Abstract
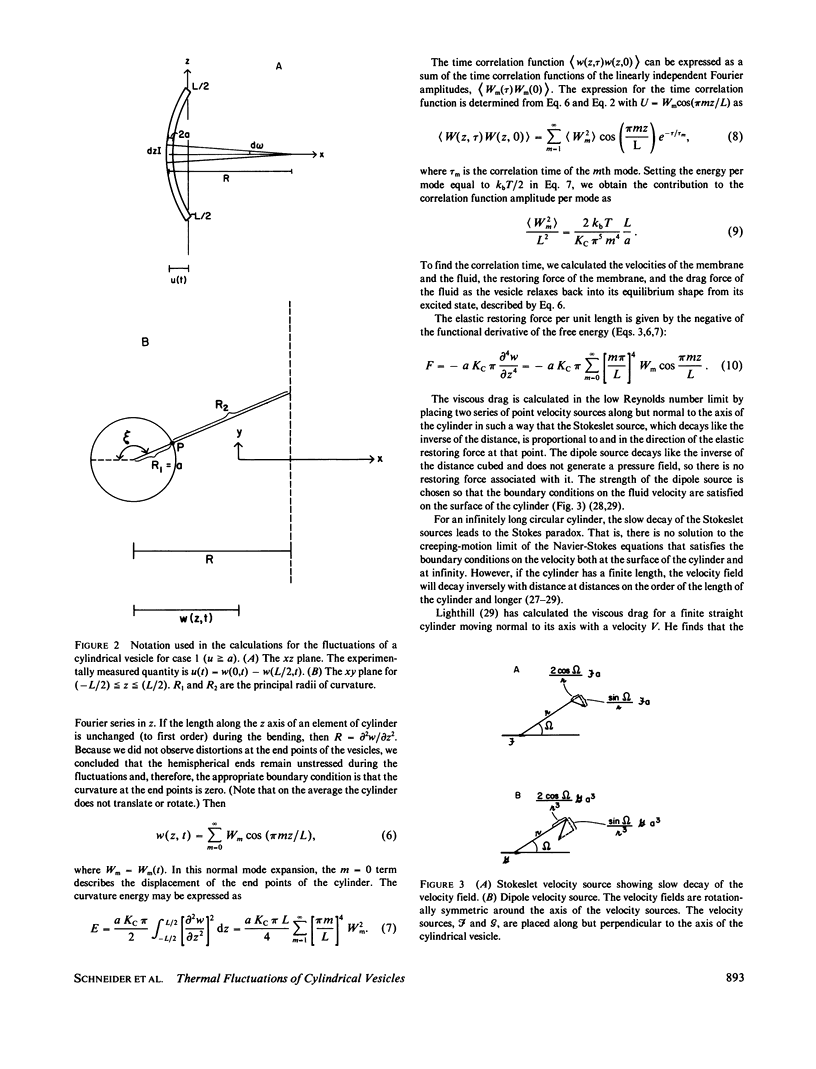
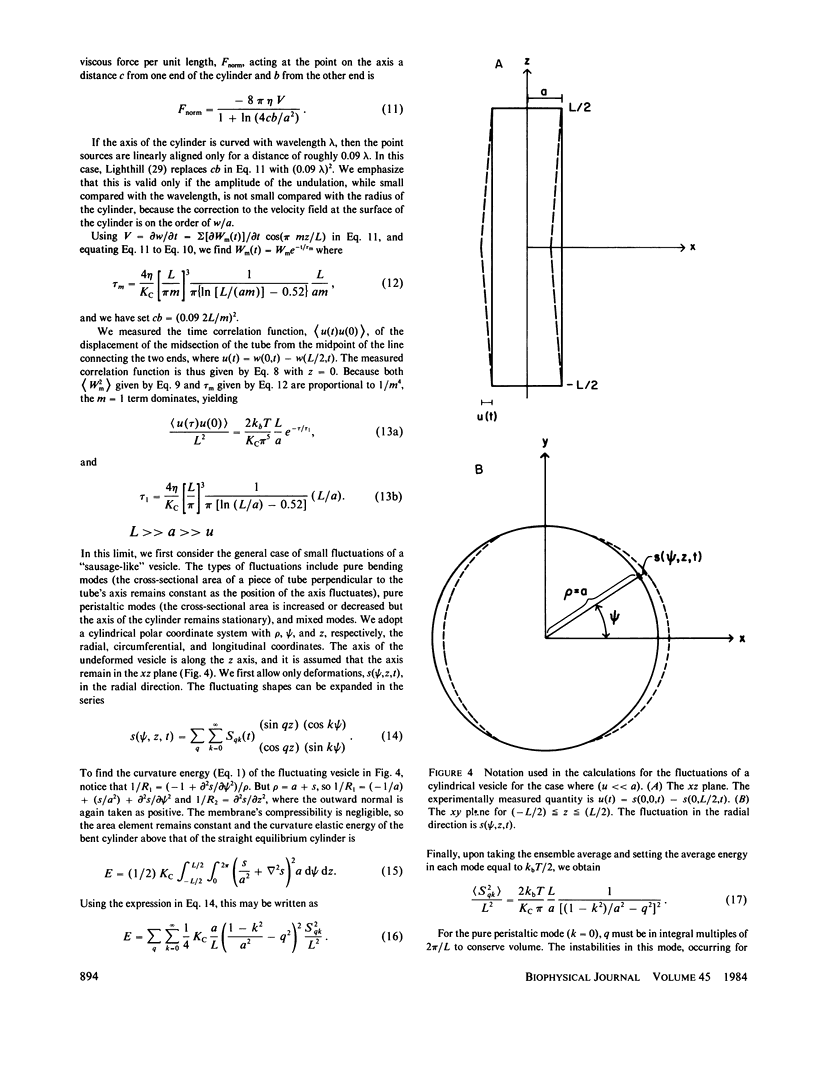
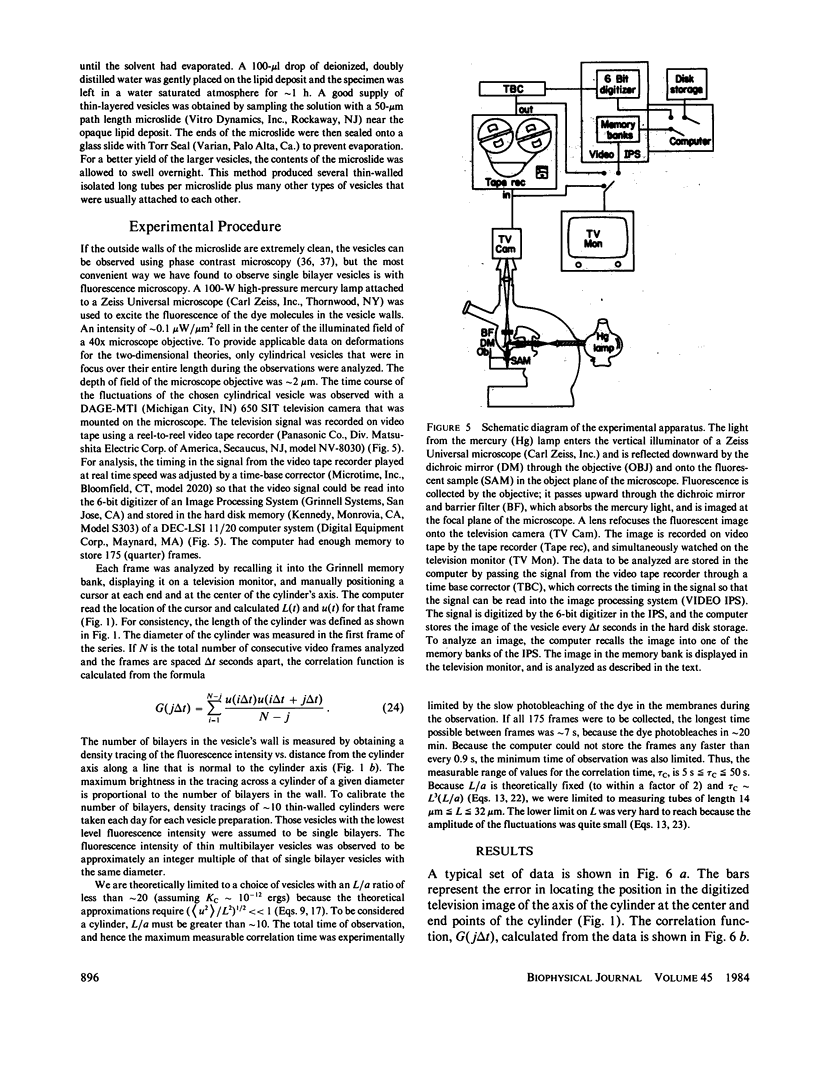
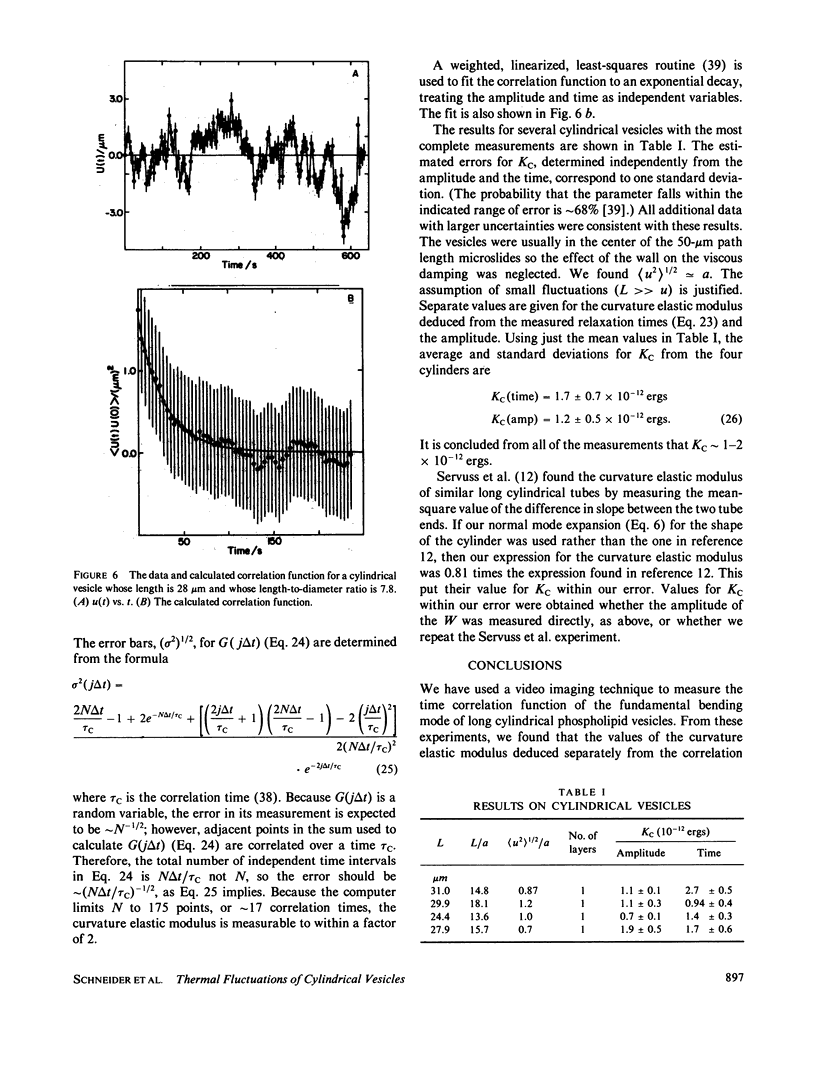
The time correlation function of the shape fluctuations of large (greater than 10 micron), cylindrical, hydrated, phospholipid-membrane vesicles consisting of one bimolecular layer was measured. The restoring force of the membrane was due to the excess curvature of a membrane element. A value for the curvature elastic modulus, Kc, was obtained from the mean-square amplitude of the normal modes of the fluctuations using the equipartition theorem. An expression for the correlation time was found by solving the dynamics of the membrane's relaxation against the low Reynolds number viscous drag of the surrounding fluid. The amplitudes and correlation times of the fundamental bending mode of the cylindrical vesicles both yield Kc = 1-2 X 10(-12) ergs.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLOWERS R., CLARKSON E. M., MAIZELS M. Flicker phenomenon in human erythrocytes. J Physiol. 1951 Apr;113(2-3):228–239. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boroske E., Elwenspoek M., Helfrich W. Osmotic shrinkage of giant egg-lecithin vesicles. Biophys J. 1981 Apr;34(1):95–109. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84839-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coakley W. T., Bater A. J., Deeley J. O. Vesicle production of heated and stressed erythrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Sep 22;512(2):318–330. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90256-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E. A. Bending elastic modulus of red blood cell membrane derived from buckling instability in micropipet aspiration tests. Biophys J. 1983 Jul;43(1):27–30. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84319-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E. A., Skalak R. Mechanics and thermodynamics of biomembranes: part 2. CRC Crit Rev Bioeng. 1979 Nov;3(4):331–418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahey P. F., Webb W. W. Lateral diffusion in phospholipid bilayer membranes and multilamellar liquid crystals. Biochemistry. 1978 Jul 25;17(15):3046–3053. doi: 10.1021/bi00608a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helfrich W. Elastic properties of lipid bilayers: theory and possible experiments. Z Naturforsch C. 1973 Nov-Dec;28(11):693–703. doi: 10.1515/znc-1973-11-1209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins J. T. Static equilibrium configurations of a model red blood cell. J Math Biol. 1977 May 23;4(2):149–169. doi: 10.1007/BF00275981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwok R., Evans E. Thermoelasticity of large lecithin bilayer vesicles. Biophys J. 1981 Sep;35(3):637–652. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84817-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lux S. E. Dissecting the red cell membrane skeleton. Nature. 1979 Oct 11;281(5731):426–429. doi: 10.1038/281426a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARPART A. K., HOFFMAN J. F. Flicker in erythrocytes; vibratory movements in the cytoplasm. J Cell Physiol. 1956 Apr;47(2):295–303. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030470208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saffman P. G., Delbrück M. Brownian motion in biological membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):3111–3113. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.3111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Servuss R. M., Harbich W., Helfrich W. Measurement of the curvature-elastic modulus of egg lecithin bilayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jul 15;436(4):900–903. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90422-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheetz M. P., Schindler M., Koppel D. E. Lateral mobility of integral membrane proteins is increased in spherocytic erythrocytes. Nature. 1980 Jun 12;285(5765):510–511. doi: 10.1038/285510a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims P. J., Waggoner A. S., Wang C. H., Hoffman J. F. Studies on the mechanism by which cyanine dyes measure membrane potential in red blood cells and phosphatidylcholine vesicles. Biochemistry. 1974 Jul 30;13(16):3315–3330. doi: 10.1021/bi00713a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. J., Nicolson G. L. The fluid mosaic model of the structure of cell membranes. Science. 1972 Feb 18;175(4023):720–731. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4023.720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waugh R. E. Surface viscosity measurements from large bilayer vesicle tether formation. I. Analysis. Biophys J. 1982 Apr;38(1):19–27. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84526-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waugh R. E. Surface viscosity measurements from large bilayer vesicle tether formation. II. Experiments. Biophys J. 1982 Apr;38(1):29–37. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84527-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb W. W. Applications of fluorescence correlation spectroscopy. Q Rev Biophys. 1976 Feb;9(1):49–68. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500002158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


