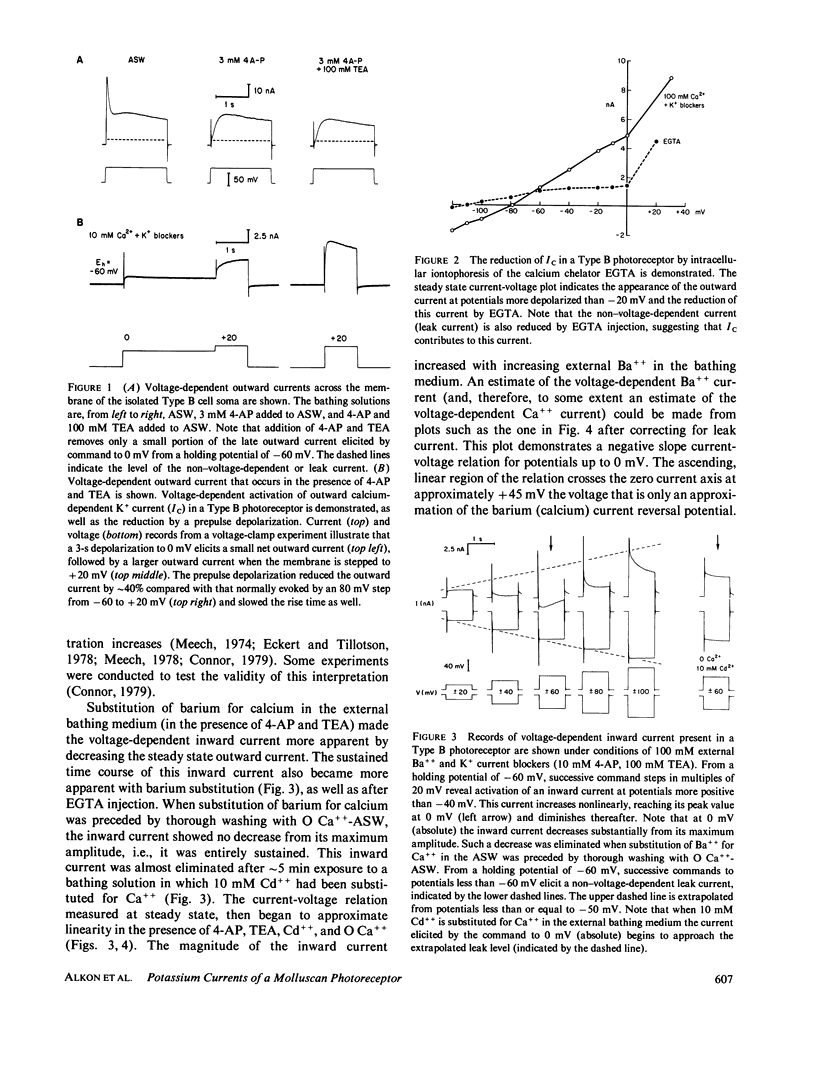
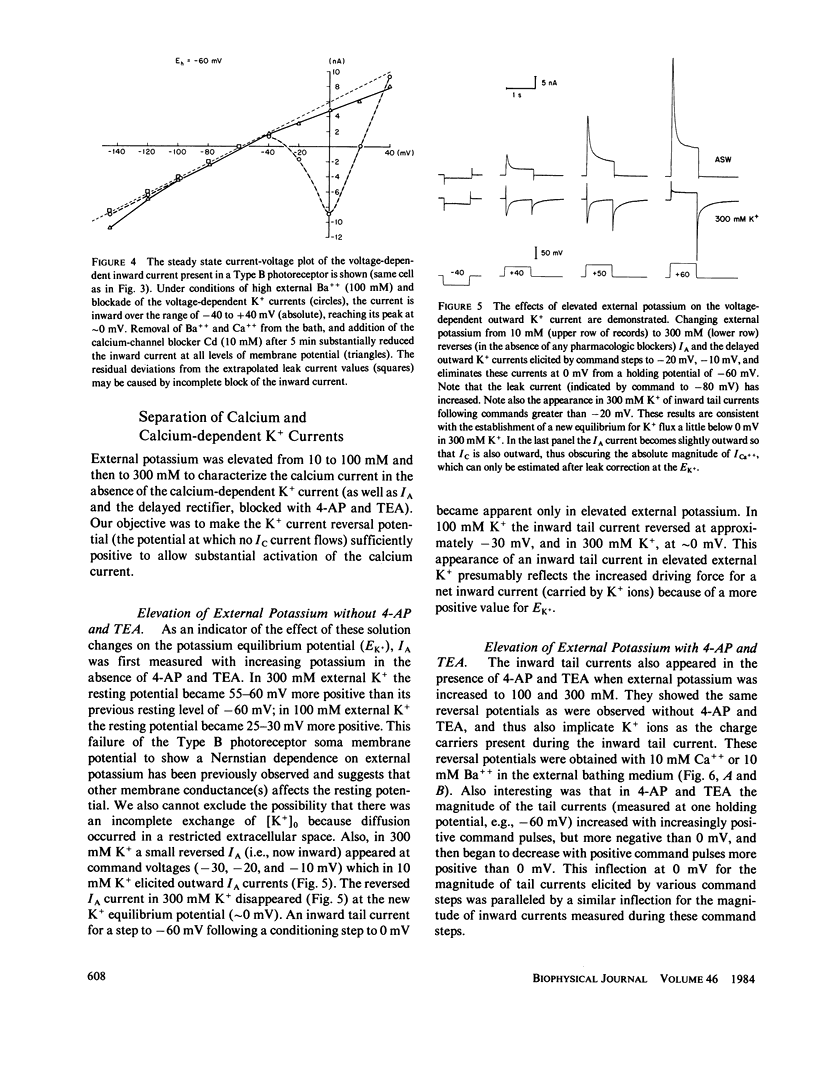
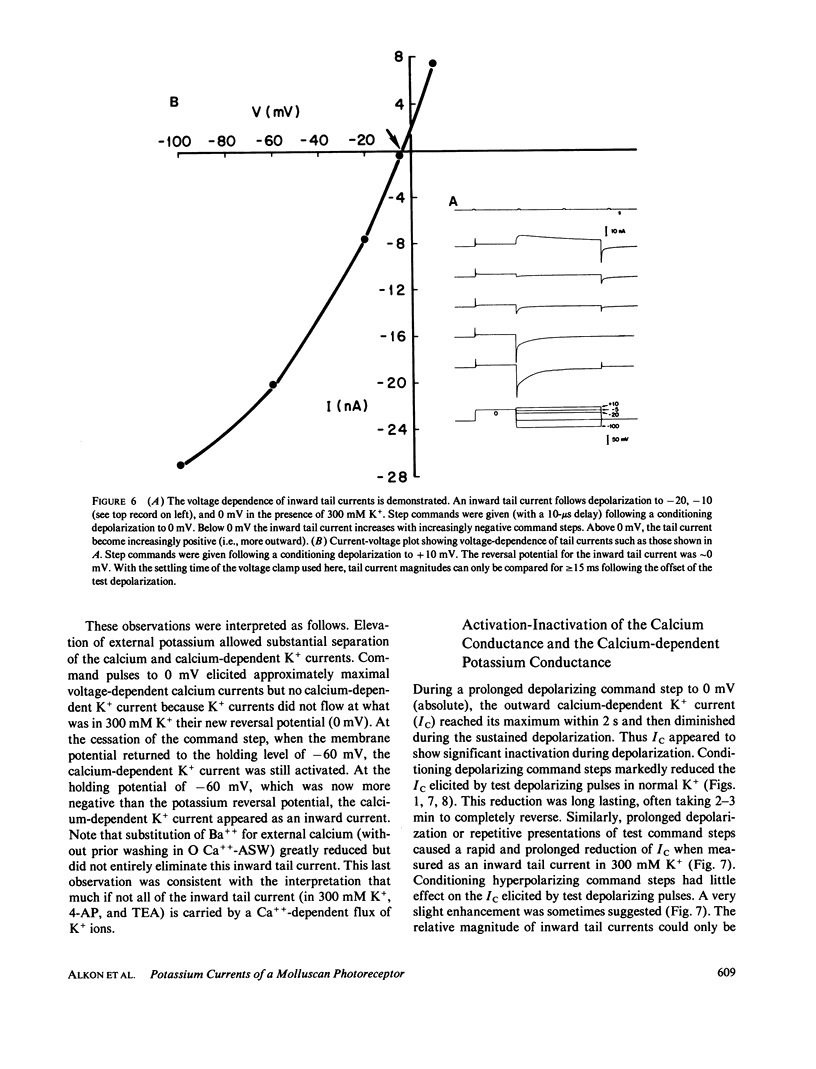
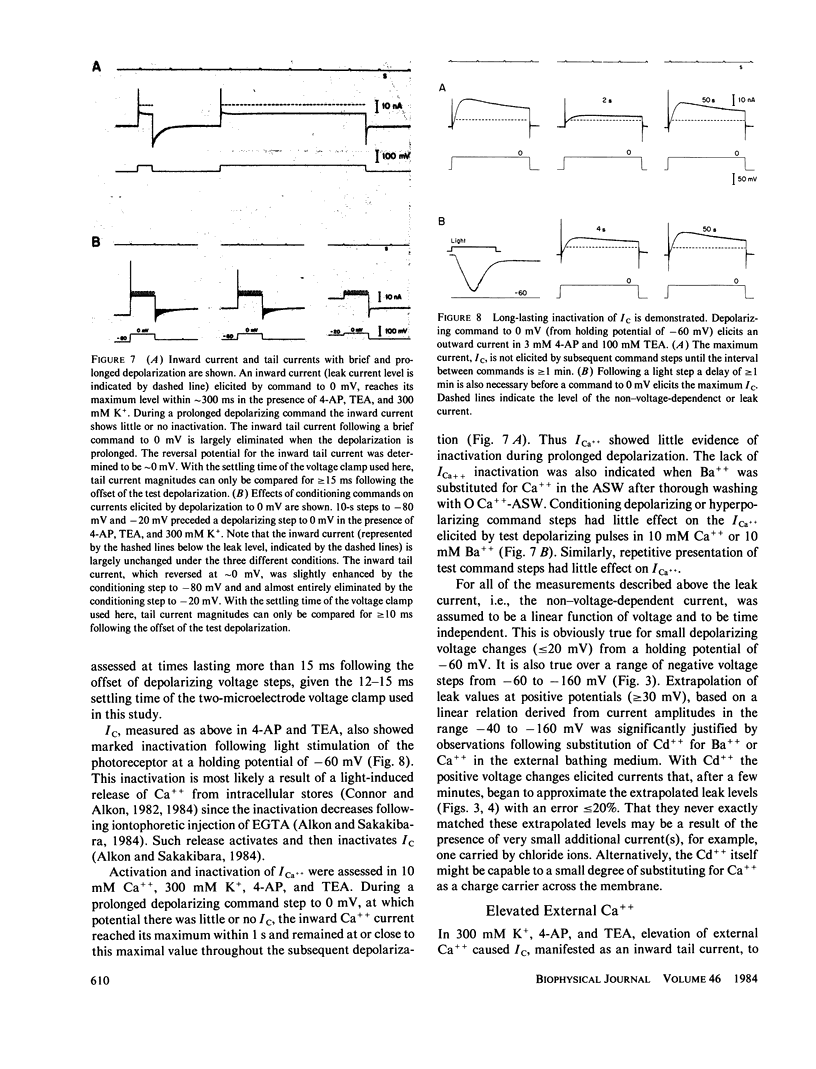
Abstract
Two-microelectrode voltage clamp studies were performed on the somata of Hermissenda Type B photoreceptors that had been isolated by axotomy from all synaptic interaction as well as any impulse-generating (i.e., active) membrane. In the presence of 2-10 mM 4-aminopyridine (4-AP) and 100 mM tetraethylammonium ion (TEA), which eliminated two previously described voltage-dependent potassium currents (IA and the delayed rectifier), a voltage-dependent outward current was apparent in the steady state responses to command voltage steps more positive than -40 mV (absolute). This current increased with increasing external Ca++. The magnitude of the outward current decreased and an inward current became apparent following EGTA injection. Substitution of external Ba++ for Ca++ also made the inward current more apparent. This inward current, which was almost eliminated after being exposed for approximately 5 min to a solution in which external Ca++ was replaced with Cd++, was maximally activated at approximately 0 mV. Elevation of external potassium allowed the calcium (ICa++) and calcium-dependent K+ (IC) currents to be substantially separated. Command pulses to 0 mV elicited maximal ICa++ but no IC because no K+ currents flowed at their new reversal potential (0 mV) in 300 mM K+. At a holding potential of -60 mV, which was now more negative than the potassium equilibrium potential, EK+, in 300 mM K+, IC appeared as an inward tail current after positive command steps. The voltage dependence of ICa++ was demonstrated with positive steps in 100 mM Ba++, 4-AP, and TEA. Other data indicated that in 10 mM Ca++, IC underwent pronounced and prolonged inactivation whereas ICa++ did not. When the photoreceptor was stimulated with a light step (with the membrane potential held at -60 mV), there was also a prolonged inactivation of IC. In elevated external Ca++, ICa++ also showed similar inactivation. These data suggest that IC may undergo prolonged inactivation due to a direct effect of elevated intracellular Ca++, as was previously shown for a voltage-dependent potassium current, IA. These results are discussed in relation to the production of training-induced changes of membrane currents on retention days of associative learning.