Abstract
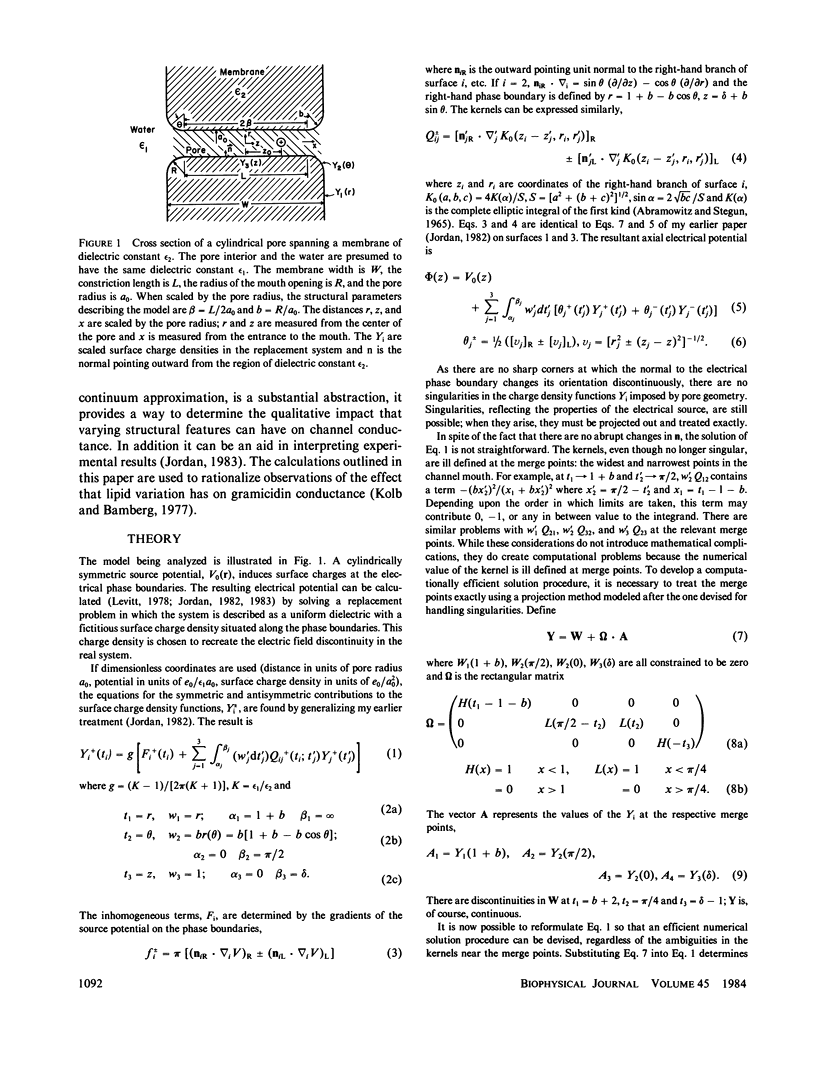
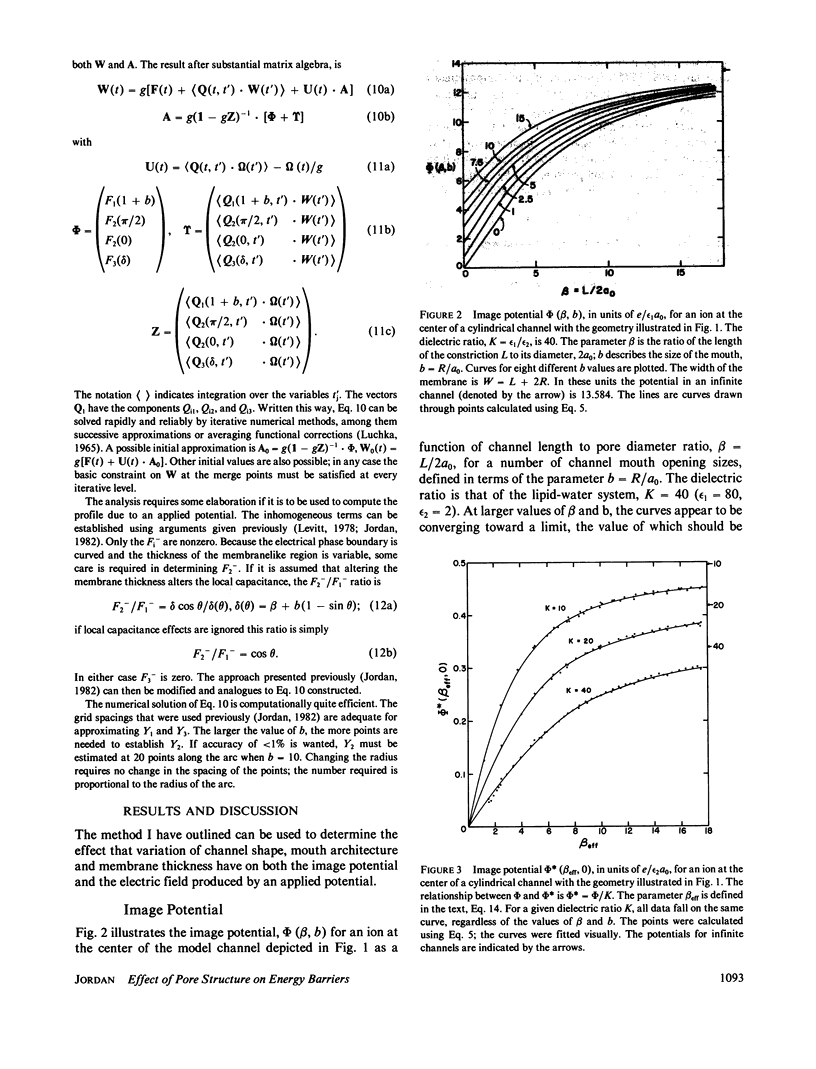
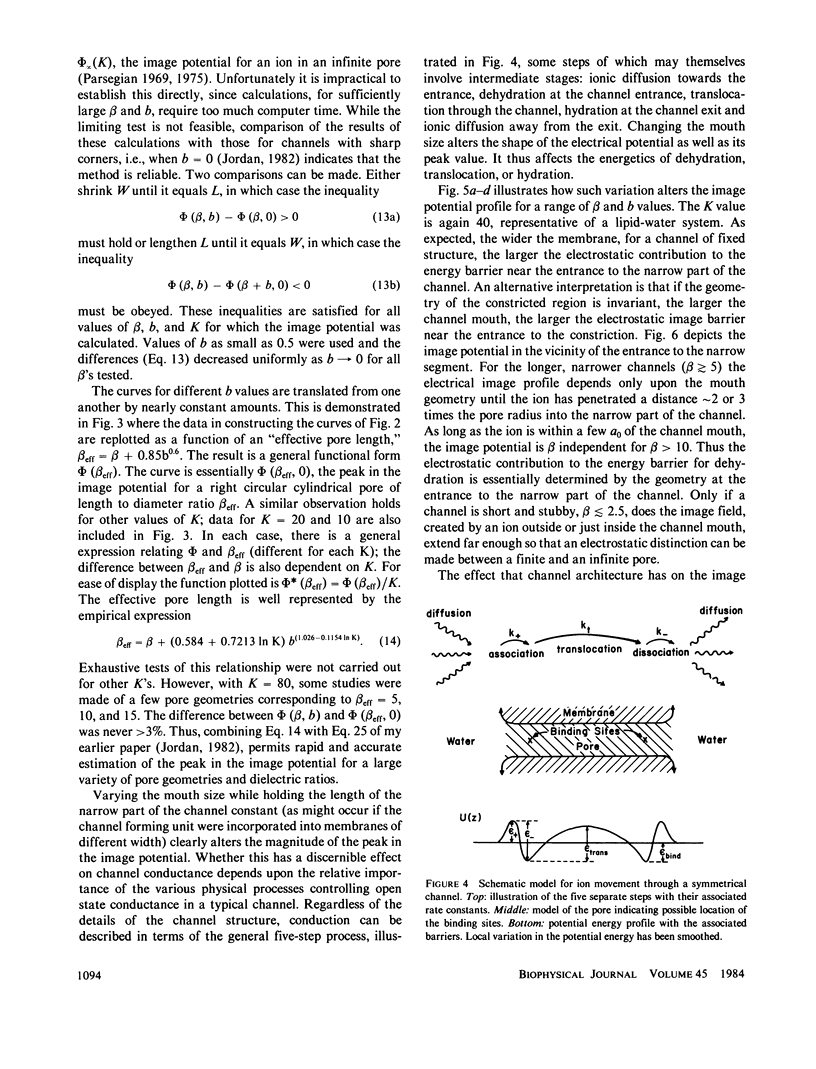
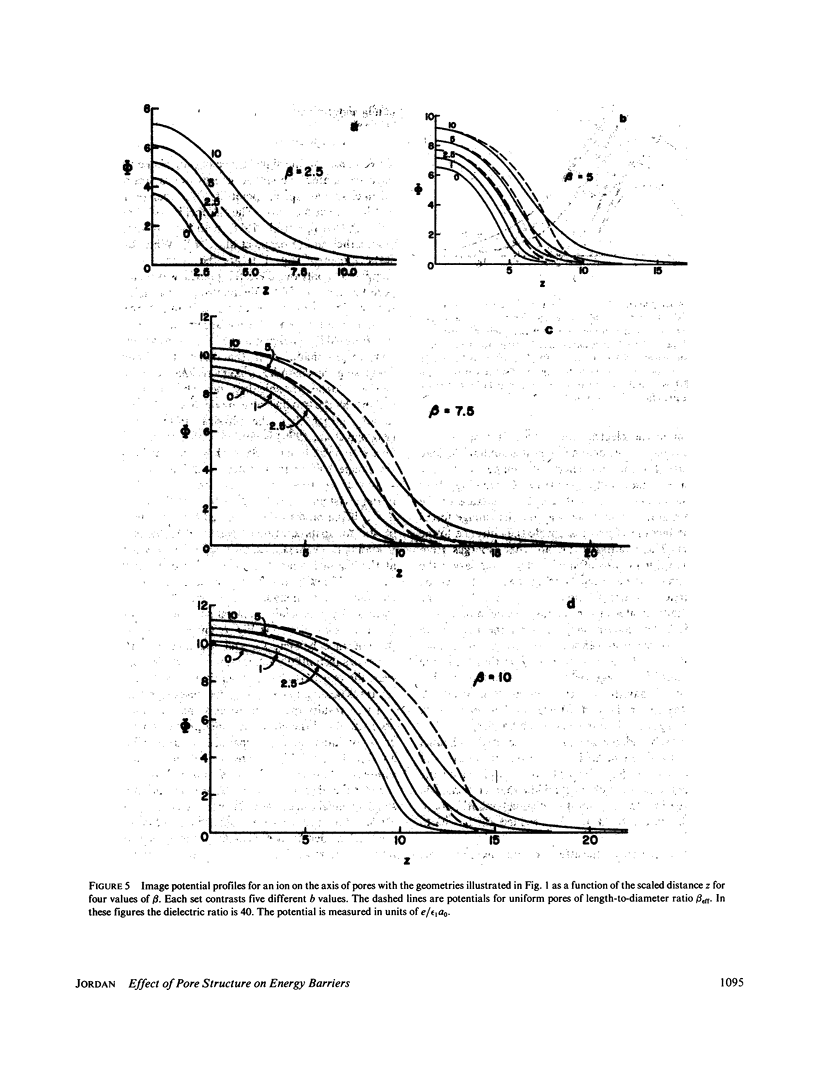
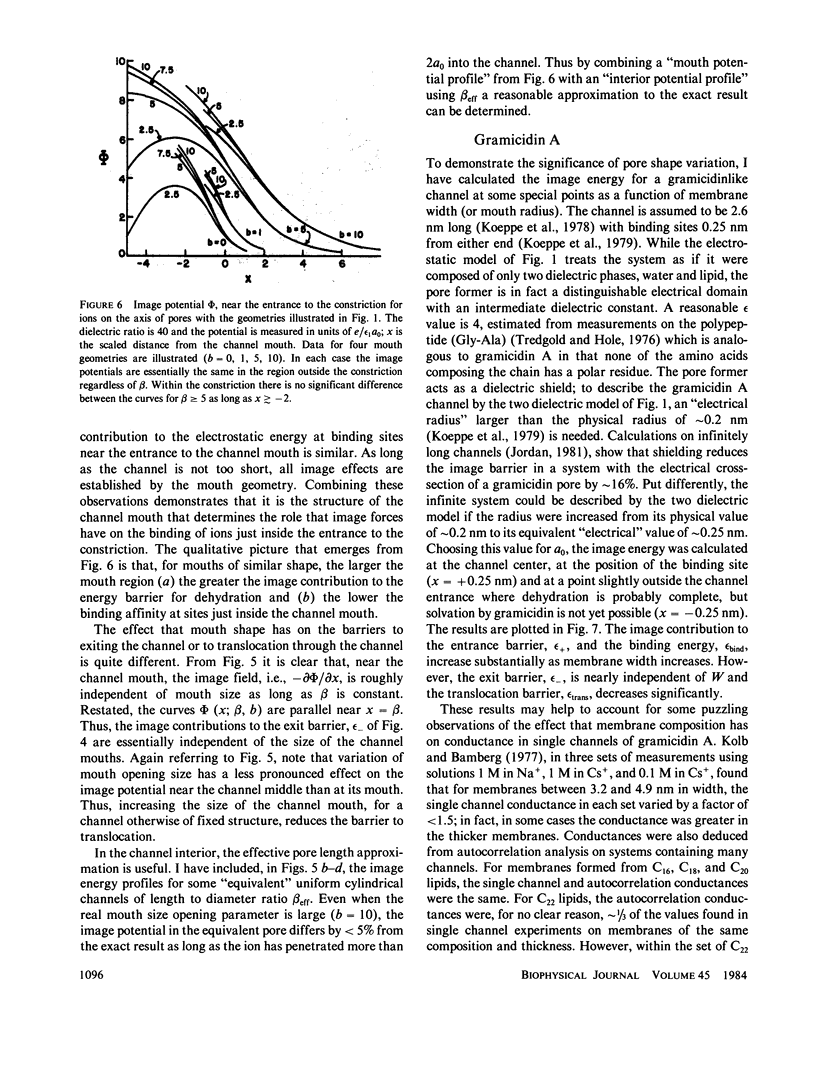
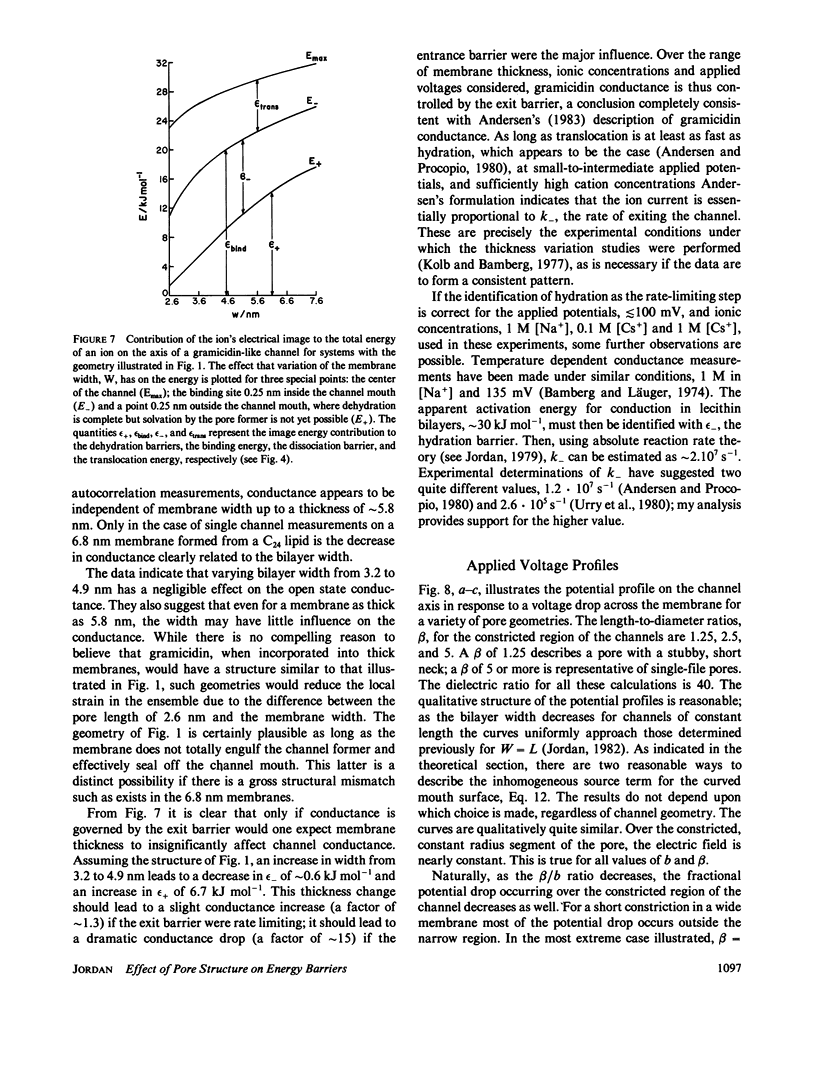
