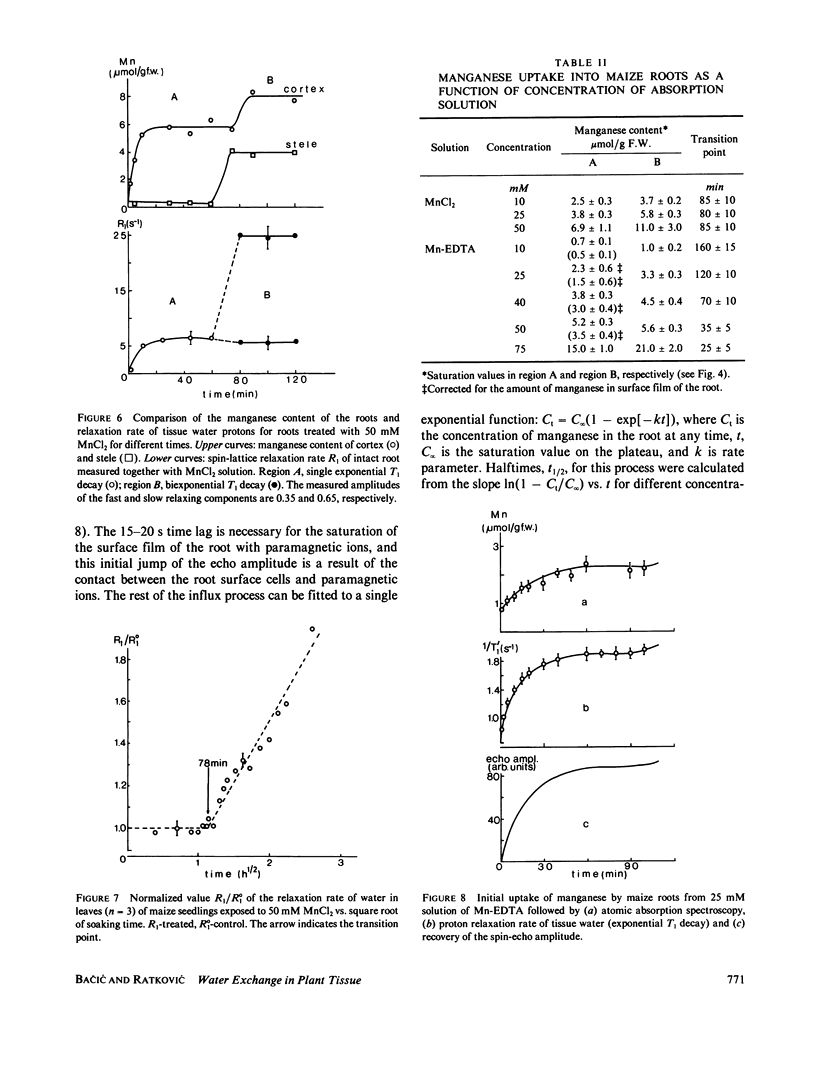
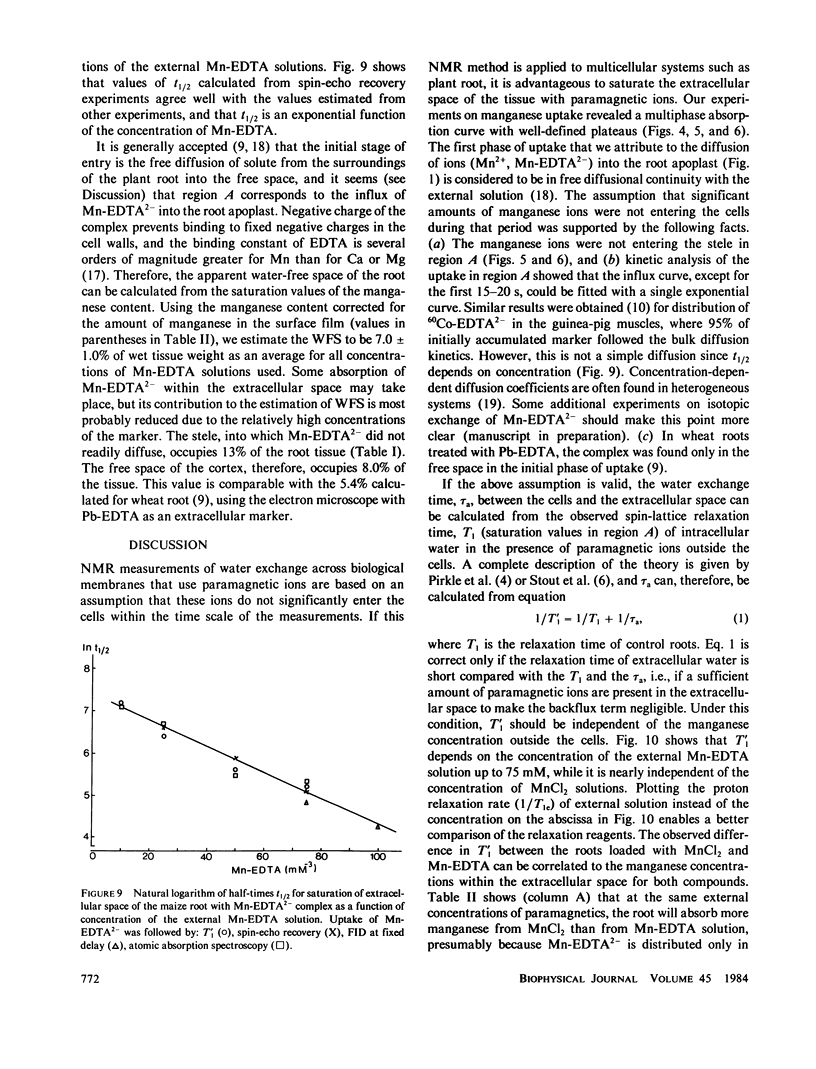
Abstract
The proton NMR relaxation of water in maize roots in the presence of paramagnetic centers, Mn2+, Mn- EDTA2 -, and dextran-magnetite was measured. It was shown that the NMR method of Conlon and Outhred (1972, Biochem. Biophys. Acta. 288:354-361) can be applied to a heterogenous multicellular system, and the water exchange time between cortical cells and the extracellular space can be calculated. The water exchange is presumably controlled by the intracellular unstirred layers. The Mn- EDTA2 - complex is a suitable paramagnetic compound for complex tissue, while the application of dextran-magnetite is probably restricted to studies of water exchange in cell suspensions. The water free space of the root and viscosity of the cells cytoplasm was estimated with the use of Mn- EDTA2 -. The convenience of proton NMR for studying the multiphase uptake of paramagnetic ions by plant root as well as their transport to leaves is demonstrated. A simple and rapid NMR technique (spin-echo recovery) for continuous measurement of the uptake process is presented.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brading A. F., Jones A. W. Distribution and kinetics of CoEDTA in smooth muscle, and its use as an extracellular marker. J Physiol. 1969 Feb;200(2):387–401. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conlon T., Outhred R. Water diffusion permeability of erythrocytes using an NMR technique. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Nov 2;288(2):354–361. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90256-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutknecht J. Membranes of Valonia ventricosa: apparent absence of water-filled pores. Science. 1967 Nov 10;158(3802):787–788. doi: 10.1126/science.158.3802.787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazlewood C. F., Chang D. C., Nichols B. L., Woessner D. E. Nuclear magnetic resonance transverse relaxation times of water protons in skeletal muscle. Biophys J. 1974 Aug;14(8):583–606. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(74)85937-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maas E. V., Moore D. P., Mason B. J. Manganese absorption by excised barley roots. Plant Physiol. 1968 Apr;43(4):527–530. doi: 10.1104/pp.43.4.527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirkle J. L., Ashley D. L., Goldstein J. H. Pulse nuclear magnetic resonance measurements of water exchange across the erythrocyte membrane employing a low Mn concentration. Biophys J. 1979 Mar;25(3):389–406. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85311-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuilov F. D., Nikiforova V. I., Nikiforov E. A. Issledovanie vliianiia paramagnitnykh primesei na spin-reshetochnuiu relaksatsiiu protonov vnutrikletochnoi vody. Biofizika. 1979 Mar-Apr;24(2):270–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stout D. G., Steponkus P. L. Nuclear magnetic resonance relaxation times and plasmalemma water exchange in ivy bark. Plant Physiol. 1978 Oct;62(4):636–641. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.4.636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stout D. G., Steponkus P. L. Water permeability of chlorella cell membranes by nuclear magnetic resonance: measured diffusion coefficients and relaxation times. Plant Physiol. 1978 Jul;62(1):146–151. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.1.146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiffin L. O. Translocation of manganese, iron, cobalt, and zinc in tomato. Plant Physiol. 1967 Oct;42(10):1427–1432. doi: 10.1104/pp.42.10.1427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. C. Metal Complexation in Xylem Fluid : II. THEORETICAL EQUILIBRIUM MODEL AND COMPUTATIONAL COMPUTER PROGRAM. Plant Physiol. 1981 Feb;67(2):301–310. doi: 10.1104/pp.67.2.301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshizaki K., Seo Y., Nishikawa H., Morimoto T. Application of pulsed-gradient 31P NMR on frog muscle to measure the diffusion rates of phosphorus compounds in cells. Biophys J. 1982 May;38(2):209–211. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84549-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