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acosta-Urquidi J., Alkon D. L., Neary J. T. Ca2+-dependent protein kinase injection in a photoreceptor mimics biophysical effects of associative learning. Science. 1984 Jun 15;224(4654):1254–1257. doi: 10.1126/science.6328653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams D. J., Gage P. W. Ionic currents in response to membrane depolarization in an Aplysia neurone. J Physiol. 1979 Apr;289:115–141. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed Z., Connor J. A. Measurement of calcium influx under voltage clamp in molluscan neurones using the metallochromic dye arsenazo III. J Physiol. 1979 Jan;286:61–82. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akon D. L., Fuortes M. G. Responses of photoreceptors in Hermissenda. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Dec;60(6):631–649. doi: 10.1085/jgp.60.6.631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alkon D. L. Associative training of Hermissenda. J Gen Physiol. 1974 Jul;64(1):70–84. doi: 10.1085/jgp.64.1.70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alkon D. L., Lederhendler I., Shoukimas J. J. Primary changes of membrane currents during retention of associative learning. Science. 1982 Feb 5;215(4533):693–695. doi: 10.1126/science.7058334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alkon D. L. Responses of hair cells to statocyst rotation. J Gen Physiol. 1975 Oct;66(4):507–530. doi: 10.1085/jgp.66.4.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alkon D. L., Shoukimas J. J., Heldman E. Calcium-mediated decrease of a voltage-dependent potassium current. Biophys J. 1982 Dec;40(3):245–250. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84479-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alkon D. L. Voltage-dependent calcium and potassium ion conductances: a contingency mechanism for an associative learning model. Science. 