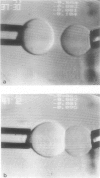
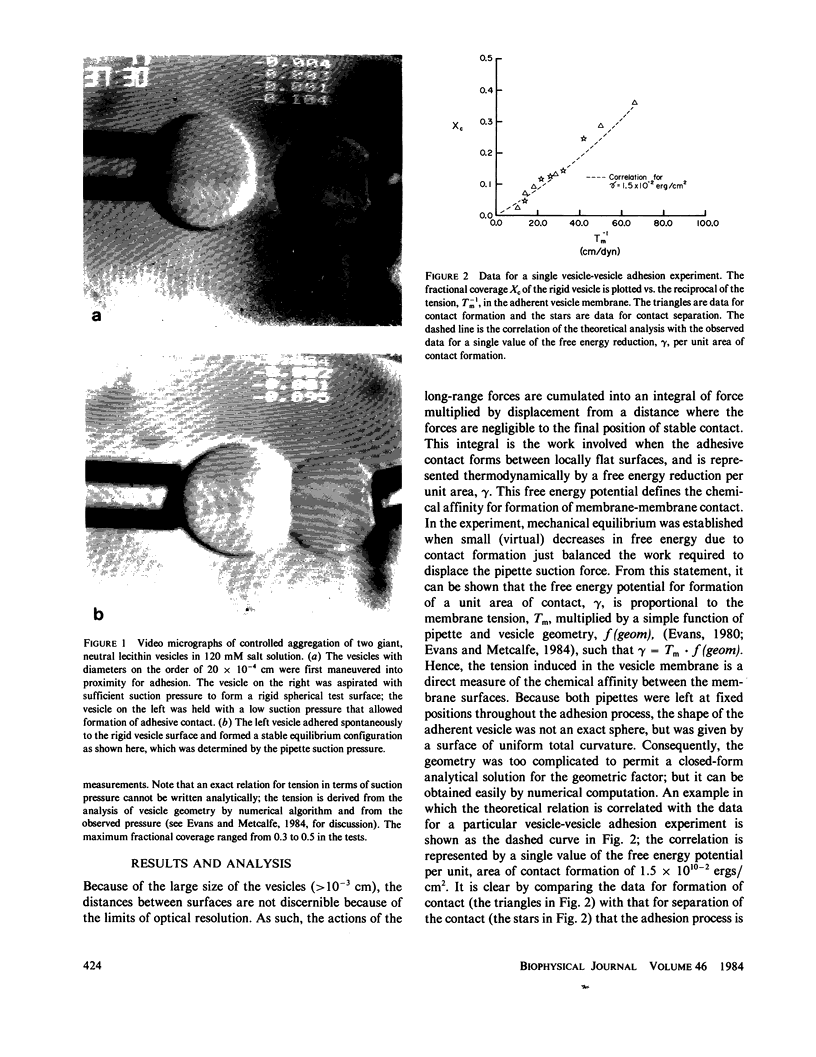
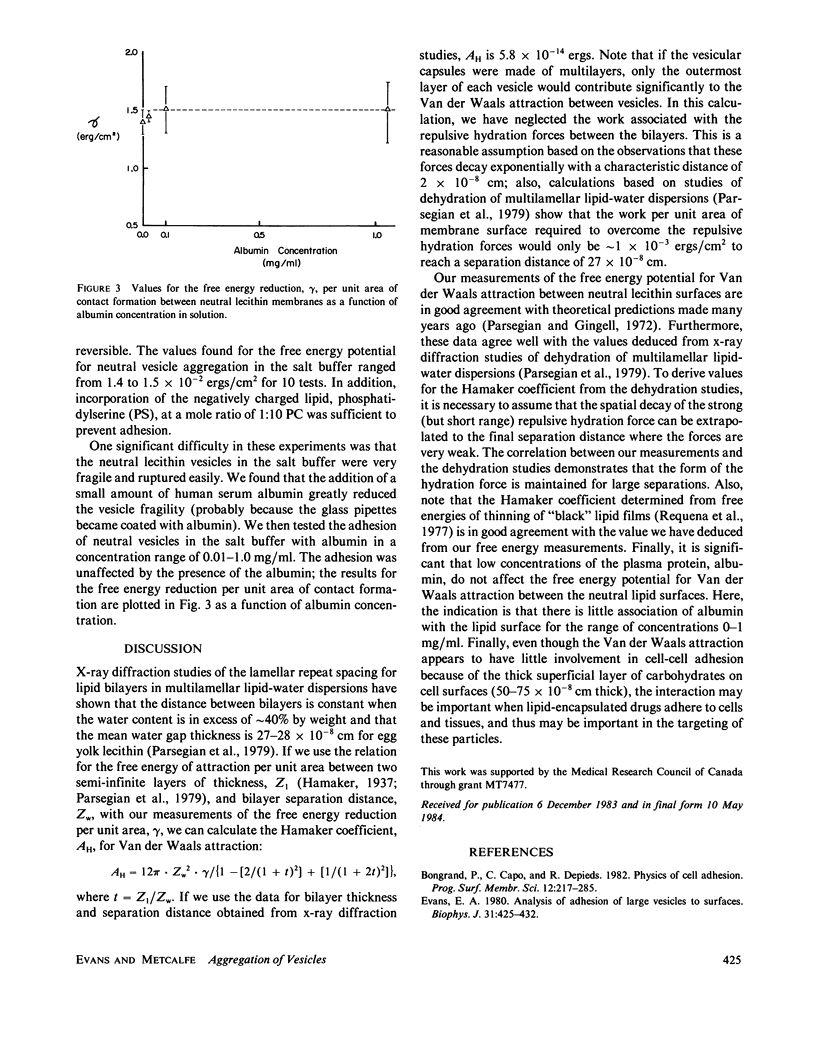
Abstract
Here, we report the first direct observation of Van der Waals' attraction between biomembrane capsules using measurements of the free energy reduction per unit area of membrane-membrane contact formation. In these studies, the membrane capsules were reconstituted neutral (egg phosphatidylcholine) lipid bilayers of giant (greater than 10(-3) cm diam) vesicles. Micromanipulation methods were used to select and maneuver two vesicles into proximity for contact; after adhesion was allowed to occur, the extent of contact formation was regulated through the vesicle membrane tensions that were controlled by micropipette suction. The free energy reduction per unit area of contact formation was proportional to the membrane tension multiplied by a simple function of the pipette and vesicle dimensions. The free energy potential for Van der Waals attraction between the neutral bilayers in 120 mM NaCl solutions was 1.5 X 10(-2) ergs/cm2. Also, when human serum albumin was added to the medium in the range of 0-1 mg/ml, the free energy potential for bilayer-bilayer adhesion was not affected. Using published values for equilibrium spacing between lipid bilayers in multilamellar lipid-water dispersions and the theoretical equation for van der Waals attraction between continuous dielectric layers, we calculated the value for the Hamaker coefficient of the Van der Waals attraction to be 5.8 X 10(-14) ergs.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Evans E. A. Analysis of adhesion of large vesicles to surfaces. Biophys J. 1980 Sep;31(3):425–431. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85069-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E., Metcalfe M. Free energy potential for aggregation of mixed phosphatidylcholine/phosphatidylserine lipid vesicles in glucose polymer (dextran) solutions. Biophys J. 1984 Apr;45(4):715–720. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84213-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nir S., Andersen M. Van der Waals interactions between cell surfaces. J Membr Biol. 1977 Feb 24;31(1-2):1–18. doi: 10.1007/BF01869396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsegian V. A., Fuller N., Rand R. P. Measured work of deformation and repulsion of lecithin bilayers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2750–2754. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]