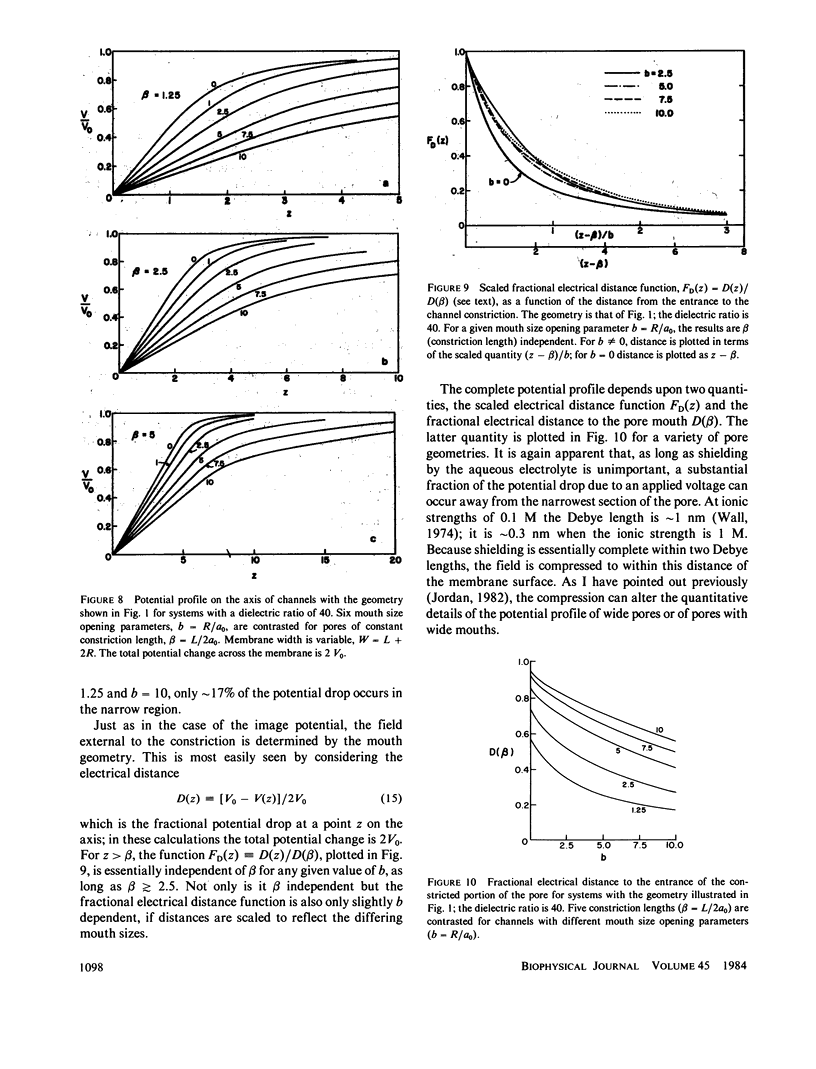
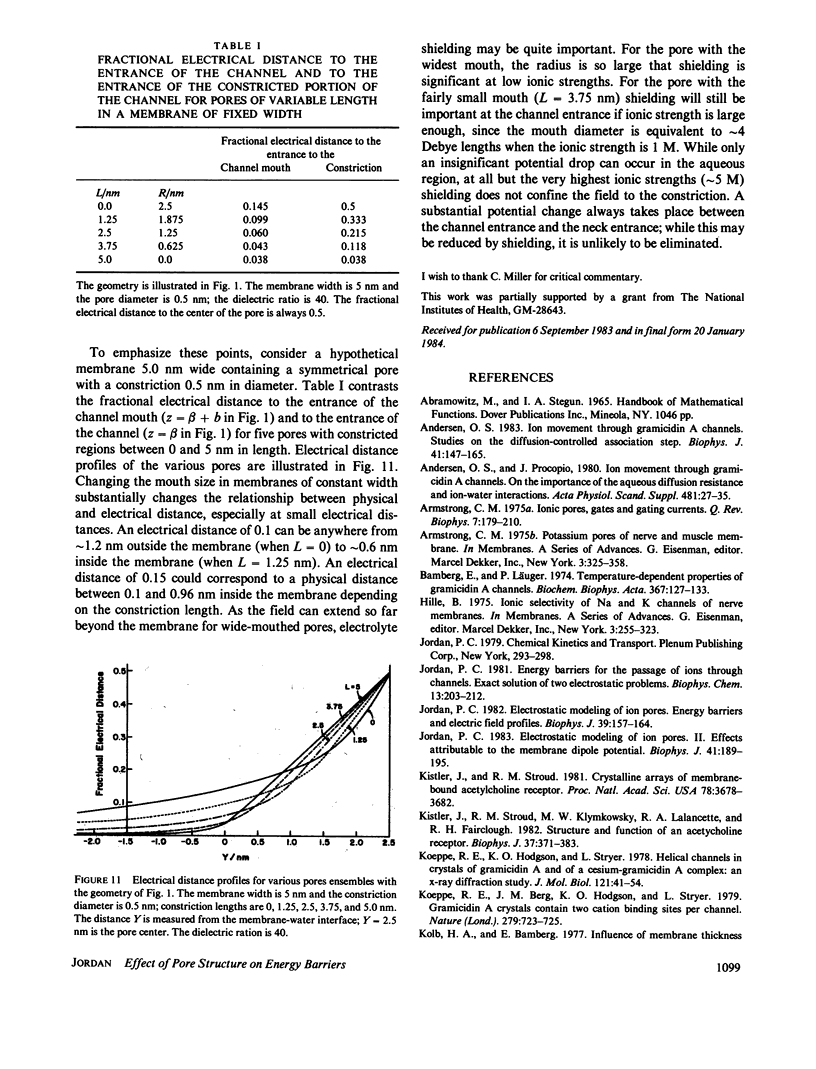
This paper presents calculations of the image potential for an ion in an aqueous pore spanning a lipid membrane and for the electric field produced in such a pore when a transmembrane potential is applied. The pore diameter may be variable. As long as the length-to-radius ratio in the narrow portion of a channel is large enough, the image potential for an ion in or near the mouth of a channel is determined by the geometry of the mouth. Within the constriction, the image potential of the ion-pore system may be reasonably approximated by constructing an "equivalent pore" of uniform diameter spanning a somewhat thinner membrane. When a transmembrane potential is applied the electric field within a constricted, constant radius, section of the model pore is constant. If the length-to-radius ratio of the narrow part of the channel is not too large or the channel ensemble has wide mouths, the field extends a significant distance into the aqueous region. The method is used to model features of the gramicidin A channel. The energy barrier for hydration (for exiting the channel) is identified with the activation energy for gramicidin conductance (Bamberg and Läuger, 1974, Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 367:127).