1979 Aug 24;205(4408):810–816. doi: 10.1126/science.223244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andresen M. C., Brown A. M., Yasui S. The role of diffusion in the photoresponse of an extraretinal photoreceptor of Aplysia. J Physiol. 1979 Feb;287:283–301. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brehm P., Eckert R., Tillotson D. Calcium-mediated inactivation of calcium current in Paramecium. J Physiol. 1980 Sep;306:193–203. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. E., Blinks J. R. Changes in intracellular free calcium concentration during illumination of invertebrate photoreceptors. Detection with aequorin. J Gen Physiol. 1974 Dec;64(6):643–665. doi: 10.1085/jgp.64.6.643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. E., Brown P. K., Pinto L. H. Detection of light-induced changes of intracellular ionized calcium concentration in Limulus ventral photoreceptors using arsenazo III. J Physiol. 1977 May;267(2):299–320. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor J. A. Calcium current in molluscan neurones: measurement under conditions which maximize its visibility. J Physiol. 1979 Jan;286:41–60. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor J. A., Stevens C. F. Voltage clamp studies of a transient outward membrane current in gastropod neural somata. J Physiol. 1971 Feb;213(1):21–30. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor J., Alkon D. L. Light- and voltage-dependent increases of calcium ion concentration in molluscan photoreceptors. J Neurophysiol. 1984 Apr;51(4):745–752. doi: 10.1152/jn.1984.51.4.745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crow T. J., Alkon D. L. Associative behavioral modification in hermissenda: cellular correlates. Science. 1980 Jul 18;209(4454):412–414. doi: 10.1126/science.209.4454.412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crow T. J., Alkon D. L. Retention of an associative behavioral change in Hermissenda. Science. 1978 Sep 29;201(4362):1239–1241. doi: 10.1126/science.694512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert R., Lux H. D. Calcium-dependent depression of a late outward current in snail neurons. Science. 