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen O. S. Ion movement through gramicidin A channels. Studies on the diffusion-controlled association step. Biophys J. 1983 Feb;41(2):147–165. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84416-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen O. S., Procopio J. Ion movement through gramicidin A channels. On the importance of the aqueous diffusion resistance and ion-water interactions. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1980;481:27–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M. Ionic pores, gates, and gating currents. Q Rev Biophys. 1974 May;7(2):179–210. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500001402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bamberg E., Läuger P. Temperature-dependent properties of gramicidin A channels. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Oct 29;367(2):127–133. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90037-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan P. C. Electrostatic modeling of ion pores. Energy barriers and electric field profiles. Biophys J. 1982 Aug;39(2):157–164. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84503-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan P. C. Electrostatic modeling of ion pores. II. Effects attributable to the membrane dipole potential. Biophys J. 1983 Feb;41(2):189–195. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84419-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan P. C. Energy barriers for passage of ions through channels. Exact solution of two electrostatic problems. Biophys Chem. 1981 Jun;13(3):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(81)80002-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kistler J., Stroud R. M. Crystalline arrays of membrane-bound acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3678–3682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kistler J., Stroud R. M., Klymkowsky M. W., Lalancette R. A., Fairclough R. H. Structure and function of an acetylcholine receptor. Biophys J. 1982 Jan;37(1):371–383. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84685-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koeppe R. E., 2nd, Berg J. M., Hodgson K. O., Stryer L. Gramicidin A crystals contain two cation binding sites per channel. Nature. 1979 Jun 21;279(5715):723–725. doi: 10.1038/279723a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koeppe R. E., 2nd, Hodgson K. O., Stryer L. Helical channels in crystals of gramicidin A and of a cesium--gramicidin A complex: an x-ray diffraction study. J Mol Biol. 1978 May 5;121(1):41–54. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90261-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb H. A., Bamberg E. Influence of membrane thickness and ion concentration on the properties of the gramicidin a channel. Autocorrelation, spectral power density, relaxation and single-channel studies. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jan 4;464(1):127–141. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90376-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latorre R., Vergara C., Hidalgo C. Reconstitution in planar lipid bilayers of a Ca2+-dependent K+ channel from transverse tubule membranes isolated from rabbit skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(3):805–809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.3.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt D. G. Electrostatic calculations for an ion channel. I. Energy and potential profiles and interactions between ions. Biophys J. 1978 May;22(2):209–219. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85485-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. Bis-quaternary ammonium blockers as structural probes of the sarcoplasmic reticulum K+ channel. J Gen Physiol. 1982 May;79(5):869–891. doi: 10.1085/jgp.79.5.869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsegian A. Energy of an ion crossing a low dielectric membrane: solutions to four relevant electrostatic problems. Nature. 1969 Mar 1;221(5183):844–846. doi: 10.1038/221844a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsegian V. A. Ion-membrane interactions as structural forces. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Dec 30;264:161–171. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb31481.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tredgold R. H., Hole P. N. Dielectric behaviour of dry synthetic polypeptides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Aug 4;443(1):137–142. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90497-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urry D. W. The gramicidin A transmembrane channel: a proposed pi(L,D) helix. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Mar;68(3):672–676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.3.672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urry D. W., Venkatachalam C. M., Spisni A., Läuger P., Khaled M. A. Rate theory calculation of gramicidin single-channel currents using NMR-derived rate constants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2028–2032. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