1977 Jul 29;197(4302):472–475. doi: 10.1126/science.17921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert R., Tillotson D. L., Brehm P. Calcium-mediated control of Ca and K currents. Fed Proc. 1981 Jun;40(8):2226–2232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert R., Tillotson D. L. Calcium-mediated inactivation of the calcium conductance in caesium-loaded giant neurones of Aplysia californica. J Physiol. 1981 May;314:265–280. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert R., Tillotson D. Potassium activation associated with intraneuronal free calcium. Science. 1978 Apr 28;200(4340):437–439. doi: 10.1126/science.644308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farley J., Richards W. G., Ling L. J., Liman E., Alkon D. L. Membrane changes in a single photoreceptor cause associative learning in Hermissenda. Science. 1983 Sep 16;221(4616):1201–1203. doi: 10.1126/science.6612335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goh Y., Alkon D. L. Sensory, interneuronal, and motor interactions within Hermissenda visual pathway. J Neurophysiol. 1984 Jul;52(1):156–169. doi: 10.1152/jn.1984.52.1.156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAGIWARA S., SAITO N. Voltage-current relations in nerve cell membrane of Onchidium verruculatum. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;148:161–179. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Byerly L. Calcium channel. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1981;4:69–125. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.04.030181.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyer C. B., Lux H. D. Control of the delayed outward potassium currents in bursting pace-maker neurones of the snail, Helix pomatia. J Physiol. 1976 Nov;262(2):349–382. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Steinberg I. Z., Walton K. Presynaptic calcium currents in squid giant synapse. Biophys J. 1981 Mar;33(3):289–321. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84898-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W. Calcium-dependent potassium activation in nervous tissues. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1978;7:1–18. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.07.060178.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Lux H. D. Differential action of TEA + on two K + -current componentss of a molluscan neurone. Pflugers Arch. 1972;336(2):87–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00592924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E. Two fast transient current components during voltage clamp on snail neurons. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Jul;58(1):36–53. doi: 10.1085/jgp.58.1.36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabata M., Alkon D. L. Positive synaptic feedback in visual system of nudibranch mollusk Hermissenda crassicornis. J Neurophysiol. 1982 Jul;48(1):174–191. doi: 10.1152/jn.1982.48.1.174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas M. V., Gorman A. L. Internal calcium changes in a bursting pacemaker neuron measured with arsenazo III. Science. 1977 Apr 29;196(4289):531–533. doi: 10.1126/science.850795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas R. C., Meech R. W. Hydrogen ion currents and intracellular pH in depolarized voltage-clamped snail neurones. Nature. 1982 Oct 28;299(5886):826–828. doi: 10.1038/299826a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S. H. Three pharmacologically distinct potassium channels in molluscan neurones. J Physiol. 1977 Feb;265(2):465–488. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tillotson D., Horn R. Inactivation without facilitation of calcium conductance in caesium-loaded neurones of Aplysia. Nature. 1978 May 25;273(5660):312–314. doi: 10.1038/273312a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tillotson D. Inactivation of Ca conductance dependent on entry of Ca ions in molluscan neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1497–1500. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West A., Barnes E., Alkon D. L. Primary changes of voltage responses during retention of associative learning. J Neurophysiol. 1982 Nov;48(5):1243–1255. doi: 10.1152/jn.1982.48.5.1243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


